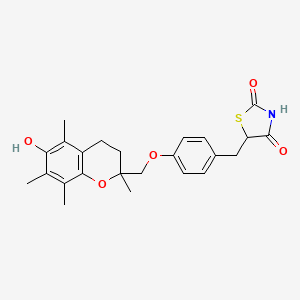
Troglitazon
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Troglitazone is an antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory drug that belongs to the thiazolidinedione class. It was initially developed to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus by improving insulin sensitivity. Troglitazone was patented in 1983 and approved for medical use in 1997. it was withdrawn from the market in 2000 due to its association with severe hepatotoxicity .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Troglitazon wurde ausgiebig für seine Anwendungen in verschiedenen Bereichen untersucht:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung zur Untersuchung der Thiazolidindionchemie und ihrer Wechselwirkungen mit anderen Molekülen verwendet.
Biologie: Wurde auf seine Auswirkungen auf zelluläre Prozesse untersucht, einschließlich Apoptose und Zellzyklusregulation.
Medizin: Wurde ursprünglich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt, indem die Insulinempfindlichkeit verbessert wurde.
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine Wirkung durch Aktivierung von Peroxisomen-Proliferator-aktivierten Rezeptoren (PPARs), insbesondere PPARγ und in geringerem Umfang PPARα. Diese Kernrezeptoren regulieren die Transkription von Genen, die am Glukose- und Lipidstoffwechsel beteiligt sind. This compound senkt die hepatische Glukosefreisetzung und erhöht die insulinabhängige Glukoseaufnahme in der Skelettmuskulatur. Darüber hinaus hat es entzündungshemmende Eigenschaften, indem es die Aktivität des Nuclear Factor kappa-B (NF-κB) reduziert und seinen Inhibitor (IκB) erhöht .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Pioglitazon: Ein weiteres Thiazolidindion mit einem ähnlichen Wirkmechanismus, jedoch mit einem besseren Sicherheitsprofil.
Rosiglitazon: Ähnlich wie Pioglitazon aktiviert es PPARγ, wurde aber mit kardiovaskulären Risiken in Verbindung gebracht.
Einzigartigkeit: this compound war das erste Thiazolidindion, das für die klinische Anwendung eingeführt wurde, und war damit ein Pionier in dieser Medikamentenklasse. Seine einzigartige Struktur beinhaltet einen Chromanring, der in anderen Thiazolidindionen nicht vorhanden ist. Trotz seiner Rücknahme lieferte this compound wertvolle Erkenntnisse für die Entwicklung sicherer und effektiverer antidiabetischer Medikamente .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Troglitazone, a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent, primarily targets the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPARα and PPARγ . These receptors regulate the transcription of numerous insulin-responsive genes that are critical for controlling glucose and lipid metabolism .
Mode of Action
Troglitazone’s mode of action is unique and dependent on the presence of insulin for activity . It binds to PPARs, leading to improved target cell response to insulin . This results in a decrease in hepatic glucose output and an increase in insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle .
Biochemical Pathways
Troglitazone affects several biochemical pathways. It decreases the rate of gluconeogenesis in the liver and increases glycolysis . This leads to a reduction in hepatic glucose output and an increase in insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle . Additionally, troglitazone has been shown to reduce inflammation, associated with a decrease in nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (IκB) .
Pharmacokinetics
Troglitazone is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, with peak concentration occurring in two to three hours . It undergoes metabolism by sulfation, glucuronidation, and oxidation to form a sulfate conjugate (M1), a glucuronide conjugate (M2), and a quinone metabolite (M3), respectively .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Troglitazone works by activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). It is a ligand to both PPARα and – more strongly – PPARγ . Troglitazone also contains an α-Tocopherol moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity in addition to its PPAR activation . It has been shown to reduce inflammation . Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle .
Cellular Effects
Troglitazone improves insulin responsiveness in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes by facilitating glucose transport activity, which thereby leads to increased rates of muscle glycogen synthesis and glucose oxidation . Troglitazone has been shown to induce apoptosis in various hepatic and nonhepatic cells .
Molecular Mechanism
Troglitazone’s mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin-responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism . Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPARα and PPARγ, with a higher affinity for PPARγ .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In a 6-month, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, troglitazone was found to significantly improve HbA1c and fasting serum glucose, while lowering insulin and C-peptide in patients with type 2 diabetes . No signs of hepatotoxicity were apparent at 2 weeks of treatment .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
Prolonged administration of troglitazone can superimpose oxidant stress, potentiate mitochondrial damage, and induce delayed hepatic necrosis in mice with genetically compromised mitochondrial function .
Metabolic Pathways
Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle . Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin-responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism .
Transport and Distribution
Troglitazone contains the structure of a unique chroman ring of vitamin E, and this structure has the potential to undergo metabolic biotransformation to form quinone metabolites, phenoxy radical intermediate, and epoxide species .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action involving nuclear receptors (PPAR), it can be inferred that Troglitazone likely interacts with these receptors in the cell nucleus .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Die Synthese von Troglitazon umfasst mehrere wichtige Schritte:
Bildung des Thiazolidindionrings: Dies wird typischerweise durch die Reaktion von Thiazolidin-2,4-dion mit einem geeigneten Benzylhalogenid unter basischen Bedingungen erreicht.
Anlagerung des Chromanrings: Der Chromanring, ein Strukturanalogon von Vitamin E, wird durch eine nucleophile Substitutionsreaktion mit einem geeigneten Chromanderivat und dem benzylierten Thiazolidindion-Zwischenprodukt eingeführt.
Endgültige Zusammenstellung: Das Endprodukt wird durch Reinigung der Zwischenprodukte und Durchführung notwendiger chemischer Modifikationen erhalten, um die gewünschte Struktur zu erreichen.
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: Die industrielle Produktion von this compound folgt ähnlichen Synthesewegen, jedoch in größerem Maßstab. Das Verfahren umfasst die Optimierung der Reaktionsbedingungen, um die Ausbeute und Reinheit zu maximieren und gleichzeitig Nebenprodukte zu minimieren. Fortschrittliche Techniken wie Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie (HPLC) werden zur Reinigung eingesetzt .
Arten von Reaktionen:
Oxidation: this compound unterliegt Oxidationsreaktionen, insbesondere in der Leber, was zur Bildung reaktiver Metaboliten führt.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen sind weniger häufig, können aber unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten.
Substitution: Nucleophile Substitutionsreaktionen sind an der Synthese von this compound beteiligt.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidationsmittel: Cytochrom-P450-Enzyme in der Leber.
Reduktionsmittel: Spezifische Reduktionsmittel unter kontrollierten Bedingungen.
Nucleophile: Verschiedene Nucleophile, die im Syntheseprozess verwendet werden.
Hauptprodukte:
Reaktive Metaboliten: Werden während der Oxidation gebildet und tragen zur Hepatotoxizität bei.
Stabile Metaboliten: Werden während Stoffwechselprozessen gebildet.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Pioglitazone: Another thiazolidinedione with a similar mechanism of action but a better safety profile.
Rosiglitazone: Similar to pioglitazone, it activates PPARγ but has been associated with cardiovascular risks.
Uniqueness: Troglitazone was the first thiazolidinedione introduced for clinical use, making it a pioneer in this drug class. Its unique structure includes a chroman ring, which is not present in other thiazolidinediones. Despite its withdrawal, troglitazone provided valuable insights into the development of safer and more effective antidiabetic drugs .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
5-[[4-[(6-hydroxy-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-3,4-dihydrochromen-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H27NO5S/c1-13-14(2)21-18(15(3)20(13)26)9-10-24(4,30-21)12-29-17-7-5-16(6-8-17)11-19-22(27)25-23(28)31-19/h5-8,19,26H,9-12H2,1-4H3,(H,25,27,28) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
GXPHKUHSUJUWKP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C2=C(CCC(O2)(C)COC3=CC=C(C=C3)CC4C(=O)NC(=O)S4)C(=C1O)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H27NO5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID8023719 | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8023719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
441.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Troglitazone is a thiazolidinedione antidiabetic agent that lowers blood glucose by improving target cell response to insulin. It has a unique mechanism of action that is dependent on the presence of insulin for activity. Troglitazone decreases hepatic glucose output and increases insulin dependent glucose disposal in skeletal muscle. Its mechanism of action is thought to involve binding to nuclear receptors (PPAR) that regulate the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes critical for the control of glucose and lipid metabolism. Troglitazone is a ligand to both PPARα and PPARγ, with a highter affinity for PPARγ. The drug also contains an α-tocopheroyl moiety, potentially giving it vitamin E-like activity. Troglitazone has been shown to reduce inflammation, and is associated with a decrase in nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) and a concomitant increase in its inhibitor (IκB). Unlike sulfonylureas, troglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
97322-87-7 | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=97322-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0097322877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8023719 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Melting Point |
184-186 °C | |
| Record name | Troglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00197 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![(6aS,6bS,10R,10aR,11aS,11bR)-10,11b-dimethyl-1,2,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,10,10a,11,11a-dodecahydrobenzo[a]fluorene-3,9-dione](/img/structure/B1681509.png)
![3-chloro-N'-(3-pyridin-4-ylpropanoyl)-6H-benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine-5-carbohydrazide;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B1681513.png)
![3-chloro-N'-[3-(furan-2-ylmethylsulfanyl)propanoyl]-6H-benzo[b][1,4]benzoxazepine-5-carbohydrazide](/img/structure/B1681515.png)
![3,5-Dichloro-N-[(2Z,3R)-3-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-methoxyimino-5-[4-[(3R)-3-[2-(methylamino)-2-oxoethyl]-2-oxopiperidin-1-yl]piperidin-1-yl]pentyl]-N-methylbenzamide](/img/structure/B1681528.png)
