Velpatasvir
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Velpatasvir ist ein direkt wirkendes antivirales Medikament, das in Kombination mit Sofosbuvir zur Behandlung chronischer Hepatitis-C-Virus (HCV)-Infektionen eingesetzt wird. Es ist wirksam gegen alle sechs Hauptgenotypen von HCV. This compound wirkt, indem es das nicht-strukturelle Protein 5A (NS5A) hemmt, das für die virale Replikation und Assemblierung essentiell ist .
Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von this compound umfasst mehrere Schritte, beginnend mit leicht zugänglichen Ausgangsmaterialien. Eine der Schlüsselzwischenstufen bei der Synthese ist eine Verbindung der Formel 5, die weiter zu this compound oder seinen pharmazeutisch verträglichen Salzen umgewandelt wird . Der Prozess beinhaltet die Verwendung verschiedener Reagenzien und Lösungsmittel, darunter Dimethylformamid (DMF) und Cäsiumcarbonat, unter kontrollierten Reaktionsbedingungen .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von this compound folgt einem ähnlichen Syntheseweg, ist jedoch für die großtechnische Herstellung optimiert. Der Prozess gewährleistet eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit des Endprodukts. Die Produktion umfasst strenge Qualitätskontrollen, um die Konsistenz und Sicherheit des Medikaments zu gewährleisten .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Velpatasvir is a potent pangenotypic inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS5A protein . The NS5A protein is a non-enzymatic viral protein that plays a key role in HCV replication, assembly, and modulation of host immune responses .
Mode of Action
This compound acts as a defective substrate for NS5A, thereby preventing viral replication . It has a significantly higher barrier to resistance than the first-generation NS5A inhibitors, making it a highly potent and reliable alternative for the treatment of chronic Hepatitis C .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound is the replication and assembly process of the HCV. By inhibiting the NS5A protein, this compound disrupts the life cycle of the virus, preventing it from multiplying and spreading .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is orally administered and reaches its highest blood plasma levels three hours after intake . It has a plasma protein binding of over 99.5% . This compound is metabolized in the liver by CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4 enzymes . It has an elimination half-life of 15 hours, and it is primarily excreted through feces (94%), with a small amount (0.4%) excreted through urine .
Result of Action
The primary molecular effect of this compound’s action is the inhibition of the HCV NS5A protein, which disrupts the virus’s replication and assembly process . On a cellular level, this results in a reduction of the viral load within the host’s body. Clinically, this leads to a sustained virologic response (SVR), which is associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality and risk of requiring a liver transplant .
Action Environment
The efficacy and safety of this compound can be influenced by various environmental factors. Substances that reduce gastric acid, such as antacids, h2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors, can reduce this compound’s bioavailability by 20–40% .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Velpatasvir interacts with the NS5A protein, inhibiting its function and thereby preventing viral replication . It has a significantly higher barrier to resistance than the first generation NS5A inhibitors .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a profound effect on cells infected with the Hepatitis C Virus. By inhibiting the NS5A protein, this compound disrupts the virus’s ability to replicate and assemble within the cell . This leads to a reduction in viral load and can ultimately result in the eradication of the virus from the body .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its action as a defective substrate for the NS5A protein . This protein is essential for the replication and assembly of the Hepatitis C Virus. By binding to NS5A, this compound prevents it from functioning properly, thereby disrupting the life cycle of the virus .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, this compound has been shown to produce rapid and sustained viral suppression at all monotherapy dose levels in HCV-infected individuals .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is metabolized in the liver by the enzymes CYP2B6, CYP2C8, and CYP3A4 . It is both an inhibitor and a substrate of the transporter proteins P-glycoprotein (Pgp), ABCG2, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3 .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues via transporter proteins including P-glycoprotein (Pgp), ABCG2, OATP1B1, and OATP1B3 .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound is not explicitly stated in the available literature. Given its mechanism of action, it is likely that it interacts with the NS5A protein in the cytoplasm where Hepatitis C Virus replication and assembly occur .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of velpatasvir involves multiple steps, starting from readily available starting materials. One of the key intermediates in the synthesis is a compound of formula 5, which is further converted to this compound or its pharmaceutically acceptable salts . The process involves the use of various reagents and solvents, including dimethylformamide (DMF) and cesium carbonate, under controlled reaction conditions .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound follows a similar synthetic route but is optimized for large-scale manufacturing. The process ensures high yield and purity of the final product. The production involves stringent quality control measures to ensure the consistency and safety of the medication .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Velpatasvir durchläuft verschiedene Arten von chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden, um verschiedene Oxidationsprodukte zu bilden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können verwendet werden, um bestimmte funktionelle Gruppen in this compound zu modifizieren.
Substitution: this compound kann Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, bei denen eine funktionelle Gruppe durch eine andere ersetzt wird.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Häufige Reagenzien, die in diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, umfassen Oxidationsmittel wie Wasserstoffperoxid, Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid und verschiedene Katalysatoren, um Substitutionsreaktionen zu erleichtern. Die Reaktionsbedingungen, wie Temperatur und pH-Wert, werden sorgfältig kontrolliert, um die gewünschten Produkte zu erhalten .
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, hängen von den spezifischen Reaktionsbedingungen und den verwendeten Reagenzien ab. Beispielsweise kann die Oxidation von this compound zur Bildung von hydroxylierten Derivaten führen, während die Reduktion deoxygenierte Produkte liefern kann .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound hat verschiedene wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen, darunter:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung verwendet, um die Mechanismen von antiviralen Wirkstoffen und ihre Wechselwirkungen mit viralen Proteinen zu untersuchen.
Biologie: Hilft beim Verständnis der Replikation und Assemblierung von HCV, liefert Einblicke in virale Lebenszyklen.
Medizin: Wird in der klinischen Forschung zur Entwicklung wirksamer Behandlungen für HCV-Infektionen eingesetzt. .
Wirkmechanismus
This compound übt seine Wirkung aus, indem es das NS5A-Protein hemmt, das für die Replikation und Assemblierung von HCV entscheidend ist. Durch die Blockierung dieses Proteins verhindert this compound, dass das Virus neue virale Partikel repliziert und zusammensetzt. Diese Hemmung führt zu einer Reduktion der Viruslast und hilft, bei Patienten ein anhaltendes virologisches Ansprechen (SVR) zu erreichen .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Velpatasvir has several scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study the mechanisms of antiviral agents and their interactions with viral proteins.
Biology: Helps in understanding the replication and assembly of HCV, providing insights into viral life cycles.
Medicine: Widely used in clinical research to develop effective treatments for HCV infections. .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Velpatasvir wird mit anderen NS5A-Inhibitoren wie Ledipasvir und Daclatasvir verglichen. Während all diese Verbindungen das NS5A-Protein hemmen, weist this compound eine höhere Resistenzbarriere auf und ist wirksam gegen alle sechs Hauptgenotypen von HCV. Dies macht es zu einer potenteren und zuverlässigeren Option zur Behandlung chronischer HCV-Infektionen .
Liste ähnlicher Verbindungen
- Ledipasvir
- Daclatasvir
- Ombitasvir
- Elbasvir
Die einzigartige Fähigkeit von this compound, alle HCV-Genotypen anzugreifen, und seine hohe Resistenzbarriere machen es zu einer wertvollen Ergänzung des Arsenals antiviraler Medikamente .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
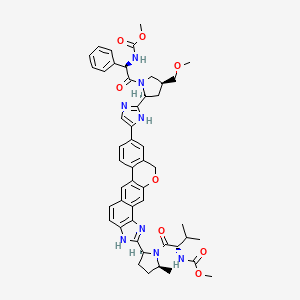
methyl N-[(1R)-2-[(2S,4S)-2-[5-[6-[(2S,5S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]-5-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-21-oxa-5,7-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.03,11.04,8.014,19]henicosa-1(13),2,4(8),5,9,11,14(19),15,17-nonaen-17-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-4-(methoxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C49H54N8O8/c1-26(2)41(54-48(60)63-5)47(59)57-27(3)12-17-38(57)45-51-36-16-14-30-20-35-33-15-13-31(19-32(33)25-65-40(35)21-34(30)43(36)53-45)37-22-50-44(52-37)39-18-28(24-62-4)23-56(39)46(58)42(55-49(61)64-6)29-10-8-7-9-11-29/h7-11,13-16,19-22,26-28,38-39,41-42H,12,17-18,23-25H2,1-6H3,(H,50,52)(H,51,53)(H,54,60)(H,55,61)/t27-,28-,38-,39-,41-,42+/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FHCUMDQMBHQXKK-CDIODLITSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1CCC(N1C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)C2=NC3=C(N2)C=CC4=CC5=C(C=C43)OCC6=C5C=CC(=C6)C7=CN=C(N7)C8CC(CN8C(=O)C(C9=CC=CC=C9)NC(=O)OC)COC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C[C@H]1CC[C@H](N1C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)C2=NC3=C(N2)C=CC4=CC5=C(C=C43)OCC6=C5C=CC(=C6)C7=CN=C(N7)[C@@H]8C[C@@H](CN8C(=O)[C@@H](C9=CC=CC=C9)NC(=O)OC)COC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C49H54N8O8 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID70722565 | |
| Record name | Velpatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70722565 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
883.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Velpatasvir's mechanism of action is likely similar to other selective NS5A inhibitors which bind domain I of NS5A consisting of amino acids 33-202. NS5A inhibitors compete with RNA for binding at this site. It is also thought that NS5A inhibitors bind the target during its action in replication when the binding site is exposed. Inhibition of NS5A is also known to produce redistribution of the protein to lipid droplets. The exact role of NS5A in RNA replication is not yet understood although it is known to be an important component. | |
| Record name | Velpatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11613 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1377049-84-7 | |
| Record name | Carbamic acid, N-[(1R)-2-[(2S,4S)-2-[5-[1,11-dihydro-2-[(2S,5S)-1-[(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutyl]-5-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl][2]benzopyrano[4′,3′:6,7]naphth[1,2-d]imidazol-9-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-4-(methoxymethyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl]-, methyl ester | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1377049-84-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Velpatasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1377049847 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Velpatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11613 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Velpatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID70722565 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | methyl N-[(1R)-2-[(2S,4S)-2-[5-[6-[(2S,5S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]-5-methylpyrrolidin-2-yl]-21-oxa-5,7-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.03,11.04,8.014,19]henicosa-1(13),2,4(8),5,9,11,14(19),15,17-nonaen-17-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-4-(methoxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-2-oxo-1-phenylethyl]carbamate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | VELPATASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/KCU0C7RS7Z | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary target of Velpatasvir?
A1: this compound specifically targets the hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A protein. [, , , , , ] This protein is essential for HCV replication, virion assembly, and modulation of the host cellular response. [, ]
Q2: How does this compound exert its antiviral activity?
A2: this compound inhibits the function of the HCV NS5A protein, a key player in viral replication and assembly. [, , , , , ] While the exact mechanism remains under investigation, it's believed that this compound binding disrupts critical protein-protein interactions within the viral replication complex. This effectively halts the production of new viral particles. [, ]
Q3: Does this compound exhibit activity against all HCV genotypes?
A3: Yes, this compound has demonstrated potent pangenotypic antiviral activity, meaning it is effective against all major HCV genotypes (genotypes 1-6). [, , , , ] This pangenotypic activity makes it a valuable therapeutic option, simplifying treatment decisions for clinicians. [, ]
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A4: The molecular formula of this compound is C45H57N7O8, and its molecular weight is 831.98 g/mol. []
Q5: Is there spectroscopic data available for this compound?
A5: While the provided research papers do not specify particular spectroscopic data for this compound, various analytical techniques are employed for its characterization. These include high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled with ultraviolet (UV) detection, often at a wavelength of 260 nm. [, , ] Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) with fluorescence detection is another method used for its sensitive and selective determination, particularly in biological matrices like human plasma. []
Q6: How stable is this compound under various storage conditions?
A6: While specific stability data is not outlined in the provided research, various studies utilize stability-indicating analytical methods, suggesting that this compound's stability profile is well-characterized. [, , ] These methods, often involving RP-HPLC or HPTLC, are designed to separate and quantify this compound from potential degradation products, allowing for the assessment of its stability under different storage conditions (temperature, humidity, light exposure). [, , ]
Q7: What are some formulation strategies used to improve this compound's bioavailability?
A7: this compound is formulated as a fixed-dose combination tablet with Sofosbuvir. [, , ] While the specific excipients used are not detailed in the provided research, the formulation is designed for oral administration and optimized for once-daily dosing. [, , ] This fixed-dose combination simplifies treatment regimens and potentially improves patient adherence. [, , ]
Q8: What types of in vitro studies have been conducted to evaluate this compound's antiviral activity?
A8: this compound's antiviral activity has been extensively evaluated in vitro using HCV replicon cell lines. [, ] These cell lines harbor a subgenomic HCV replicon, which allows for the continuous replication of the viral RNA. By measuring the inhibition of viral replication in these cells, researchers can determine the potency and efficacy of this compound. [, ]
Q9: Has resistance to this compound been observed in clinical trials?
A10: Yes, resistance to this compound has been observed in clinical trials, particularly in patients infected with HCV genotype 3 or those with pre-existing resistance-associated substitutions (RASs). [, , , ] These substitutions typically occur in the NS5A region of the HCV genome and can reduce the binding affinity of this compound to its target, leading to decreased drug efficacy. [, , , ]
Q10: What are the most common resistance-associated substitutions (RASs) for this compound?
A11: The most common RASs for this compound are found in the NS5A protein, with variations depending on the HCV genotype. For genotype 1a, common substitutions include M28G, A92K, and Y93H/N/R/W. In genotype 1b, the A92K substitution is frequently observed. [] Notably, the Y93H substitution can arise across multiple genotypes (1a, 1b, 2a, 3a, 4a). [] Genotype 6a exhibits distinct RASs, such as L31V and P32A/L/Q/R, which confer high-level resistance. [] The emergence of L31V in genotype 6a can further facilitate the development of resistance to Pibrentasvir via the emergence of L28S. []
Q11: Are there any specific biomarkers or diagnostics used in relation to this compound therapy?
A12: The primary biomarker for monitoring the effectiveness of this compound therapy is the HCV RNA level in the blood. Achieving a sustained virologic response (SVR), defined as undetectable HCV RNA at a specified time point after treatment completion, is the primary goal of therapy and signifies viral eradication. [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ]
Q12: What is known about the pharmacokinetics of this compound?
A13: this compound exhibits favorable pharmacokinetic properties. It is administered orally and is rapidly absorbed, reaching peak plasma concentrations within a few hours. [, ] It displays a long half-life, allowing for once-daily dosing. [, ]
Q13: Are there any known drug interactions with this compound?
A14: Yes, this compound is primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) enzyme in the liver. [, , ] Concomitant administration of this compound with strong CYP3A4 inducers (e.g., rifampin, carbamazepine) can decrease its plasma concentrations, potentially leading to reduced efficacy. [, , ] Conversely, strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, ritonavir) can increase this compound exposure, necessitating dosage adjustments. [, , ] Additionally, the coadministration of this compound with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can reduce its absorption. [, ] This interaction can be mitigated by instructing patients to take this compound with a soda beverage, which enhances its solubility and absorption in the presence of PPIs. [, ]
Q14: What are the common adverse events associated with this compound?
A15: this compound is generally well-tolerated. The most common adverse events reported in clinical trials were typically mild and transient, including headache, fatigue, nausea, and nasopharyngitis. [, , , ]
Q15: Are there any specific patient populations where this compound use requires caution?
A16: Caution is advised when using this compound in patients with decompensated cirrhosis, as they may require ribavirin addition to the regimen for optimal outcomes. [, , ] Close monitoring for adverse events is essential in these patients. [, , ]
Q16: What are some areas of ongoing research related to this compound?
A16: Ongoing research efforts are focused on:
- Optimizing treatment duration: While 12 weeks of sofosbuvir-velpatasvir is effective for most patients, researchers are exploring shorter durations (e.g., 8 weeks) in specific populations to simplify treatment and reduce costs. [, ]
- Addressing resistance: Developing new HCV antivirals with distinct mechanisms of action is crucial to combat the emergence of resistance to existing drugs like this compound. [, ]
- Improving treatment outcomes in challenging populations: Research continues to optimize this compound-based regimens for patients with decompensated cirrhosis, those who have failed prior DAA therapy, and individuals with specific HCV genotypes that may be more challenging to treat. [, , , , , ]
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.




![5-[3-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperidin-1-yl]propoxy]-1,3-benzothiazole;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B611587.png)
![(2R)-2-[[(4S)-4-[(3R,8R,9R,10S,13S,14R,17S)-3-hydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-dodecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)propanoic acid](/img/structure/B611590.png)