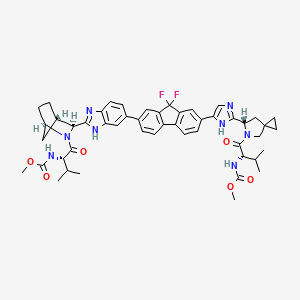
Ledipasvir
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Ledipasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent used primarily for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It was developed by Gilead Sciences and is commonly used in combination with sofosbuvir under the brand name Harvoni. This compound targets the non-structural protein 5A (NS5A) of the hepatitis C virus, which is essential for viral replication and assembly .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Ledipasvir hat bedeutende Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, insbesondere in den Bereichen Chemie, Biologie, Medizin und Industrie:
Chemie: this compound dient als Modellverbindung zur Untersuchung von antiviralen Mitteln und deren Synthese.
Biologie: Es wird verwendet, um die Replikationsmechanismen des Hepatitis-C-Virus und die Rolle von NS5A bei der Virusassemblierung zu untersuchen.
Medizin: This compound wird in Kombination mit Sofosbuvir zur Behandlung chronischer Hepatitis-C-Infektionen eingesetzt und erzielt hohe Heilungsraten und minimale Nebenwirkungen
Industrie: Die Produktion und Formulierung von this compound tragen zu den Bemühungen der pharmazeutischen Industrie bei, wirksame antivirale Therapien zu entwickeln
Wirkmechanismus
This compound hemmt das nicht-strukturelle Protein 5A (NS5A) des Hepatitis-C-Virus, das für die Virus-RNA-Replikation und die Assemblierung von HCV-Virionen entscheidend ist. Durch die Verhinderung der Hyperphosphorylierung von NS5A stört this compound die Produktion von viralen Proteinen, wodurch die Virusreplikation und -assemblierung gehemmt werden .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Ledipasvir primarily targets the Non-Structural Protein 5A (NS5A) of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . NS5A is a multifunctional protein that plays crucial roles in viral RNA replication and the assembly of HCV virions .
Mode of Action
This compound acts as an inhibitor of the HCV NS5A protein . This inhibition disrupts the normal functioning of the NS5A protein, thereby impeding the life cycle of the HCV .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound is the replication of the HCV RNA genome . By inhibiting the NS5A protein, this compound disrupts the replication of the viral RNA, which in turn affects the assembly of new HCV virions . This leads to a decrease in the overall viral load within the host.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound exhibits a bioavailability of 76% . It reaches maximum plasma concentrations 4 to 4.5 hours after ingestion . This compound is more than 98% protein-bound and is predominantly eliminated fecally, with minimal metabolism in the liver . The elimination half-life of this compound is approximately 47 hours .
Result of Action
The inhibition of the NS5A protein by this compound results in a significant reduction in HCV RNA replication . This leads to a decrease in the production of new HCV virions, thereby reducing the overall viral load within the host. The ultimate goal of this compound treatment is to achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), which is defined as the absence of detectable HCV RNA 12 weeks after the completion of therapy . Achieving SVR is associated with long-term health benefits, including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Action Environment
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Ledipasvir interacts with the NS5A protein, a phosphoprotein that plays an essential role in the replication of the hepatitis C virus . By binding to this protein, this compound disrupts the replication process of the virus .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a profound effect on cells infected with the hepatitis C virus. It inhibits the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the viral load within the cells . This can lead to a decrease in the severity of the disease and potentially to a complete cure .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its interaction with the NS5A protein. This compound binds to this protein, preventing it from assisting in the replication of the viral RNA . This stops the virus from multiplying and spreading to other cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound have been observed to be both rapid and long-lasting . The drug quickly reduces the viral load in cells, and this effect can be sustained over a long period, leading to a sustained virological response .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
While specific studies on dosage effects in animal models were not found in the search results, clinical studies have shown that this compound, in combination with other antiviral drugs, is effective in treating hepatitis C in humans .
Metabolic Pathways
It is known that the drug works by interfering with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus, specifically by inhibiting the NS5A protein .
Transport and Distribution
Given its effectiveness in reducing viral load, it can be inferred that the drug is able to reach the sites of viral replication within the cells .
Subcellular Localization
Given that it targets the NS5A protein, which is involved in the replication of the hepatitis C virus, it is likely that the drug localizes to the sites within the cell where this process takes place .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of Ledipasvir involves multiple steps, including the preparation of key intermediates. One method involves the preparation of a high-purity intermediate, (1R, 3S, 4S)-N-tertbutyloxycarbonyl-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-3-carboxylic acid, through enzymatic hydrolysis . Another method involves late-stage cyclopropanation and fluorination processes, which provide a novel and efficient route for the preparation of this compound with a total yield of 20% over eight linear steps .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of this compound focuses on optimizing yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. The process typically involves the use of high-purity intermediates and environmentally friendly reaction conditions. The methods are designed to be scalable for large-scale production, ensuring high selectivity and reduced production costs .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Ledipasvir durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter:
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen sind bei this compound weniger verbreitet.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen, insbesondere unter Beteiligung von Halogenatomen, sind bei der Synthese von this compound relevanter
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Häufige Reagenzien, die bei der Synthese und Reaktion von this compound verwendet werden, umfassen Acetonitril, Essigsäure und Isopropylether. Reaktionsbedingungen beinhalten oft erhöhte Temperaturen und kontrollierte Umgebungen, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten .
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Das Hauptprodukt, das aus den Reaktionen mit this compound gebildet wird, ist der endgültige pharmazeutische Wirkstoff, der zur Behandlung von Hepatitis C verwendet wird. Andere Zwischenprodukte und Nebenprodukte werden typischerweise durch Reinigungsprozesse entfernt .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Sofosbuvir: Ein weiteres direkt wirkendes Antiviral, das in Kombination mit Ledipasvir eingesetzt wird. Es hemmt die NS5B-Polymerase von HCV.
Daclatasvir: Ein NS5A-Inhibitor, der this compound ähnelt, aber andere pharmakokinetische Eigenschaften aufweist.
Ombitasvir: Ein weiterer NS5A-Inhibitor, der in Kombination mit anderen antiviralen Mitteln zur Behandlung von HCV eingesetzt wird
Einzigartigkeit von this compound
This compound ist aufgrund seiner hohen Wirksamkeit gegen mehrere HCV-Genotypen und seiner Fähigkeit, Sustained Virologic Response (SVR)-Raten von über 95% in Kombination mit Sofosbuvir zu erreichen, einzigartig. Seine lange Halbwertszeit und minimalen Nebenwirkungen machen es zu einer bevorzugten Wahl für die HCV-Behandlung .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(6S)-6-[5-[9,9-difluoro-7-[2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-yl]-3H-benzimidazol-5-yl]fluoren-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]heptan-5-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C49H54F2N8O6/c1-24(2)39(56-46(62)64-5)44(60)58-23-48(15-16-48)21-38(58)42-52-22-37(55-42)28-9-13-32-31-12-8-26(18-33(31)49(50,51)34(32)19-28)27-10-14-35-36(20-27)54-43(53-35)41-29-7-11-30(17-29)59(41)45(61)40(25(3)4)57-47(63)65-6/h8-10,12-14,18-20,22,24-25,29-30,38-41H,7,11,15-17,21,23H2,1-6H3,(H,52,55)(H,53,54)(H,56,62)(H,57,63)/t29-,30+,38-,39-,40-,41-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VRTWBAAJJOHBQU-KMWAZVGDSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)CC1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)C9C1CCC(C1)N9C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)C[C@H]1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)[C@@H]9[C@H]1CC[C@H](C1)N9C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C49H54F2N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID90154829 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
889.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ledipasvir is an inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS5A protein required for viral RNA replication and assembly of HCV virions. Although its exact mechanism of action is unknown, it is postulated to prevent hyperphosphorylation of NS5A which is required for viral production. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1256388-51-8 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1256388-51-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1256388518 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Methyl[(2S)-1-{(6S)-6-[5-(9,9-difluoro-7-{2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-{(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-3-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-6-yl}-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl}-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LEDIPASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/013TE6E4WV | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details












Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details












Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![4-O-(19-ethyl-14,18-dioxo-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4,6,8,10,15(20)-heptaen-19-yl) 1-O-[2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl] butanedioate](/img/structure/B612184.png)