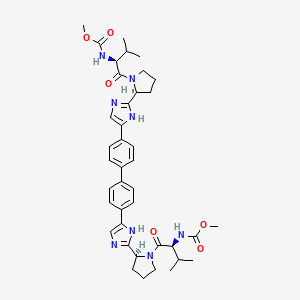
Daclatasvir
Descripción general
Descripción
Daclatasvir es un medicamento antiviral que se utiliza en combinación con otros medicamentos para tratar infecciones por el virus de la hepatitis C (VHC). Se comercializa con el nombre de marca Daklinza. This compound actúa inhibiendo la proteína NS5A del VHC, que es esencial para la replicación viral . Este compuesto es particularmente eficaz contra los genotipos 1, 3 y 4 del VHC .
Mecanismo De Acción
Daclatasvir ejerce sus efectos antivirales uniéndose al extremo N-terminal dentro del Dominio 1 de la proteína no estructural 5A (NS5A) del VHC. Esta unión inhibe la replicación del ARN viral y el ensamblaje de viriones, evitando eficazmente que el virus se multiplique y se propague . La inhibición de NS5A interrumpe la formación del complejo de replicación viral, lo que lleva a una disminución de la carga viral y a la eliminación final de la infección .
Compuestos similares:
Sofosbuvir: Otro medicamento antiviral que se utiliza en combinación con this compound para tratar el VHC. Inhibe la ARN polimerasa NS5B del VHC.
Ledipasvir: Similar a this compound, inhibe la proteína NS5A, pero tiene diferentes propiedades farmacocinéticas.
Velpatasvir: Otro inhibidor de NS5A con un espectro de actividad más amplio contra varios genotipos de VHC.
Singularidad de this compound: this compound es único debido a su alta selectividad y potencia contra la NS5A del VHC. Tiene un perfil farmacocinético bien caracterizado, lo que permite una administración oral una vez al día. Además, this compound ha demostrado eficacia en pacientes con enfermedad hepática avanzada y en aquellos coinfectados con VIH .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Daclatasvir tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Química: Sirve como un compuesto modelo para estudiar el diseño y la síntesis de fármacos antivirales.
Biología: this compound se utiliza para estudiar los mecanismos de replicación viral y el papel de NS5A en el VHC.
Medicina: Es un componente crucial de las terapias combinadas para tratar infecciones crónicas por VHC, lo que lleva a altas tasas de respuesta virológica sostenida.
Industria: La producción y la formulación de this compound se estudian para mejorar los procesos de fabricación y los sistemas de administración de fármacos
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Daclatasvir exerts its antiviral action by preventing RNA replication and virion assembly via binding to NS5A, a nonstructural phosphoprotein encoded by HCV . Binding to the N-terminus of the D1 domain of NS5A prevents its interaction with host cell proteins and membranes required for virion replication complex assembly .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a profound effect on viral load with onset that is more rapid than had been seen previously with either NS3 protease or NS5B polymerase inhibitors . It disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound works by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A . It targets both the cis- and trans-acting functions of NS5A and disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound undergoes rapid absorption, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration of 1–2 h and an elimination half-life of 10 to 14 h observed in single-ascending dose studies . Steady state was achieved by day 4 in multiple-ascending dose studies .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In-vivo animal studies suggested that this compound concentrates in livers (mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys), with liver-to-serum or liver-to-plasma area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) ratios ranging from 1.9 to 17 in the different animal species tested .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound has low-to-moderate clearance with the predominant route of elimination via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion . Renal clearance is a minor route of elimination for this compound .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely to be found in close proximity to the HCV NS5A protein, which is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane where the HCV replication complex is located .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas de síntesis y condiciones de reacción: La síntesis de daclatasvir implica múltiples pasos, comenzando con materiales de partida disponibles comercialmente. . Las condiciones de reacción normalmente implican el uso de disolventes orgánicos, catalizadores y temperaturas controladas para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza.
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de this compound sigue una ruta sintética similar, pero se optimiza para la producción a gran escala. Esto implica el uso de reactores de alta eficiencia, procesos de flujo continuo y estrictas medidas de control de calidad para garantizar la coherencia y el cumplimiento de las normas reglamentarias .
3. Análisis de las reacciones químicas
Tipos de reacciones: this compound se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: this compound puede oxidarse bajo condiciones específicas, lo que lleva a la formación de derivados oxidados.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción pueden modificar los anillos de imidazol u otros grupos funcionales dentro de la molécula.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes:
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen el peróxido de hidrógeno y el permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Se utilizan agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio y el hidruro de aluminio y litio.
Sustitución: Se emplean varios agentes halogenantes y nucleófilos para las reacciones de sustitución.
Principales productos formados: Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen derivados oxidados, análogos reducidos y compuestos sustituidos con propiedades farmacológicas modificadas .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Types of Reactions: Daclatasvir undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized under specific conditions, leading to the formation of oxidized derivatives.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can modify the imidazole rings or other functional groups within the molecule.
Substitution: Substitution reactions can occur at the biphenyl core or the imidazole rings, leading to the formation of different analogs.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include hydrogen peroxide and potassium permanganate.
Reduction: Reducing agents such as sodium borohydride and lithium aluminum hydride are used.
Substitution: Various halogenating agents and nucleophiles are employed for substitution reactions.
Major Products Formed: The major products formed from these reactions include oxidized derivatives, reduced analogs, and substituted compounds with modified pharmacological properties .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Sofosbuvir: Another antiviral medication used in combination with daclatasvir for treating HCV. It inhibits the HCV RNA polymerase NS5B.
Ledipasvir: Similar to this compound, it inhibits the NS5A protein but has different pharmacokinetic properties.
Velpatasvir: Another NS5A inhibitor with a broader spectrum of activity against various HCV genotypes.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique due to its high selectivity and potency against HCV NS5A. It has a well-characterized pharmacokinetic profile, allowing for once-daily oral administration. Additionally, this compound has shown efficacy in patients with advanced liver disease and those co-infected with HIV .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C40H50N8O6/c1-23(2)33(45-39(51)53-5)37(49)47-19-7-9-31(47)35-41-21-29(43-35)27-15-11-25(12-16-27)26-13-17-28(18-14-26)30-22-42-36(44-30)32-10-8-20-48(32)38(50)34(24(3)4)46-40(52)54-6/h11-18,21-24,31-34H,7-10,19-20H2,1-6H3,(H,41,43)(H,42,44)(H,45,51)(H,46,52)/t31-,32-,33-,34-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FKRSSPOQAMALKA-CUPIEXAXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C40H50N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID901026404 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
738.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Freely soluble (>700 mg/mL) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
NS5A is a viral nonstructural phospoprotein that is part of a functional replication complex in charge of viral RNA genome amplification on endoplasmic reticulum membranes. It has the ability to bind to HCV RNA. It is shown to have two distinct functions in HCV RNA replication based on phosphorylated states. Maintaining the HCV replication complex is mediated by the cis-acting function of basally phosphorylated NS5A and the trans-acting function of hyperphosphorylated NS5A modulates HCV assembly and infectious particle formation. Daclatasvir is shown to disrupt hyperphosphorylated NS5A proteins thus interfere with the function of new HCV replication complexes. It is also reported that daclatasvir also blocks both intracellular viral RNA synthesis and virion assembly/secretion in vivo. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1009119-64-5 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1009119-64-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DACLATASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/LI2427F9CI | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.


![7-[3-(4-Acetyl-3-hydroxy-2-propylphenoxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-4-oxo-8-propylchromene-2-carboxylic acid](/img/structure/B1662943.png)
![7,8-Dihydro-2-methyl-1H-thiopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one](/img/structure/B1662944.png)