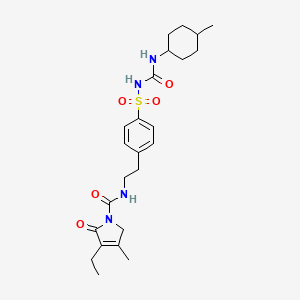
Glimepiride
Descripción general
Descripción
La Glimepirida es un medicamento antidiabético dentro de la clase de las sulfonilureas, prescrito principalmente para el manejo de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2. Se considera una opción de segunda línea en comparación con la metformina, debido a la seguridad y eficacia bien establecidas de la metformina . La Glimepirida funciona principalmente aumentando la cantidad de insulina liberada por el páncreas . Fue patentada en 1979 y aprobada para uso médico en 1995 .
Mecanismo De Acción
La Glimepirida actúa como un secretagogo de insulina. Estimula la liberación de insulina de las células beta pancreáticas al bloquear los canales de potasio sensibles a ATP, causando la despolarización de las células beta y la subsiguiente secreción de insulina . Además, aumenta la actividad de los receptores de insulina intracelulares, mejorando la respuesta del cuerpo a la insulina .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Glimepiride stimulates insulin release from pancreatic β-cells and may act via extrapancreatic mechanisms . It is administered once daily to patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in whom glycemic control is not achieved by diet and exercise alone .
Cellular Effects
This compound lowers blood glucose by stimulating insulin secretions from functioning pancreatic beta cells and by inducing extra-pancreatic effects, thereby decreasing insulin resistance . It potentially binds to ATP-sensitive potassium channel receptors on the pancreatic beta cell surface, causing depolarization of the membrane which stimulates calcium ion influx through voltage-sensitive calcium channels .
Molecular Mechanism
The increase in intracellular calcium ion concentration induced by this compound triggers the secretion of insulin . This compound attaches itself to receptors on the surface of pancreatic ß-cells that are dependent on adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Insulin release, a calcium influx, and potassium outflow result from the closure of these channels and membrane depolarization .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
A new crystalline form of this compound has been synthesized and characterized, showing different solubility and melting properties from the reported polymorphs . The crystal structure of this new form is more thermodynamically stable than the previously reported forms .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
Specific dosage effects of this compound in animal models are not mentioned in the available literature. Like other sulfonylureas, this compound is used based on its well-established glucose-lowering action .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in the metabolic pathway that regulates blood glucose levels. It stimulates insulin release from pancreatic β-cells, which plays a crucial role in glucose metabolism .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción
La Glimepirida se sintetiza mediante un proceso de varios pasos que involucra varios intermediarios. Los pasos clave incluyen la formación del anillo de pirrol y la unión del grupo sulfonilurea. Las condiciones de reacción suelen implicar el uso de disolventes orgánicos, catalizadores y temperaturas controladas para asegurar las transformaciones químicas deseadas .
Métodos de producción industrial
La producción industrial de Glimepirida implica la síntesis a gran escala utilizando condiciones de reacción optimizadas para maximizar el rendimiento y la pureza. El proceso incluye pasos de purificación como la cristalización y la filtración para obtener el producto final en una forma adecuada para su uso farmacéutico .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones
La Glimepirida experimenta varias reacciones químicas, incluyendo:
Oxidación: Implica la adición de oxígeno o la eliminación de hidrógeno.
Reducción: Implica la adición de hidrógeno o la eliminación de oxígeno.
Sustitución: Implica la sustitución de un grupo funcional por otro.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes
Los reactivos comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen agentes oxidantes como el permanganato de potasio, agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio, y varios catalizadores para facilitar las reacciones .
Principales productos formados
Los principales productos formados a partir de estas reacciones dependen de las condiciones y los reactivos específicos utilizados. Por ejemplo, la oxidación de la Glimepirida puede llevar a la formación de sulfóxidos o sulfonas .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
La Glimepirida tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Compuestos similares
- Glipizida
- Gliburida
- Metformina
- Semaglutida
Unicidad
La Glimepirida es única entre las sulfonilureas debido a su mayor duración de acción y menor riesgo de hipoglucemia en comparación con otras sulfonilureas de segunda generación . También tiene menos efectos cardiovasculares, lo que la convierte en una opción más segura para pacientes con problemas cardiovasculares .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
4-ethyl-3-methyl-N-[2-[4-[(4-methylcyclohexyl)carbamoylsulfamoyl]phenyl]ethyl]-5-oxo-2H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H34N4O5S/c1-4-21-17(3)15-28(22(21)29)24(31)25-14-13-18-7-11-20(12-8-18)34(32,33)27-23(30)26-19-9-5-16(2)6-10-19/h7-8,11-12,16,19H,4-6,9-10,13-15H2,1-3H3,(H,25,31)(H2,26,27,30) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WIGIZIANZCJQQY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCC1=C(CN(C1=O)C(=O)NCCC2=CC=C(C=C2)S(=O)(=O)NC(=O)NC3CCC(CC3)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H34N4O5S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID5040675, DTXSID20861130 | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5040675 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
490.6 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>73.6 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), Partly miscible, 3.84e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | SID49648856 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
ATP-sensitive potassium channels on pancreatic beta cells that are gated by intracellular ATP and ADP. The hetero-octomeric complex of the channel is composed of four pore-forming Kir6.2 subunits and four regulatory sulfonylurea receptor (SUR) subunits. Alternative splicing allows the formation of channels composed of varying subunit isoforms expressed at different concentrations in different tissues. In pancreatic beta cells, ATP-sensitive potassium channels play a role as essential metabolic sensors and regulators that couple membrane excitability with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS). When there is a decrease in the ATP:ADP ratio, the channels are activated and open, leading to K+ efflux from the cell, membrane hyperpolarization, and suppression of insulin secretion. In contrast, increased uptake of glucose into the cell leads to elevated intracellular ATP:ADP ratio, leading to the closure of channels and membrane depolarization. Depolarization leads to activation and opening of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels and consequently an influx of calcium ions into the cell. Elevated intracellular calcium levels causes the contraction of the filaments of actomyosin responsible for the exocytosis of insulin granules stored in vesicles. Glimepiride blocks the ATP-sensitive potassium channel by binding non-specifically to the B sites of both sulfonylurea receptor-1 (SUR1) and sulfonylurea receptor-2A (SUR2A) subunits as well as the A site of SUR1 subunit of the channel to promote insulin secretion from the beta cell. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
261361-60-8, 93479-97-1, 684286-46-2 | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=261361-60-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0093479971 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride, cis- | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0684286462 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | glimepiride | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759809 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID5040675 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 3-Ethyl-2,5-dihydro-4-methyl-N-[2-[4-[[[[(4-methylcyclohexyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]sulfonyl]phenyl]ethyl]-2-oxo-1H-pyrrole-1-carboxamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID20861130 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | GLIMEPIRIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6KY687524K | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | GLIMEPIRIDE, CIS- | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/24T6XIR2MZ | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
207 °C | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00222 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Glimepiride | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014367 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of Glimepiride?
A1: this compound is a third-generation sulfonylurea derivative that acts as an oral anti-hyperglycemic agent. Its primary mechanism of action involves binding to sulfonylurea receptors (SUR1) on pancreatic β-cells. [, ] This binding leads to the closure of ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels, causing membrane depolarization and subsequent opening of voltage-gated calcium channels. The influx of calcium ions triggers the exocytosis of insulin-containing granules, leading to increased insulin secretion and ultimately lowering blood glucose levels. [, , , , , , , ]
Q2: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A4: The molecular formula of this compound is C24H34N4O5S, and its molecular weight is 490.62 g/mol. [, ]
Q3: Are there different polymorphic forms of this compound, and how do they differ?
A5: Yes, this compound exists in different polymorphic forms. Research has identified three distinct polymorphs: Form I, Form II, and a novel Form III. [] These forms differ in their physicochemical properties, including solubility, melting point, and stability. Notably, Form III exhibits a higher melting point (276.2°C) compared to Form I and Form II, and its X-ray diffraction pattern distinguishes it from the other forms. []
Q4: What spectroscopic techniques are commonly employed to characterize this compound?
A4: Various spectroscopic techniques are employed in the characterization and analysis of this compound. These include:
- Fourier-transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy: FTIR helps identify functional groups and assess drug-excipient compatibility in formulations. [, , ]
- X-ray diffraction (XRD): XRD is crucial for identifying and characterizing the different polymorphic forms of this compound. [, , ]
- Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC): DSC provides insights into thermal transitions and polymorphic transformations of this compound. [, ]
Q5: How does this compound perform in solid dispersions with polyethylene glycol (PEG)?
A7: Studies have shown that this compound exhibits enhanced solubility and dissolution rates when formulated as solid dispersions with PEG 20000. [, ] The solubility of this compound increases proportionally with the concentration of PEG 20000 in a pH 7.4 buffer. [] This improvement is attributed to the amorphization of this compound within the PEG matrix, as confirmed by XRD studies. []
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.


![(1R,3R,6R,7S,8S,9R,10S,13S,16S,17R)-8-tert-butyl-6,9,17-trihydroxy-16-methyl-2,4,14,19-tetraoxahexacyclo[8.7.2.01,11.03,7.07,11.013,17]nonadecane-5,15,18-trione](/img/structure/B1671515.png)