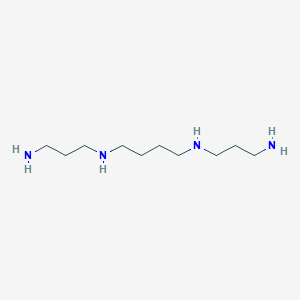
Spermine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
La spermine est une polyamine naturelle impliquée dans le métabolisme cellulaire et présente dans toutes les cellules eucaryotes. Elle est dérivée de l'acide aminé ornithine et joue un rôle crucial dans la stabilisation de la structure hélicoïdale des acides nucléiques, en particulier dans les virus . La this compound est également connue pour son rôle de piégeur de radicaux libres intracellulaires, protégeant l'ADN des dommages oxydatifs .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Spermine has a wide range of applications in scientific research:
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Spermine is a polyamine that interacts with several targets within the cell. Its primary targets include This compound synthase , This compound oxidase , and DNA . This compound synthase is the enzyme responsible for the synthesis of this compound from spermidine . This compound oxidase is involved in the catabolism of this compound . DNA is another significant target of this compound, where it acts as a binder . This compound is also known to interact with other targets such as the Ornithine decarboxylase , Extracellular calcium-sensing receptor , Beta-1 adrenergic receptor , and Beta-2 adrenergic receptor .
Mode of Action
This compound is derived from spermidine by this compound synthase . It is a small organic cation that is absolutely required for eukaryotic cell growth . This compound is normally found in millimolar concentrations in the nucleus . It functions directly as a free radical scavenger , forming a variety of adducts that prevent oxidative damage to DNA . Oxidative damage to DNA by reactive oxygen species is a continual problem that cells must guard against to survive . Hence, this compound is a major natural intracellular compound capable of protecting DNA from free radical attack . This compound is also implicated in the regulation of gene expression, the stabilization of chromatin, and the prevention of endonuclease-mediated DNA fragmentation .
Biochemical Pathways
The biosynthesis of this compound in animals starts with the decarboxylation of ornithine by the enzyme Ornithine decarboxylase in the presence of PLP . This decarboxylation gives putrescine . Thereafter, the enzyme spermidine synthase effects two N-alkylation by decarboxy-S-adenosyl methionine . The intermediate is spermidine . Plants employ additional routes to this compound .
Pharmacokinetics
A study on spermidine, a related polyamine, suggests that dietary polyamines may be presystemically converted into other polyamines, which then enter systemic circulation . This could potentially apply to this compound as well, but more research is needed to confirm this.
Result of Action
This compound is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize the helical structure, particularly in viruses . It functions as an intracellular free radical scavenger to protect DNA from free radical attack . This compound is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen .
Action Environment
This compound has been shown to protect plants from a variety of environmental insults . In the context of Fusarium graminearum, a plant pathogen, spermidine was found to play a crucial role in responding to environmental stresses .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Spermine interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. The precursor for the synthesis of this compound is the amino acid ornithine . This compound biosynthesis in animals starts with the decarboxylation of ornithine by the enzyme Ornithine decarboxylase in the presence of PLP . This decarboxylation gives putrescine, which is then converted to this compound .
Cellular Effects
This compound has been shown to protect cells from a variety of environmental insults . It is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses . It functions as an intracellular free radical scavenger to protect DNA from free radical attack . This compound also plays a role in enhancing antioxidant defense mechanisms, glyoxalase systems, methylglyoxal (MG) detoxification, and creating tolerance for drought-induced oxidative stress in plants .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound exerts its effects at the molecular level through various mechanisms. It functions directly as a free radical scavenger, forming a variety of adducts that prevent oxidative damage to DNA . It also interferes with the binding and stabilization of certain DNA intercalators to DNA .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Over time, this compound’s effects can change in laboratory settings. For instance, drought stress increases endogenous this compound in plants, and exogenous application of this compound improves the plants’ ability to tolerate drought stress .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound can vary with different dosages in animal models. For example, supplementation of cells with exogenous this compound decreases matrix mineralization in a dose-dependent manner .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in several metabolic pathways. In one pathway, L-glutamine is the precursor to L-ornithine, after which the synthesis of this compound from L-ornithine follows the same pathway as in animals . Another pathway in plants starts with decarboxylation of L-arginine to produce agmatine .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported into the mitochondrial matrix by an electrophoretic mechanism having the negative electrical membrane potential (ΔΨ) as the driving force . The presence of phosphate increases this compound uptake by reducing ΔpH and enhancing ΔΨ .
Subcellular Localization
This compound is primarily found in the nucleus . Subcellular localization studies indicate that this compound is a cytosolic protein undergoing proteasomal control .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies Synthétiques et Conditions de Réaction : La spermine est synthétisée à partir de la spermidine par l'action de l'enzyme this compound synthase. Le processus implique le transfert d'un groupe aminopropyle à la spermidine . Les conditions de réaction nécessitent généralement la présence de S-adénosyl méthionine décarboxylée comme cofacteur .
Méthodes de Production Industrielle : La production industrielle de la this compound implique la décarboxylation de l'ornithine pour produire de la putrescine, qui est ensuite convertie en spermidine. Enfin, la spermidine est transformée en this compound par des réactions de N-alkylation . Le processus est optimisé pour la production à grande échelle en contrôlant les conditions de réaction telles que la température, le pH et la concentration des réactifs .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de Réactions : La spermine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment l'oxydation, la réduction et la substitution .
Réactifs et Conditions Courants :
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction impliquant la this compound sont moins courantes mais peuvent se produire dans des conditions spécifiques avec des agents réducteurs.
Substitution : La this compound peut participer à des réactions de substitution, en particulier en présence de nucléophiles forts.
Principaux Produits : Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent le peroxyde d'hydrogène, les aminoaldéhydes et divers dérivés de la this compound substitués .
4. Applications de la Recherche Scientifique
La this compound a une large gamme d'applications dans la recherche scientifique :
Chimie : La this compound est utilisée dans la précipitation de l'ADN et l'isolement de la chromatine.
5. Mécanisme d'Action
La this compound exerce ses effets par plusieurs mécanismes :
Piégeage des Radicaux Libres : La this compound agit comme un piégeur de radicaux libres, protégeant l'ADN des dommages oxydatifs.
Régulation Génétique : Elle est impliquée dans la régulation de l'expression génique et la stabilisation de la chromatine.
Interaction avec les Cibles Moléculaires : La this compound se lie à l'ADN, empêchant la fragmentation de l'ADN induite par l'endonuclease et stabilisant la structure hélicoïdale.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
La spermine fait partie d'une famille de polyamines qui comprend la spermidine, la putrescine et la cadavérine .
Spermidine : Similaire à la this compound mais avec un groupe aminopropyle de moins.
Putrescine : Un précurseur de la spermidine et de la this compound, elle joue un rôle dans la croissance et la différenciation cellulaires.
La this compound est unique en raison de son nombre plus élevé de groupes amino, ce qui améliore sa capacité à stabiliser les acides nucléiques et à protéger contre les dommages oxydatifs .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
N,N'-bis(3-aminopropyl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C10H26N4/c11-5-3-9-13-7-1-2-8-14-10-4-6-12/h13-14H,1-12H2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PFNFFQXMRSDOHW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C(CCNCCCN)CNCCCN | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C10H26N4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
71052-31-8 | |
| Record name | 1,4-Butanediamine, N1,N4-bis(3-aminopropyl)-, homopolymer | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=71052-31-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9058781 | |
| Record name | N1,N4-Bis(3-aminopropyl)-1,4-butanediamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9058781 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
202.34 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid; Absorbs carbon dioxide from air; [Merck Index] Colorless solidified mass or fragments; mp = 28-30 deg C; [Sigma-Aldrich MSDS], Solid | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases | |
| URL | https://haz-map.com/Agents/21744 | |
| Description | Haz-Map® is an occupational health database designed for health and safety professionals and for consumers seeking information about the adverse effects of workplace exposures to chemical and biological agents. | |
| Explanation | Copyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
150-150 °C | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00127 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Solubility |
> 100 mg/mL | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00127 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Spermine is derived from spermidine by spermine synthase. Spermine is a polyamine, a small organic cations that is absolutely required for eukaryotic cell growth. Spermine, is normally found in millimolar concentrations in the nucleus. Spermine functions directly as a free radical scavenger, and forms a variety of adducts that prevent oxidative damage to DNA. Oxidative damage to DNA by reactive oxygen species is a continual problem that cells must guard against to survive. Hence, spermine is a major natural intracellular compound capable of protecting DNA from free radical attack. Spermine is also implicated in the regulation of gene expression, the stabilization of chromatin, and the prevention of endonuclease-mediated DNA fragmentation. | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00127 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
71-44-3, 68956-56-9 | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=71-44-3 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000071443 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Hydrocarbons, terpene processing by-products | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0068956569 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00127 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | spermine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=268508 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | 1,4-Butanediamine, N1,N4-bis(3-aminopropyl)- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | N1,N4-Bis(3-aminopropyl)-1,4-butanediamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9058781 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 4,9-diazadodecamethylenediamine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.686 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SPERMINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2FZ7Y3VOQX | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
29 °C | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00127 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Spermine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0001256 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.

![[4-(2-Chlorophenyl)phenyl]methanol](/img/structure/B22076.png)