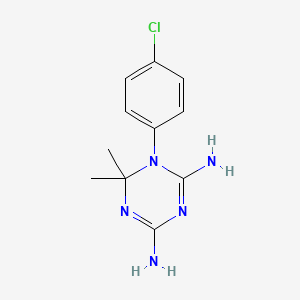
シクログアニル
概要
説明
シクログアニルは、ジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤であり、抗マラリア薬プログアニルの代謝産物です。プログアニルの抗マラリア作用の主な原因となります。
科学的研究の応用
Cycloguanil has several scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: Cycloguanil is used as a model compound in studying dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors.
Biology: Cycloguanil’s role as a dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor makes it valuable in studying cellular processes involving folate metabolism.
作用機序
シクログアニルは、マラリア原虫における核酸合成に不可欠な酵素であるジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼを阻害することでその効果を発揮します。 この酵素を阻害することで、シクログアニルは原虫のDNAとRNAを合成する能力を阻害し、最終的にその死をもたらします 。 含まれる分子標的と経路には、葉酸経路と核酸の合成があります .
類似化合物の比較
シクログアニルは、ピリメタミンやメトトレキサートなどの他のジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤と構造的に類似しています。シクログアニルは、マラリア原虫に対する特異的な活性においてユニークです。類似の化合物には、以下が含まれます。
ピリメタミン: 抗マラリア治療で使用される別のジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤です。
メトトレキサート: がん治療で使用されるジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤です.
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Cycloguanil plays a significant role in biochemical reactions, particularly in the inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase . This enzyme is crucial for the synthesis of nucleic acids, and its inhibition disrupts the reproduction of the malaria parasite . Cycloguanil interacts with this enzyme, leading to the disruption of deoxythymidylate synthesis .
Cellular Effects
Cycloguanil exerts its effects on various types of cells, particularly those infected by the malaria parasite. By inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase, it disrupts the parasite’s ability to reproduce within the host cell . This impacts cell function and can influence cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Cycloguanil involves its binding to dihydrofolate reductase, inhibiting the enzyme and disrupting the synthesis of nucleic acids . This prevents the malaria parasite from reproducing within the host cell .
Metabolic Pathways
Cycloguanil is involved in the metabolic pathway related to the inhibition of dihydrofolate reductase . It interacts with this enzyme, disrupting the synthesis of nucleic acids and affecting metabolic flux and metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
Cycloguanil is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It is known to be a substrate of organic cation transporters and multidrug and toxin extrusion proteins , which play a role in its distribution within cells.
準備方法
シクログアニルは、複数段階のプロセスを経て合成することができます。 この中間体は、その後アセトンと縮合してシクログアニルを生成します 。工業生産方法は、反応条件を最適化して収率と純度を最大化することを含む場合があります。
化学反応の分析
シクログアニルは、以下を含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: シクログアニルは、特定の条件下で酸化され、さまざまな酸化生成物を生成します。
還元: 還元反応は、シクログアニルをその還元型に変換することができます。
置換: シクログアニルは、特定の官能基が他の官能基に置き換えられる置換反応を起こすことができます。
これらの反応で使用される一般的な試薬と条件には、酸化剤、還元剤、触媒などがあります。 これらの反応から生成される主要な生成物は、使用される特定の試薬と条件によって異なります .
科学研究への応用
シクログアニルは、以下を含むいくつかの科学研究への応用があります。
化学: シクログアニルは、ジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤の研究におけるモデル化合物として使用されています。
生物学: シクログアニルは、ジヒドロ葉酸レダクターゼ阻害剤としての役割から、葉酸代謝に関与する細胞プロセスを研究する上で価値があります。
医学: シクログアニルは、主に抗マラリア研究、特に薬剤耐性マラリア株と戦うために他の薬剤と組み合わせて使用されています.
類似化合物との比較
Cycloguanil is structurally similar to other dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors, such as pyrimethamine and methotrexate. cycloguanil is unique in its specific activity against the Plasmodium parasite. Similar compounds include:
Pyrimethamine: Another dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used in antimalarial treatments.
Methotrexate: A dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor used in cancer therapy.
特性
IUPAC Name |
1-(4-chlorophenyl)-6,6-dimethyl-1,3,5-triazine-2,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H14ClN5/c1-11(2)16-9(13)15-10(14)17(11)8-5-3-7(12)4-6-8/h3-6H,1-2H3,(H4,13,14,15,16) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
QMNFFXRFOJIOKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1(N=C(N=C(N1C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl)N)N)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C11H14ClN5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
152-53-4 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000516212 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9022867 | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9022867 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
251.71 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
516-21-2 | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=516-21-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000516212 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB14763 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cycloguanil | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9022867 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | CYCLOGUANIL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/26RM326WVN | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
A: Cycloguanil inhibits the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. [, , , ] This enzyme is crucial for the parasite's folate metabolism, which in turn is essential for DNA synthesis and cell division. [, , ]
A: By blocking DHFR, cycloguanil disrupts the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid, a coenzyme vital for the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, the building blocks of DNA. [, ] This ultimately leads to the death of the parasite. [, ] Research has also shown that cycloguanil can impact downstream signaling pathways, such as STAT3 transcriptional activity, further contributing to its antimalarial effects. []
A: While primarily known for its activity against malaria parasites, cycloguanil also demonstrates inhibitory activity against Trypanosoma brucei PTR1 (TbPTR1), the enzyme pteridine reductase. [] This suggests potential as a dual PTR and DHFR inhibitor for treating human African trypanosomiasis. []
ANone: The provided research papers focus primarily on the biological activity and pharmacokinetic properties of cycloguanil. Information regarding its material compatibility and stability under various conditions is not extensively discussed.
ANone: Cycloguanil itself doesn't possess catalytic properties. It functions as an enzyme inhibitor rather than a catalyst. It is primarily used for its antimalarial properties due to its inhibitory effect on DHFR.
A: Yes, computational techniques like molecular docking and quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) studies have been employed. [, ] These methods help predict the binding affinities of cycloguanil analogs with wild-type and mutant P. falciparum DHFR. [, ] Researchers have used programs like GOLD, FlexX, Glide, and Molegro to analyze and visualize interactions with the DHFR active site. []
A: Molecular docking studies suggest that P. falciparum DHFR exhibits stereoselectivity when binding to R and S enantiomers of cycloguanil analogs. [] Cycloguanil analogs with alkyl chain substituents favor binding to the R enantiomer as it minimizes steric hindrance with the Phe58 residue in the DHFR active site. [] Conversely, analogs with phenol chain substituents prefer the S enantiomer, avoiding steric clashes with Leu46 and Met55. []
ANone: The provided scientific research papers primarily focus on characterizing the mechanism of action, resistance patterns, and structure-activity relationships of cycloguanil and its analogs. They do not extensively cover aspects such as SHE regulations, detailed toxicology profiles, drug delivery strategies, environmental impact, or other points mentioned in questions 8-26.
A: Researchers frequently use in vitro drug susceptibility tests, often employing isotopic methods, to assess the efficacy of cycloguanil against Plasmodium falciparum. [, , , , ] These tests involve culturing the parasite in the presence of varying concentrations of cycloguanil and measuring its growth inhibition. [, , , , ] The concentration at which parasite growth is inhibited by 50% (IC50) is often used to compare the drug sensitivity of different parasite isolates. [, , , , ]
A: Yes, the composition of the culture medium can significantly influence the in vitro activity of cycloguanil. [] Studies have demonstrated that standard RPMI medium or RPMI with low concentrations of folate and para-aminobenzoic acid leads to higher IC50 values for cycloguanil compared to folate and para-aminobenzoic acid-free RPMI. [] These findings highlight the importance of carefully controlling for medium composition when performing in vitro drug susceptibility assays.
ANone: While the provided research focuses on specific aspects of cycloguanil's activity and resistance, detailed toxicological data and long-term safety profiles are not extensively discussed.
ANone: The provided research papers predominantly concentrate on the mechanisms of action, resistance patterns, and structure-activity relationships of cycloguanil and its analogs. Information regarding drug delivery, biomarkers, detailed analytical techniques, environmental impact, or other points mentioned in questions 13-26 is limited within these specific research papers.
A: Cycloguanil has a history dating back to the mid-20th century, emerging as a key player in antimalarial research. [] Initially, it was observed that the antimalarial activity of the prodrug chloroguanide hydrochloride was largely attributed to its dihydrotriazine metabolite, later identified as cycloguanil. [] This led to the development of cycloguanil pamoate, a poorly water-soluble salt form designed for intramuscular depot administration, to achieve prolonged antimalarial effects. []
A: Research on cycloguanil demonstrates the synergy between various scientific disciplines, including parasitology, pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, and computational chemistry. [, ] Understanding the mechanism of action, resistance mechanisms, and structure-activity relationships through both in vitro and in vivo studies has been crucial in guiding the development of more effective antimalarial therapies. [, ] The identification of cycloguanil as a potential inhibitor of Trypanosoma brucei PTR1 highlights the potential for cross-disciplinary applications in combating other parasitic diseases. []
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。







![5-methyl-2-[(2R)-6-methylhept-5-en-2-yl]phenol](/img/structure/B1669342.png)

