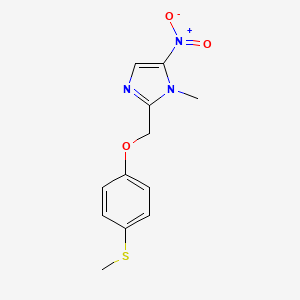
フェキシニダゾール
概要
説明
フェキシニダゾールは、主に抗寄生虫薬として使用される5-ニトロイミダゾール誘導体です。 トリパノソーマ・ブルセイ・ガンビエンセが原因で起こるアフリカトリパノソーマ症(睡眠病)に有効であり、シャガス病の治療においても有効性が示されています . この化合物は、睡眠病の初期および後期段階の両方に対して、世界初の経口治療薬となったことで注目されています .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: フェキシニダゾールは、市販の前駆体から出発する複数段階のプロセスによって合成されます。 主要なステップには、イミダゾールのニトロ化、それに続くアルキル化、およびメチルスルファニルフェノキシ基を導入するための後続の反応が含まれます。 反応条件は、通常、制御された温度と特定の触媒の使用を伴い、高い収率と純度を確保します .
工業生産方法: フェキシニダゾールの工業生産には、実験室規模の合成プロセスを拡大することが含まれます。 これには、収率を最大化し、不純物を最小限に抑えるために、反応条件を最適化することが含まれます。 このプロセスは、温度、圧力、および反応時間を正確に制御した大型反応器で行われます。 結晶化や濾過などの精製工程が用いられて最終製品が得られます .
科学的研究の応用
Fexinidazole has a wide range of applications in scientific research:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study nitroimidazole chemistry and its reactivity.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cellular processes and its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Medicine: Primarily used to treat African trypanosomiasis and being explored for Chagas disease treatment.
Industry: Potential applications in developing new antiparasitic drugs and studying drug resistance mechanisms
作用機序
フェキシニダゾールは、寄生虫のDNA合成を阻害する活性代謝物に代謝されることによってその効果を発揮します。 この化合物は、寄生虫内の特定の酵素を活性化すると考えられており、寄生虫の細胞構造を損傷する活性酸素種の産生につながります。 最終的には、寄生虫の死をもたらします .
類似化合物:
ニフルチモックス: シャガス病の治療に用いられる別のニトロイミダゾールです。
ベンゾニダゾール: シャガス病に使用され、フェキシニダゾールと構造と機能が似ています。
メトロニダゾール: 細菌感染症と原生動物感染症に広く使用されているニトロイミダゾールです.
フェキシニダゾールのユニークさ: フェキシニダゾールは、経口バイオアベイラビリティとアフリカトリパノソーマ症の初期と後期の両方の段階に対する有効性によって際立っています。 静脈内投与を必要とする他の治療法とは異なり、フェキシニダゾールは経口投与できるため、リソースが限られている地域でのアクセスが容易になり、投与が容易になります .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Fexinidazole is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death . It interacts with enzymes within the parasites that result in their death .
Cellular Effects
Fexinidazole has a broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6 . Therefore, it is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . It has been shown to be non-inferior to existing nifurtimox / eflornithine combination therapy in late-stage T. brucei gambiense infection .
Molecular Mechanism
Fexinidazole is believed to work by turning on certain enzymes within the parasites that result in their death . It is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Fexinidazole is well absorbed, although the rate and extent of absorption are less than dose-proportional . After a 14-day administration schedule, the mean C max and AUC last increased by 1.17 and 1.34, or by 1.5 and 1.61, when the dose was either doubled or tripled .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In the mouse model, fexinidazole cures both the first, hemolymphatic, and the second, meningoencephalitic stage of the infection, the latter at 100 mg/kg twice daily for 5 days . The dosage effects of fexinidazole were found to be dose-dependent in a mouse model of human African trypanosomiasis .
Metabolic Pathways
Following absorption, fexinidazole is rapidly converted to its M1 metabolite, which undergoes a slower transformation to M2 over time . These metabolites have equivalent biological activity to the parent and contribute significantly to the in vivo efficacy .
Transport and Distribution
Fexinidazole is well-absorbed and readily distributes throughout the body, including the brain . Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled fexinidazole in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues .
Subcellular Localization
Fexinidazole is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . This suggests that it can localize to various subcellular compartments where the parasites reside.
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Fexinidazole is synthesized through a multi-step process starting from commercially available precursors. The key steps involve the nitration of imidazole, followed by alkylation and subsequent reactions to introduce the methylsulfanylphenoxy group. The reaction conditions typically involve controlled temperatures and the use of specific catalysts to ensure high yield and purity .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of fexinidazole involves scaling up the laboratory synthesis process. This includes optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and minimize impurities. The process is carried out in large reactors with precise control over temperature, pressure, and reaction time. Purification steps such as crystallization and filtration are employed to obtain the final product .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: フェキシニダゾールは、次のようないくつかの種類の化学反応を起こします。
酸化: ニトロ基は、特定の条件下でアミンに還元できます。
置換: イミダゾール環は、求核置換反応を起こすことができます。
一般的な試薬と条件:
酸化: 一般的な試薬には、過酸化水素と金属触媒があります。
置換: アミンやチオールなどの求核剤が使用されます。
加水分解: 酸性または塩基性溶液が使用されます.
主な生成物:
ニトロ基の還元: アミン誘導体の生成をもたらします。
置換反応: さまざまな置換されたイミダゾール誘導体を生成します。
加水分解: より単純な分子に化合物が分解される可能性があります.
4. 科学研究の応用
フェキシニダゾールは、科学研究において幅広い用途があります。
化学: ニトロイミダゾールの化学とその反応性を研究するためのモデル化合物として使用されています。
生物学: 細胞プロセスに対する影響と治療薬としての可能性について調査されています。
医学: 主にアフリカトリパノソーマ症の治療に使用されており、シャガス病の治療についても研究されています。
類似化合物との比較
Nifurtimox: Another nitroimidazole used to treat Chagas disease.
Benznidazole: Used for Chagas disease, similar in structure and function to fexinidazole.
Metronidazole: A widely used nitroimidazole for bacterial and protozoal infections.
Uniqueness of Fexinidazole: Fexinidazole stands out due to its oral bioavailability and effectiveness against both early and late stages of African trypanosomiasis. Unlike other treatments that require intravenous administration, fexinidazole can be taken orally, making it more accessible and easier to administer in resource-limited settings .
特性
IUPAC Name |
1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H13N3O3S/c1-14-11(13-7-12(14)15(16)17)8-18-9-3-5-10(19-2)6-4-9/h3-7H,8H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MIWWSGDADVMLTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1C(=CN=C1COC2=CC=C(C=C2)SC)[N+](=O)[O-] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H13N3O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID00208448 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
279.32 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is caused by two subspecies of _Trypanosoma brucei_, _T. brucei gambiense_ and _T. brucei rhodesiense_, with _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT accounting for ~97% of the total disease burden. Transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly, HAT begins as a local infection at the bite site before disseminating throughout the blood and reticuloendothelial system (first or hemolymphatic stage) and eventually crossing the blood-brain barrier (second or meningoencephalitic stage). First stage _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT is characterized by fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, pruritus, and other non-specific symptoms. Progression to the second stage results in progressive deterioration of neurological function, including sleep disturbances (HAT is also referred to as sleeping sickness), tremors, ataxia, abnormal behaviour, confusion, and coma; myocarditis and endocrine hypothalamic-hypophyseal dysfunction may also be present. If left untreated, HAT is fatal. Fexinidazole is the first all-oral treatment for _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT. Both fexinidazole and its two main metabolites, a sulfoxide (M1) and sulfone (M2) metabolite, possess _in vitro_ activity against _T. brucei gambiense_, _T. brucei rhodesiense_, and _T. brucei brucei_ in the 0.2-0.9 μg/mL range. Further studies revealed _in vivo_ efficacy in HAT animal models and acceptable toxicity profiles, both in animal and human subjects. Crucially, fexinidazole was shown to be non-inferior to existing [nifurtimox]/[eflornithine] combination therapy (NECT) in late-stage _T. brucei gambiense_ infection. The precise mechanism of action of fexinidazole remains unknown. However, it is suggested that bacterial-like nitroreductases encoded by trypanosomes activate fexinidazole and its M1/M2 metabolites through reduction to form reactive intermediates capable of damaging DNA and proteins. Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled fexinidazole in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6. Therefore, fexinidazole is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain, which is consistent with its efficacy against both early and late-stage infections. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
59729-37-2 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59729-37-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0059729372 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | FEXINIDAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/306ERL82IR | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。
![3-Chloro-2,6-Dimethyl-5-{4-[4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]phenyl}pyridin-4-Ol](/img/structure/B1672545.png)
![3-[(2-Bromophenyl)methoxy]-5-[6-(trifluoromethyl)benzimidazol-1-yl]thiophene-2-carboxamide](/img/structure/B1672548.png)
![1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-[4-[2-chloroethylcarbamoyl(nitroso)amino]-2,3-dihydroxybutyl]-1-nitrosourea](/img/structure/B1672557.png)
