レディパスビル
概要
説明
レディパスビルは、主に慢性C型肝炎ウイルス(HCV)感染症の治療に使用される、直接作用型抗ウイルス剤です。ギリアド・サイエンシズ社によって開発され、ハーボニーという商品名でソフォスブビルとの併用で広く使用されています。 レディパスビルは、ウイルス複製とアセンブリに不可欠なC型肝炎ウイルスの非構造タンパク質5A(NS5A)を標的としています .
製法
合成経路と反応条件
レディパスビルの合成には、重要な中間体の調製など、複数のステップが含まれます。 ある方法では、酵素加水分解による高純度の中間体である(1R, 3S, 4S)-N-tert-ブトキシカルボニル-2-アザビシクロ[2.2.1]ヘプタン-3-カルボン酸の調製が関与しています . 別の方法では、後期段階のシクロプロパン化とフッ素化プロセスが関与し、これにより、8つの直線的なステップで20%の総収率でレディパスビルを調製するための新規で効率的な経路が提供されます .
工業的製造方法
レディパスビルの工業的製造は、収率、純度、および費用対効果の最適化に焦点を当てています。このプロセスは、通常、高純度の中間体と環境に優しい反応条件の使用を伴います。 これらの方法は、大規模生産に対応するように設計されており、高い選択性と製造コストの削減が保証されます .
科学的研究の応用
Ledipasvir has significant applications in scientific research, particularly in the fields of chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry:
Chemistry: Ledipasvir serves as a model compound for studying antiviral agents and their synthesis.
Biology: It is used to study the replication mechanisms of the hepatitis C virus and the role of NS5A in viral assembly.
Medicine: Ledipasvir, in combination with sofosbuvir, is used to treat chronic hepatitis C infections, achieving high cure rates and minimal side effects
Industry: The production and formulation of Ledipasvir contribute to the pharmaceutical industry’s efforts to develop effective antiviral therapies
作用機序
レディパスビルは、HCVビリオンのウイルスRNA複製とアセンブリに不可欠なC型肝炎ウイルスの非構造タンパク質5A(NS5A)を阻害します。 レディパスビルは、NS5Aの過剰リン酸化を阻害することにより、ウイルスタンパク質の産生を阻害し、それによりウイルス複製とアセンブリを阻害します .
類似の化合物との比較
類似の化合物
ソフォスブビル: レディパスビルとの併用で使用される別の直接作用型抗ウイルス剤です。これは、HCVのNS5Bポリメラーゼを阻害します。
ダクラタスビル: レディパスビルと類似したNS5A阻害剤ですが、薬物動態特性が異なります。
レディパスビルのユニークさ
レディパスビルは、複数のHCV遺伝型に対する高い効力と、ソフォスブビルとの併用で95%を超える持続ウイルス学的反応(SVR)率を達成できることからユニークです。 レディパスビルは、長い半減期と最小限の副作用により、HCV治療の選択肢として好まれています .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Ledipasvir interacts with the NS5A protein, a phosphoprotein that plays an essential role in the replication of the hepatitis C virus . By binding to this protein, Ledipasvir disrupts the replication process of the virus .
Cellular Effects
Ledipasvir has a profound effect on cells infected with the hepatitis C virus. It inhibits the replication of the virus, thereby reducing the viral load within the cells . This can lead to a decrease in the severity of the disease and potentially to a complete cure .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Ledipasvir involves its interaction with the NS5A protein. Ledipasvir binds to this protein, preventing it from assisting in the replication of the viral RNA . This stops the virus from multiplying and spreading to other cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Ledipasvir have been observed to be both rapid and long-lasting . The drug quickly reduces the viral load in cells, and this effect can be sustained over a long period, leading to a sustained virological response .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
While specific studies on dosage effects in animal models were not found in the search results, clinical studies have shown that Ledipasvir, in combination with other antiviral drugs, is effective in treating hepatitis C in humans .
Metabolic Pathways
It is known that the drug works by interfering with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus, specifically by inhibiting the NS5A protein .
Transport and Distribution
Given its effectiveness in reducing viral load, it can be inferred that the drug is able to reach the sites of viral replication within the cells .
Subcellular Localization
Given that it targets the NS5A protein, which is involved in the replication of the hepatitis C virus, it is likely that the drug localizes to the sites within the cell where this process takes place .
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of Ledipasvir involves multiple steps, including the preparation of key intermediates. One method involves the preparation of a high-purity intermediate, (1R, 3S, 4S)-N-tertbutyloxycarbonyl-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptane-3-carboxylic acid, through enzymatic hydrolysis . Another method involves late-stage cyclopropanation and fluorination processes, which provide a novel and efficient route for the preparation of Ledipasvir with a total yield of 20% over eight linear steps .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of Ledipasvir focuses on optimizing yield, purity, and cost-effectiveness. The process typically involves the use of high-purity intermediates and environmentally friendly reaction conditions. The methods are designed to be scalable for large-scale production, ensuring high selectivity and reduced production costs .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類
レディパスビルは、以下を含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
還元: レディパスビルでは還元反応はあまり一般的ではありません。
一般的な試薬と条件
レディパスビルの合成と反応で使用される一般的な試薬には、アセトニトリル、酢酸、ジイソプロピルエーテルなどがあります。 反応条件は、多くの場合、高収率と高純度を確保するために、高温と制御された環境を伴います .
生成される主要な生成物
レディパスビルを含む反応から生成される主要な生成物は、C型肝炎の治療に使用される最終的な有効医薬品成分です。 他の中間体や副生成物は、通常、精製プロセスによって除去されます .
科学研究への応用
レディパスビルは、特に化学、生物学、医学、産業の分野において、科学研究において重要な用途があります。
化学: レディパスビルは、抗ウイルス剤とその合成を研究するためのモデル化合物として役立ちます。
生物学: これは、C型肝炎ウイルスの複製機構と、NS5Aのウイルスアセンブリにおける役割を研究するために使用されます。
医学: レディパスビルは、ソフォスブビルとの併用で、慢性C型肝炎感染症の治療に使用されており、高い治癒率と最小限の副作用を実現しています
類似化合物との比較
Similar Compounds
Sofosbuvir: Another direct-acting antiviral used in combination with Ledipasvir. It inhibits the NS5B polymerase of HCV.
Daclatasvir: An NS5A inhibitor similar to Ledipasvir but with different pharmacokinetic properties.
Ombitasvir: Another NS5A inhibitor used in combination with other antiviral agents for HCV treatment
Uniqueness of Ledipasvir
Ledipasvir is unique due to its high potency against multiple HCV genotypes and its ability to achieve sustained virologic response (SVR) rates of over 95% when used in combination with sofosbuvir. Its long half-life and minimal side effects make it a preferred choice for HCV treatment .
特性
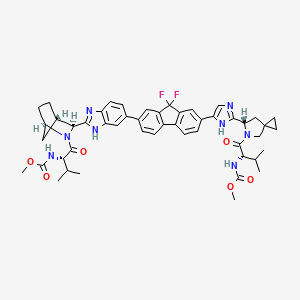
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(6S)-6-[5-[9,9-difluoro-7-[2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-3-yl]-3H-benzimidazol-5-yl]fluoren-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]heptan-5-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C49H54F2N8O6/c1-24(2)39(56-46(62)64-5)44(60)58-23-48(15-16-48)21-38(58)42-52-22-37(55-42)28-9-13-32-31-12-8-26(18-33(31)49(50,51)34(32)19-28)27-10-14-35-36(20-27)54-43(53-35)41-29-7-11-30(17-29)59(41)45(61)40(25(3)4)57-47(63)65-6/h8-10,12-14,18-20,22,24-25,29-30,38-41H,7,11,15-17,21,23H2,1-6H3,(H,52,55)(H,53,54)(H,56,62)(H,57,63)/t29-,30+,38-,39-,40-,41-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VRTWBAAJJOHBQU-KMWAZVGDSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)CC1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)C9C1CCC(C1)N9C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CC2(CC2)C[C@H]1C3=NC=C(N3)C4=CC5=C(C=C4)C6=C(C5(F)F)C=C(C=C6)C7=CC8=C(C=C7)N=C(N8)[C@@H]9[C@H]1CC[C@H](C1)N9C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C49H54F2N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID90154829 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
889.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ledipasvir is an inhibitor of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS5A protein required for viral RNA replication and assembly of HCV virions. Although its exact mechanism of action is unknown, it is postulated to prevent hyperphosphorylation of NS5A which is required for viral production. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1256388-51-8 | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1256388-51-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1256388518 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09027 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ledipasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90154829 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Methyl[(2S)-1-{(6S)-6-[5-(9,9-difluoro-7-{2-[(1R,3S,4S)-2-{(2S)-2-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]-3-methylbutanoyl}-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-3-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-6-yl}-9H-fluoren-2-yl)-1H-imidazol-2-yl]-5-azaspiro[2.4]hept-5-yl}-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LEDIPASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/013TE6E4WV | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details












Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details












試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。
![Thioacetic acid S-[(S)-6-[[(R)-5-oxopyrrolidine-2-ylcarbonyl]amino]-6-(phenylcarbamoyl)hexyl] ester](/img/structure/B612170.png)

![4-O-(19-ethyl-14,18-dioxo-17-oxa-3,13-diazapentacyclo[11.8.0.02,11.04,9.015,20]henicosa-1(21),2,4,6,8,10,15(20)-heptaen-19-yl) 1-O-[2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-yl] butanedioate](/img/structure/B612184.png)