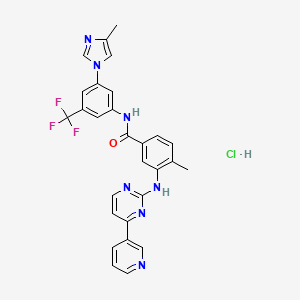
Nilotinibhydrochlorid
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Nilotinib hydrochloride is a medication primarily used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) that is positive for the Philadelphia chromosome. It is a second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor developed to overcome resistance to imatinib, another tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Nilotinib hydrochloride is marketed under the brand name Tasigna and is known for its efficacy in treating both newly diagnosed and imatinib-resistant CML .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Nilotinibhydrochlorid hat mehrere Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung verwendet, um die Synthese und Stabilität von Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitoren zu untersuchen.
Biologie: Untersucht wegen seiner Auswirkungen auf zelluläre Signalwege und seinem Potenzial, andere Kinasen zu hemmen.
Medizin: Wird hauptsächlich zur Behandlung der chronisch-myeloischen Leukämie eingesetzt. .
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound übt seine Wirkung aus, indem es die Tyrosinkinase-Aktivität des BCR-ABL-Proteins hemmt, das vom Philadelphia-Chromosom produziert wird. Es bindet an die ATP-Bindungsstelle des BCR-ABL-Proteins und verhindert so dessen Phosphorylierungsaktivität. Diese Hemmung blockiert die nachgeschalteten Signalwege, die für das Überleben und die Proliferation von Leukämiezellen entscheidend sind .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Imatinib: Der Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitor der ersten Generation, der zur Behandlung von CML eingesetzt wird. This compound wurde entwickelt, um die Resistenz gegen Imatinib zu überwinden.
Dasatinib: Ein weiterer Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitor der zweiten Generation, der zur Behandlung von CML eingesetzt wird.
Bosutinib: Ein Tyrosinkinase-Inhibitor der dritten Generation, der zur Behandlung von CML eingesetzt wird.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound: this compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seiner höheren Potenz und Spezifität für das BCR-ABL-Protein im Vergleich zu Imatinib. Es ist auch wirksam gegen mehrere imatinib-resistente BCR-ABL-Mutationen, was es zu einer wertvollen Option für Patienten macht, die nicht auf Imatinib ansprechen .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Nilotinib hydrochloride, also known as AMN107, is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor . It primarily targets BCR-ABL , c-kit , and PDGF . These proteins play a crucial role in cell signaling pathways that control cell growth and proliferation .
Mode of Action
Nilotinib inhibits the tyrosine kinase activity of the BCR-ABL protein . It binds to the ATP-binding site of BCR-ABL, thereby inhibiting tyrosine kinase activity . This inhibition prevents the phosphorylation and activation of proteins involved in the BCR-ABL signal transduction pathway .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by Nilotinib is the BCR-ABL signal transduction pathway . By inhibiting the tyrosine kinase activity of the BCR-ABL protein, Nilotinib disrupts the signaling pathway, which leads to a decrease in the proliferation of leukemic cells .
Pharmacokinetics
Nilotinib is rapidly absorbed, with a peak serum concentration approximately 3 hours after dosing . The metabolism of Nilotinib is primarily via hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 . The bioavailability of Nilotinib is increased by up to 82% when given with a high-fat meal compared with the fasted state .
Result of Action
The inhibition of the BCR-ABL protein by Nilotinib results in the reduction of leukemic cell proliferation . This leads to a decrease in the number of leukemic cells in patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) that is Philadelphia chromosome positive .
Action Environment
The efficacy and stability of Nilotinib can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the bioavailability of Nilotinib is significantly increased when taken with a high-fat meal . Additionally, exposure to Nilotinib can be significantly reduced by the induction of CYP3A4 with rifampicin and significantly increased by the inhibition of CYP3A with ketoconazole .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Nilotinib hydrochloride plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the activity of several tyrosine kinases, including BCR-ABL, c-KIT, and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR). It binds to the ATP-binding site of these kinases, preventing their phosphorylation and subsequent activation. This inhibition disrupts the signaling pathways that promote cell proliferation and survival . Nilotinib hydrochloride also interacts with other biomolecules such as EPHA3, EPHA8, DDR1, DDR2, MAPK11, and ZAK, further contributing to its anti-leukemic effects .
Cellular Effects
Nilotinib hydrochloride exerts significant effects on various cell types and cellular processes. In leukemic cells, it inhibits the BCR-ABL kinase, leading to reduced cell proliferation and increased apoptosis. This compound also affects cell signaling pathways, including those mediated by c-KIT and PDGFR, which are involved in cell growth and differentiation . Additionally, nilotinib hydrochloride influences gene expression and cellular metabolism, contributing to its therapeutic efficacy in CML .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of action of nilotinib hydrochloride involves its binding to the ATP-binding site of the BCR-ABL kinase, stabilizing its inactive conformation. This binding prevents the phosphorylation of downstream signaling proteins, thereby inhibiting the proliferation of leukemic cells . Nilotinib hydrochloride also inhibits other tyrosine kinases, such as c-KIT and PDGFR, by a similar mechanism, further contributing to its anti-cancer effects .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of nilotinib hydrochloride have been observed to change over time. The compound is relatively stable, but its efficacy can decrease due to degradation and the development of resistance in leukemic cells . Long-term studies have shown that continuous exposure to nilotinib hydrochloride can lead to sustained inhibition of BCR-ABL kinase activity and prolonged survival of treated cells . Resistance mechanisms, such as mutations in the BCR-ABL gene, can reduce its effectiveness over time .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of nilotinib hydrochloride vary with different dosages. At therapeutic doses, it effectively inhibits the proliferation of leukemic cells and reduces tumor burden . At higher doses, nilotinib hydrochloride can cause toxic effects, including hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity . Studies have shown that there is a threshold dose above which the adverse effects outweigh the therapeutic benefits .
Metabolic Pathways
Nilotinib hydrochloride is primarily metabolized in the liver through oxidation and hydroxylation, mainly by the enzyme CYP3A4 . The main circulating component in the serum is the parent drug, with its metabolites contributing minimally to its pharmacological activity . The metabolic pathways of nilotinib hydrochloride involve interactions with various enzymes and cofactors, affecting metabolic flux and metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
Within cells and tissues, nilotinib hydrochloride is transported and distributed through various mechanisms. It is highly protein-bound in the plasma, with a protein binding rate of approximately 98% . The compound is also an inhibitor of the OATP-1B1 transporter, which affects its distribution and accumulation in specific tissues . The distribution coefficient (D) for nilotinib hydrochloride in n-octanol/0.1 N HCl buffer at 37°C is 0.08, indicating its hydrophilic nature .
Subcellular Localization
Nilotinib hydrochloride is localized within specific subcellular compartments, influencing its activity and function. Studies have shown that it can be internalized by cells and distributed within the cytoplasm and nucleus . The subcellular localization of nilotinib hydrochloride is crucial for its therapeutic effects, as it needs to reach its target kinases to exert its inhibitory action .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Die Synthese von Nilotinibhydrochlorid umfasst mehrere Schritte, beginnend mit der Herstellung der Kernstruktur, die ein Benzamid-Derivat umfasst. Der Prozess beinhaltet typischerweise die folgenden Schritte:
Bildung der Kernstruktur: Die Kernstruktur wird durch Reaktion von 4-Methyl-3-nitrobenzoesäure mit 4-Methyl-1H-imidazol in Gegenwart eines Kupplungsmittels synthetisiert.
Bildung des Hydrochloridsalzes: Der letzte Schritt beinhaltet die Umwandlung der Zwischenverbindung in this compound durch Reaktion mit Salzsäure.
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren: Die industrielle Produktion von this compound folgt einem ähnlichen Syntheseweg, der jedoch für die großtechnische Produktion optimiert ist. Der Prozess stellt sicher, dass eine stabile kristalline Form von this compound gebildet wird, die für seine pharmazeutische Formulierung unerlässlich ist .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Nilotinibhydrochlorid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden, was zur Bildung von Abbauprodukten führt.
Reduktion: Die Nitrogruppe in der Zwischenverbindung wird während der Synthese zu einem Amin reduziert.
Substitution: Die Synthese beinhaltet Substitutionsreaktionen, um funktionelle Gruppen in die Kernstruktur einzuführen.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Katalytische Hydrierung: Raney-Nickel in Methanol wird für den Reduktionsschritt verwendet.
Salzsäure: Wird zur Bildung des Hydrochloridsalzes verwendet.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden:
This compound: Das Hauptprodukt, das aus der Synthese entsteht.
Abbauprodukte: Werden während der Oxidation und anderer Stressbedingungen gebildet
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Imatinib: The first-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor used to treat CML. Nilotinib hydrochloride was developed to overcome resistance to imatinib.
Dasatinib: Another second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor used to treat CML.
Bosutinib: A third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor used for CML treatment.
Uniqueness of Nilotinib Hydrochloride: Nilotinib hydrochloride is unique due to its higher potency and specificity for the BCR-ABL protein compared to imatinib. It is also effective against several imatinib-resistant BCR-ABL mutations, making it a valuable option for patients who do not respond to imatinib .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
4-methyl-N-[3-(4-methylimidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]benzamide;hydrochloride | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H22F3N7O.ClH/c1-17-5-6-19(10-25(17)37-27-33-9-7-24(36-27)20-4-3-8-32-14-20)26(39)35-22-11-21(28(29,30)31)12-23(13-22)38-15-18(2)34-16-38;/h3-16H,1-2H3,(H,35,39)(H,33,36,37);1H | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VTGGYCCJUPYZSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)C(=O)NC2=CC(=CC(=C2)C(F)(F)F)N3C=C(N=C3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5.Cl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C28H23ClF3N7O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60238968 | |
| Record name | Nilotinib hydrochloride anhydrous | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60238968 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
566.0 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
923288-95-3 | |
| Record name | Nilotinib hydrochloride anhydrous | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0923288953 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nilotinib hydrochloride anhydrous | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60238968 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 4-Methyl-N-[3-(4-methylimidazol-1-yl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-[(4-pyridin-3-ylpyrimidin-2-yl)amino]benzamide hydrochloride | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | NILOTINIB HYDROCHLORIDE ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/K37N7BYX3X | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details




Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.

![methyl (4R)-4-[(10S,13R,14R,17R)-4,4,10,13,14-pentamethyl-3,7,11,15-tetraoxo-2,5,6,12,16,17-hexahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoate](/img/structure/B1258723.png)
![(1aR,7R,7aR,7bS)-1,1,7,7a-tetramethyl-2,3,5,6,7,7b-hexahydro-1aH-cyclopropa[a]naphthalene](/img/structure/B1258724.png)
![6-(4-methoxyphenyl)-6,7-dihydropyrrolo[2,1-d][1,5]benzothiazepin-7-ol](/img/structure/B1258735.png)
![5-[(2,4,5-Trihydroxyphenyl)methyl]imidazolidine-2,4-dione](/img/structure/B1258737.png)
