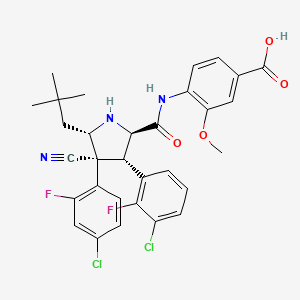
Ombitasvir
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Ombitasvir ist ein antivirales Medikament, das zur Behandlung von Hepatitis-C-Virus (HCV)-Infektionen eingesetzt wird. Es handelt sich um ein direkt wirkendes antivirales Mittel, das das nicht-strukturelle Protein 5A (NS5A) hemmt, das für die Virusreplikation und die Virusteilchenbildung essentiell ist . This compound wird häufig in Kombination mit anderen antiviralen Mitteln wie Paritaprevir, Ritonavir und Dasabuvir eingesetzt, um bei Patienten mit chronischer Hepatitis C eine anhaltende virologische Antwort (SVR) zu erzielen .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Ombitasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent that primarily targets the nonstructural protein 5A (NS5A) of the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . NS5A is a multifunctional protein that plays crucial roles in viral replication and assembly .
Mode of Action
This compound acts by inhibiting NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . By binding to NS5A, this compound disrupts the formation of the replication complex, thereby preventing the replication of the HCV RNA genome .
Biochemical Pathways
The inhibition of NS5A by this compound disrupts the HCV replication cycle. This disruption prevents the production of new viral particles, thereby reducing the viral load in patients with HCV infection . The exact biochemical pathways affected by this compound are still under investigation.
Pharmacokinetics
This compound displays linear pharmacokinetics with minimal accumulation . It is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism . This compound is a substrate of P-glycoprotein, a protein that pumps foreign substances out of cells . It is eliminated via metabolism and biliary excretion, with a negligible amount of unchanged drug excreted in urine . The elimination half-life of this compound is approximately 21 to 25 hours .
Result of Action
The result of this compound’s action is a significant reduction in HCV viral load, leading to a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of daily therapy . SVR and eradication of HCV infection are associated with significant long-term health benefits, including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Ombitasvir is a potent inhibitor of NS5A, a protein essential for viral replication and virion assembly . It displays linear pharmacokinetics over the dose range evaluated . This compound is predominantly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by oxidative metabolism, and has low potential for drug interactions .
Cellular Effects
This compound, as part of combination therapy, is used to treat chronic Hepatitis C, an infectious liver disease caused by infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . It acts by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A, which is essential for viral replication and virion assembly .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves the inhibition of the HCV protein NS5A . NS5A is a protein that is essential for viral replication and virion assembly. By inhibiting this protein, this compound prevents the virus from replicating and assembling new virions .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, this compound has shown to be effective in achieving a sustained virologic response (SVR) after 12 weeks of daily therapy . The treatment with this compound is associated with very minimal side effects, with the most common being headache and fatigue .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is mainly metabolized by amide hydrolysis followed by CYP2C8-mediated oxidative metabolism . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Transport and Distribution
This compound displays high plasma protein binding (~99.9%) and has an apparent volume of distribution of 173 liters . The drug is mainly excreted in the feces (90.2%) with very little excreted in the urine (1.91%) .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that this compound likely interacts with the HCV NS5A protein within the host cell where the viral replication and assembly occur .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von Ombitasvir umfasst mehrere Schritte, darunter die Bildung von Schlüsselzwischenprodukten und deren anschließende Kupplung. Die Reaktionsbedingungen umfassen häufig die Verwendung organischer Lösungsmittel, Katalysatoren und Reagenzien wie Acetonitril, Phosphatpuffer und Ammoniumacetat .
Industrielle Produktionsverfahren
In der industriellen Produktion wird this compound unter Verwendung großtechnischer chemischer Verfahren synthetisiert, die eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit gewährleisten. Das Verfahren umfasst die Optimierung der Reaktionsbedingungen, Reinigungsschritte und Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen, um die behördlichen Anforderungen zu erfüllen. Hochleistungsflüssigchromatographie (HPLC) und Flüssigchromatographie-Tandem-Massenspektrometrie (LC-MS/MS) sind gängige Analysetechniken zur Überwachung der Synthese und zur Sicherstellung der Qualität des Endprodukts .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
Reaktionstypen
This compound durchläuft verschiedene Arten von chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Substitution: Die Synthese von this compound umfasst Substitutionsreaktionen, um verschiedene funktionelle Gruppen am Pyrrolidinring einzuführen.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Häufige Reagenzien, die bei der Synthese und Reaktion von this compound verwendet werden, sind Acetonitril, Phosphatpuffer, Ammoniumacetat und verschiedene organische Lösungsmittel. Die Reaktionsbedingungen werden sorgfältig kontrolliert, um die gewünschten chemischen Umwandlungen zu erreichen und die Stabilität der Verbindung zu gewährleisten .
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Zu den Hauptprodukten, die bei den Reaktionen mit this compound gebildet werden, gehören seine aktiven Metaboliten, die die antivirale Aktivität beibehalten und zur gesamten therapeutischen Wirkung beitragen .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions
Ombitasvir undergoes several types of chemical reactions, including:
Substitution: The synthesis of this compound involves substitution reactions to introduce various functional groups onto the pyrrolidine ring.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Common reagents used in the synthesis and reactions of this compound include acetonitrile, phosphate buffer, ammonium acetate, and various organic solvents. The reaction conditions are carefully controlled to achieve the desired chemical transformations and ensure the stability of the compound .
Major Products Formed
The major products formed from the reactions involving this compound include its active metabolites, which retain the antiviral activity and contribute to the overall therapeutic effect .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Ombitasvir hat mehrere Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, darunter:
Medizin: this compound wird in erster Linie zur Behandlung chronischer Hepatitis-C-Infektionen eingesetzt. .
Chemie: Die Synthese und Analyse von this compound haben zur Entwicklung fortschrittlicher Analysetechniken und -methoden für die Untersuchung komplexer organischer Verbindungen beigetragen
Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine antivirale Wirkung durch Hemmung des nicht-strukturellen Proteins 5A (NS5A) des Hepatitis-C-Virus. NS5A ist essentiell für die Virusreplikation und -assemblierung, und seine Hemmung stört den viralen Lebenszyklus, was zu einer Verringerung der Viruslast führt . This compound bindet an NS5A und verhindert dessen Wechselwirkung mit anderen viralen und zellulären Komponenten, wodurch die Replikation des Virus gehemmt wird .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ombitasvir gehört zu einer Klasse von direkt wirkenden Antiviralen, die als NS5A-Hemmer bekannt sind. Zu den ähnlichen Verbindungen in dieser Klasse gehören:
Ledipasvir: Ein weiterer NS5A-Hemmer, der in Kombination mit Sofosbuvir zur Behandlung von Hepatitis C eingesetzt wird.
Daclatasvir: Ein NS5A-Hemmer, der in Kombination mit anderen antiviralen Mitteln zur Behandlung von Hepatitis C eingesetzt wird.
Elbasvir: Ein NS5A-Hemmer, der in Kombination mit Grazoprevir zur Behandlung von Hepatitis C eingesetzt wird.
Im Vergleich zu diesen ähnlichen Verbindungen ist this compound einzigartig in seiner Kombination mit Paritaprevir, Ritonavir und Dasabuvir, die ein umfassendes antivirales Regime mit hoher Wirksamkeit und minimalen Nebenwirkungen bieten .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
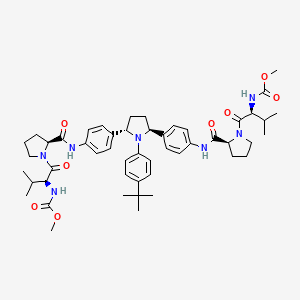
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[[4-[(2S,5S)-1-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-5-[4-[[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carbonyl]amino]phenyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]phenyl]carbamoyl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C50H67N7O8/c1-30(2)42(53-48(62)64-8)46(60)55-28-10-12-40(55)44(58)51-35-20-14-32(15-21-35)38-26-27-39(57(38)37-24-18-34(19-25-37)50(5,6)7)33-16-22-36(23-17-33)52-45(59)41-13-11-29-56(41)47(61)43(31(3)4)54-49(63)65-9/h14-25,30-31,38-43H,10-13,26-29H2,1-9H3,(H,51,58)(H,52,59)(H,53,62)(H,54,63)/t38-,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
PIDFDZJZLOTZTM-KHVQSSSXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)C3CCC(N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C(=O)NC2=CC=C(C=C2)[C@@H]3CC[C@H](N3C4=CC=C(C=C4)C(C)(C)C)C5=CC=C(C=C5)NC(=O)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C50H67N7O8 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID201027920 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
894.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Ombitasvir is an inhibitor of the HCV non-structural protein 5A. While the precise role of this protein is unknown, it is essential to viral replication and virion assembly. Potential modes of action of NS5A inhibitors like Elbasvir include blocking signaling interactions, redistribution of NS5A from the endoplasmic reticulum to the surface of lipid droplets, and modification of the HCV replication complex. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1258226-87-7 | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1258226-87-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=1258226877 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09296 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Ombitasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201027920 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | OMBITASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2302768XJ8 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.