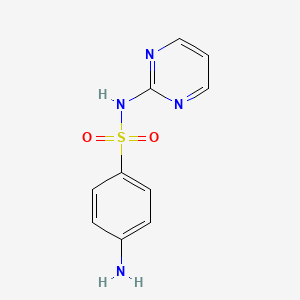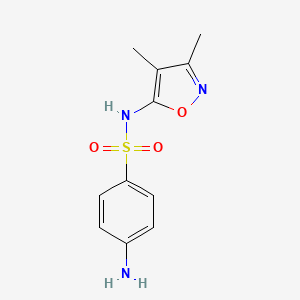
Sulfisoxazole
Descripción general
Descripción
Sulfisoxazol es un antibiótico sulfonamida utilizado para prevenir y tratar una variedad de infecciones bacterianas. Es eficaz contra una amplia gama de organismos grampositivos y gramnegativos. Sulfisoxazol funciona inhibiendo la síntesis bacteriana de ácido dihidrofolico, que es esencial para el crecimiento y la replicación bacteriana .
Mecanismo De Acción
Sulfisoxazol ejerce sus efectos inhibiendo la enzima dihidroptoroato sintetasa. Esta enzima es crucial para la síntesis bacteriana de ácido dihidrofolico, un precursor de la síntesis de ácido nucleico. Al impedir la condensación de pteridina con ácido para-aminobenzoico, sulfisoxazol detiene eficazmente el crecimiento y la replicación bacteriana .
Compuestos Similares:
Sulfametoxazol: Otro antibiótico sulfonamida con un mecanismo de acción similar pero diferente farmacocinética.
Sulfadiazina: Utilizado principalmente en el tratamiento de la toxoplasmosis.
Sulfapiridina: Utilizado en el tratamiento de la dermatitis herpetiforme.
Singularidad: Sulfisoxazol es único por su naturaleza de acción corta y su eficacia contra un amplio espectro de especies bacterianas. Es particularmente útil en terapias combinadas para mejorar la eficacia antibacteriana .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Sulfisoxazol tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones en la investigación científica:
Química: Se utiliza como compuesto modelo en estudios de química y reactividad de sulfonamida.
Biología: Sulfisoxazol se utiliza para estudiar mecanismos de resistencia bacteriana y los efectos de los antibióticos en el crecimiento bacteriano.
Industria: Sulfisoxazol se utiliza en la industria farmacéutica para la producción de fármacos antibacterianos.
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Sulfisoxazole plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by acting as a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. This enzyme is essential for the bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid. By inhibiting this enzyme, this compound prevents the condensation of pteridine with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), thereby halting the production of dihydrofolic acid . This inhibition disrupts the bacterial folate pathway, which is vital for DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis.
Cellular Effects
This compound affects various types of cells and cellular processes. It primarily targets bacterial cells, inhibiting their growth and proliferation. By blocking the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid, this compound disrupts the production of nucleotides, which are essential for DNA replication and cell division . This leads to the inhibition of bacterial growth and the eventual death of the bacterial cells. Additionally, this compound can influence cell signaling pathways and gene expression by altering the availability of folate derivatives required for these processes .
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, this compound exerts its effects by binding to the active site of dihydropteroate synthetase, thereby competitively inhibiting the enzyme. This binding prevents the enzyme from interacting with its natural substrate, PABA, and subsequently inhibits the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid . The inhibition of dihydrofolic acid synthesis leads to a depletion of tetrahydrofolate, a cofactor required for the synthesis of purines, thymidine, and certain amino acids. This disruption in nucleotide synthesis ultimately hampers bacterial DNA replication and cell division .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound can change over time. The stability of this compound is influenced by factors such as pH, temperature, and light exposure. Studies have shown that this compound remains stable under acidic conditions but can degrade under alkaline conditions . Over time, the degradation of this compound can lead to a reduction in its antibacterial efficacy. Long-term exposure to this compound in in vitro and in vivo studies has shown that bacterial cells can develop resistance mechanisms, such as the overproduction of PABA or mutations in dihydropteroate synthetase .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. At therapeutic doses, this compound effectively inhibits bacterial growth and treats infections. At higher doses, this compound can exhibit toxic effects, such as hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity . Studies in animal models have shown that this compound can cause liver and kidney damage at high doses, leading to elevated levels of liver enzymes and renal dysfunction . Additionally, prolonged exposure to high doses of this compound can result in hematological abnormalities, such as anemia and leukopenia .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized in the liver through acetylation and glucuronidation pathways. The major metabolite of this compound is N4-acetylthis compound, which is excreted in the urine . The metabolic pathways of this compound involve enzymes such as N-acetyltransferase and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase . These enzymes facilitate the conjugation of this compound with acetyl and glucuronide groups, enhancing its solubility and excretion. The metabolism of this compound can also affect metabolic flux and metabolite levels, influencing the overall pharmacokinetics of the drug .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through passive diffusion and active transport mechanisms. It is widely distributed throughout the body, including the liver, kidneys, lungs, and cerebrospinal fluid . This compound can cross the blood-brain barrier and achieve therapeutic concentrations in the central nervous system. The transport of this compound is facilitated by transporters such as organic anion transporters (OATs) and multidrug resistance proteins (MRPs) . These transporters play a crucial role in the uptake and efflux of this compound, affecting its localization and accumulation in different tissues .
Subcellular Localization
This compound exhibits subcellular localization within bacterial cells, primarily targeting the cytoplasm where dihydropteroate synthetase is located . The compound does not require specific targeting signals or post-translational modifications for its activity. Instead, it diffuses into the bacterial cell and interacts with the enzyme directly in the cytoplasm . The subcellular localization of this compound is crucial for its inhibitory effects on dihydropteroate synthetase and subsequent disruption of folate metabolism .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas Sintéticas y Condiciones de Reacción: La preparación de sulfisoxazol implica una reacción de condensación donde 3-aminoisoxazol se hace reaccionar con cloruro de p-acetamido-bencenosulfonilo en presencia de tolueno y piridina. Esta reacción se lleva a cabo típicamente durante 20-24 horas. El producto resultante se somete a hidrólisis con sosa cáustica líquida, seguida de una reacción de formación de sal para obtener sulfisoxazol sódico .
Métodos de Producción Industrial: La producción industrial de sulfisoxazol sigue rutas sintéticas similares pero a mayor escala. El proceso implica un control cuidadoso de las condiciones de reacción para asegurar un alto rendimiento y pureza. El producto final se cristaliza y purifica a menudo para cumplir con los estándares farmacéuticos .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de Reacciones: Sulfisoxazol se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, incluyendo:
Oxidación: Sulfisoxazol puede oxidarse bajo condiciones específicas para formar diferentes derivados.
Reducción: También puede sufrir reacciones de reducción, aunque estas son menos comunes.
Sustitución: Sulfisoxazol puede participar en reacciones de sustitución, particularmente involucrando el grupo sulfonamida.
Reactivos y Condiciones Comunes:
Oxidación: Los agentes oxidantes comunes incluyen peróxido de hidrógeno y permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Se pueden utilizar agentes reductores como el borohidruro de sodio.
Sustitución: Los reactivos como los haluros de alquilo y los cloruros de acilo se utilizan a menudo en reacciones de sustitución.
Productos Principales: Los productos principales formados a partir de estas reacciones dependen de las condiciones y los reactivos específicos utilizados. Por ejemplo, la oxidación puede conducir a la formación de derivados de sulfona .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Sulfamethoxazole: Another sulfonamide antibiotic with a similar mechanism of action but different pharmacokinetics.
Sulfadiazine: Used primarily in the treatment of toxoplasmosis.
Sulfapyridine: Used in the treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis.
Uniqueness: Sulfisoxazole is unique in its short-acting nature and its effectiveness against a broad spectrum of bacterial species. It is particularly useful in combination therapies to enhance antibacterial efficacy .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
4-amino-N-(3,4-dimethyl-1,2-oxazol-5-yl)benzenesulfonamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H13N3O3S/c1-7-8(2)13-17-11(7)14-18(15,16)10-5-3-9(12)4-6-10/h3-6,14H,12H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
NHUHCSRWZMLRLA-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=C(ON=C1C)NS(=O)(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C11H13N3O3S | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
2200-44-4 (mono-hydrochloride salt), 6155-81-3 (mono-lithium salt) | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole [USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000127695 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6021292 | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6021292 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
267.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Sulfisoxazole is an odorless white to yellowish crystalline powder. Slightly bitter taste. Acid to litmus. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>40.1 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 72.5 °F (NTP, 1992), White to off-white, odorless, crystalline powder. Sol in alcohol; freely sol in water. /Diethanolamine salt/, Soluble in alcohol, SOL IN DIETHYL ETHER (1 IN 800); SOL IN 5% AQ SODIUM BICARBONATE (1 IN 30), 1 G IN ABOUT 6700 ML WATER; SOL IN DIL HYDROCHLORIC ACID; 1 G IN ABOUT 10 ML BOILING ALCOHOL, In water, 300 mg/L at 37 °C, pH 4.5, 3.13e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID859862 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Sulfisoxazole is a competitive inhibitor of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. It inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by preventing the condensation of the pteridine with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), a substrate of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. The inhibited reaction is necessary in these organisms for the synthesis of folic acid., The sulfonamides are bacteriostatic agents and the spectrum of activity is similar for all. Sulfonamides inhibit bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by preventing the condensation of the pteridine with aminobenzoic acid through competitive inhibition of the enzyme dihydropteroate synthetase. Resistant strains have altered dihydropteroate synthetase with reduced affinity for sulfonamides or produce increased quantities of aminobenzoic acid., Sulfonamides are usually bacteriostatic in action. Sulfonamides interfere with the utilization of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA) in the biosynthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid (the reduced form of folic acid) cofactors in susceptible bacteria. Sulfonamides are structural analogs of PABA and appear to interfere with PABA utilization by competitively inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase, which catalyzes the formation of dihydropteroic acid (a precursor of tetrahydrofolic acid) from PABA and pteridine; however, other mechanism(s) affecting the biosynthetic pathway also may be involved. Compounds such as pyrimethamine and trimethoprim, which block later stages in the synthesis of folic acid, act synergistically with sulfonamides. Only microorganisms that synthesize their own folic acid are inhibited by sulfonamides; animal cells and bacteria which are capable of utilizing folic acid precursors or preformed folic acid are not affected by these drugs. The antibacterial activity of the sulfonamides is reportedly decreased in the presence of blood or purulent body exudates. /Sulfonamides/ | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Colorless prisms, White to slightly yellowish crystalline powder | |
CAS No. |
127-69-5 | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=127-69-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole [USP:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000127695 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757343 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=38588 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=33807 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=13120 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-(3,4-dimethyl-5-isoxazolyl)- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6021292 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Sulfafurazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.004.418 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/740T4C525W | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
383 to 388 °F (NTP, 1992), 194 °C, MP: 191 °C, MP: 195-198 °C | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/21051 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00263 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SULFISOXAZOLE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/797 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Sulfisoxazole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014408 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: How does sulfisoxazole exert its antibacterial effect?
A1: this compound, like other sulfonamides, acts as a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthase, an enzyme crucial for folic acid synthesis in bacteria. [, ] This inhibition disrupts the production of essential nucleic acids, ultimately hindering bacterial growth and proliferation. [, , , ]
Q2: Does this compound impact the growth rate of Mycobacterium tuberculosis?
A2: Yes, research demonstrates that this compound delays the generation time of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in a concentration-dependent manner. [] This delayed generation time likely stems from the inhibition of essential cell material synthesis, such as purine derivatives. []
Q3: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A4: The molecular formula of this compound is C11H13N3O3S, and its molecular weight is 267.3 g/mol. [, ]
Q4: What spectroscopic data is available for characterizing this compound?
A5: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with UV detection is a widely employed technique for separating and quantifying this compound in biological samples like plasma. [] Thin layer chromatography (TLC) can be utilized as a complementary technique to assess the purity of this compound and detect manufacturing impurities. []
Q5: How does protein binding influence the pharmacokinetics of this compound?
A6: Studies in rats have shown a strong link between the serum protein binding of this compound and its clearance. [] Increased serum free fractions of this compound correlate with higher total, metabolic, and renal clearances. [, , , ] The unbound renal clearance of this compound is notably reduced in renal transplant patients and shows a strong correlation with creatinine clearance. []
Q6: What is the impact of age on the pharmacokinetics of this compound?
A7: Pharmacokinetic studies have observed higher plasma levels of this compound in elderly subjects compared to younger individuals following oral administration. [] This difference is attributed to diminished renal function, leading to a longer plasma half-life and decreased total body and renal clearances in the elderly population. []
Q7: How is this compound metabolized?
A8: One of the primary metabolic pathways of this compound is acetylation, resulting in the formation of N4-acetyl this compound. [, ] This metabolic process is particularly relevant in patients with impaired renal function, as the accumulation of the N4-acetyl metabolite in urine can potentially exceed its solubility. []
Q8: What infections has this compound been used to treat?
A10: this compound has been employed in the treatment of various bacterial infections, including urinary tract infections, otitis media, plague, Haemophilus influenzae meningitis, and chancroid. [, , , , , , ]
Q9: Has this compound shown efficacy in preventing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis?
A11: An animal study indicated a synergistic effect when erythromycin and this compound were co-administered to immunosuppressed rats, effectively preventing Pneumocystis carinii pneumonitis in 90% of the animals. [] This combination also demonstrated therapeutic benefits in rats with established infections. []
Q10: Does this compound interact with other drugs?
A13: this compound has shown interaction with propofol in animal models, enhancing propofol's anesthetic effects. [] This interaction doesn't appear to be related to changes in protein binding or plasma concentrations. []
Q11: Does the use of this compound raise concerns regarding bilirubin displacement in newborns?
A14: Research indicates that this compound can displace bilirubin from albumin, potentially increasing the risk of kernicterus in newborns, particularly those with jaundice. [, ] This displacement effect has been observed both in vitro and in vivo, raising concerns about the use of this compound in this population. []
Q12: Is there evidence of antimicrobial resistance to this compound?
A15: Yes, antimicrobial resistance to this compound is a growing concern. Studies have reported widespread resistance to this compound in Escherichia coli and Salmonella isolates from livestock and poultry. [, , , ] This highlights the need for responsible antimicrobial stewardship to minimize the development and spread of resistance. [, ]
Q13: What are the potential adverse effects associated with this compound?
A16: While generally considered safe, this compound can cause adverse reactions, with allergic responses being the most common. [, ] These reactions can manifest as skin rashes, eosinophilia, and drug fever. [] Rare but serious reactions have also been reported. [, ]
Q14: Has this compound demonstrated carcinogenic potential in animal studies?
A17: In a bioassay conducted on rats and mice, this compound administration via gavage did not result in a statistically significant increase in tumor incidence compared to control groups. [] This suggests that this compound might not possess a significant carcinogenic risk under the specific conditions of this study.
Q15: Does this compound have any potential applications beyond its antibacterial properties?
A18: Recent research suggests that this compound might hold promise in cancer treatment. Studies have shown that it can inhibit tumor growth and metastasis in breast cancer models, potentially by modulating the immune response and inhibiting exosomal PD-L1. [, ] Further research is needed to explore these promising avenues.
Q16: Could this compound play a role in addressing cancer-associated cachexia?
A19: Preliminary studies in mouse models indicate that this compound administration might partially mitigate cancer-induced weight loss by preserving fat mass. [] This effect is attributed to the potential inhibition of lipolysis. [] Further research is necessary to validate these findings and determine the clinical relevance of this compound in cachexia management.
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.