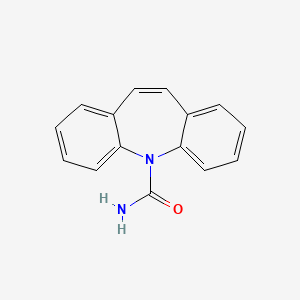
Carbamazépine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
La carbamazepine est un anticonvulsivant et un analgésique bien connu, principalement utilisé dans le traitement de l'épilepsie et de la douleur neuropathique. Elle est également utilisée comme traitement de deuxième intention pour le trouble bipolaire et comme traitement d'appoint dans la schizophrénie. Découverte en 1953 par le chimiste suisse Walter Schindler, la carbamazepine a été commercialisée pour la première fois en 1962 et est depuis devenue un incontournable de la prise en charge de diverses affections neurologiques .
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Carbamazepine primarily targets voltage-gated sodium channels in their inactive conformation . These channels play a crucial role in the generation and propagation of action potentials in neurons, which are fundamental for the transmission of signals in the nervous system .
Mode of Action
Carbamazepine binds preferentially to voltage-gated sodium channels, preventing repetitive and sustained firing of an action potential . By inhibiting the activity of these channels, carbamazepine stabilizes hyper-excited neural membranes, inhibits synaptic transmission, and promotes the cessation of rapid, repetitive firing of neurons .
Biochemical Pathways
Carbamazepine affects several biochemical pathways. It is known to induce the CYP3A4 enzyme , accelerating the metabolism of concurrently prescribed anticonvulsants . It also interferes with other ion channels for calcium and potassium . Furthermore, carbamazepine can modulate the expression of certain genes, such as gabra1, grin1b, grin2b, gad1b, and abat .
Pharmacokinetics
Carbamazepine exhibits a bioavailability of approximately 100% . It is metabolized in the liver by the CYP3A4 enzyme . The active metabolite of carbamazepine is carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide . The elimination half-life of carbamazepine is 36 hours after a single dose and 16–24 hours after repeated dosing . It is excreted in urine (72%) and feces (28%) .
Result of Action
At the molecular level, carbamazepine has been found to increase the levels of neurotransmitters like Glutamate (Glu) and Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid (GABA), and decrease the levels of Acetylcholine (ACh) and Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) . At the cellular level, carbamazepine can cause changes in the structure of cells and organelles, potentially reducing the functions of gills and digestive glands .
Action Environment
Environmental factors can influence the action of carbamazepine. For instance, the fish plasma model demonstrated that environmental levels of carbamazepine underestimated the bioconcentration factors in plasma . This suggests that the environmental concentration of carbamazepine can affect its bioavailability and efficacy .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Carbamazepine has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound in studies of drug metabolism and reaction mechanisms.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on neuronal activity and neurotransmitter release.
Medicine: Extensively studied for its therapeutic effects in epilepsy, neuropathic pain, and bipolar disorder.
Industry: Employed in the development of new pharmaceutical formulations and drug delivery systems .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Carbamazepine works by stabilizing the electrical activity in the brain and nerves . It stops electrical signals from building up in the nerve cells in the brain and also reduces the release of a chemical (neurotransmitter) called glutamate . It is structurally similar to tricyclic antidepressants such as imipramine .
Cellular Effects
Carbamazepine has a significant impact on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by stabilizing the electric signals in your nerves . This stops the pain signals being sent to your brain . It also has effects on serotonin systems but the relevance to its antiseizure effects is uncertain .
Molecular Mechanism
Carbamazepine is a sodium channel blocker . It binds preferentially to voltage-gated sodium channels in their inactive conformation, which prevents repetitive and sustained firing of an action potential . It also acts at adenosine receptors and as an anti-cholinergic .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
On chronic administration, carbamazepine induces its own metabolism sometimes leading to requirement for increasing the dose after the first month of therapy to maintain effect . Carbamazepine metabolism is induced by phenobarbital and phenytoin but inhibited by valproate and lamotrigine .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, carbamazepine at certain doses has shown to reduce immobility in the behavioral despair model . It neither modified the methamphetamine anorectic effect, nor induced anorexia when administered alone .
Metabolic Pathways
Carbamazepine is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily by CYP3A4, to carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide which is pharmacologically active . Additional isoenzymes that contribute to the metabolism of carbamazepine include CYP2C8, CYP2B6, CYP2E1, CYP1A2, and CYP2A6 .
Transport and Distribution
Carbamazepine is rapidly absorbed with a bioavailability of 75–85% . Its volume of distribution is 0.8–2.0 L/kg, and plasma protein binding is 75% . The protein binding of the pharmacologically active metabolite, carbamazepine-10,11-epoxide, is 50% .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction
La carbamazepine est synthétisée à partir de l'iminostilbène par réaction avec de l'urée dans un milieu protonant. Ce processus implique la formation d'un intermédiaire, qui est ensuite converti en carbamazepine. Les conditions de réaction comprennent généralement l'utilisation d'un solvant organique et d'un agent acide pour faciliter la conversion .
Méthodes de production industrielle
En milieu industriel, la carbamazepine est produite par un processus de synthèse continue. Cette méthode utilise une spectroscopie Raman validée en ligne et une modélisation cinétique pour surveiller et optimiser les conditions de réaction. Le réacteur continu à agitation (CSTR) est utilisé pour maintenir un équilibre dynamique et garantir une qualité de produit constante .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
La carbamazepine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : La carbamazepine peut être oxydée pour former l'époxyde de carbamazepine-10,11, un métabolite actif.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent reconvertir l'époxyde de carbamazepine-10,11 en carbamazepine.
Substitution : La carbamazepine peut subir des réactions de substitution, en particulier en présence de nucléophiles forts
Réactifs et conditions courants
Oxydation : Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le peroxymonosulfate et d'autres peroxydes.
Réduction : Des agents réducteurs tels que le borohydrure de sodium peuvent être utilisés.
Substitution : Des nucléophiles forts comme l'amide de sodium sont souvent utilisés.
Principaux produits
Oxydation : Époxyde de carbamazepine-10,11
Réduction : Carbamazepine
Substitution : Divers dérivés substitués en fonction du nucléophile utilisé
Applications de la recherche scientifique
La carbamazepine a un large éventail d'applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisée comme composé modèle dans des études sur le métabolisme des médicaments et les mécanismes réactionnels.
Biologie : Étudiée pour ses effets sur l'activité neuronale et la libération de neurotransmetteurs.
Médecine : Étudiée de manière approfondie pour ses effets thérapeutiques dans l'épilepsie, la douleur neuropathique et le trouble bipolaire.
Industrie : Utilisée dans le développement de nouvelles formulations pharmaceutiques et de systèmes d'administration de médicaments .
Mécanisme d'action
La carbamazepine exerce ses effets principalement en inhibant le déclenchement des canaux sodiques. Cette action réduit la réponse nerveuse polysynaptique et inhibe la potentialisation post-tétanique, stabilisant ainsi les membranes nerveuses hyperexcitables. Le composé affecte également la libération de neurotransmetteurs et module la transmission synaptique .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
La carbamazepine est souvent comparée à d'autres anticonvulsivants comme l'oxcarbazépine et l'acétate d'eslicarbazépine. Bien que les trois composés partagent un mécanisme d'action similaire, inhibant les canaux sodiques voltage-dépendants, ils diffèrent par leurs profils pharmacocinétiques et leur sélectivité pour l'état inactivé du canal sodique. L'oxcarbazépine et l'acétate d'eslicarbazépine sont des dérivés plus récents présentant des profils de sécurité améliorés et moins d'effets secondaires .
Composés similaires
- Oxcarbazépine
- Acétate d'eslicarbazépine
- Phénytoïne
- Valproate
La carbamazepine reste un composé unique et précieux dans le traitement des troubles neurologiques en raison de son efficacité bien établie et de ses antécédents de recherche approfondis.
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
benzo[b][1]benzazepine-11-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C15H12N2O/c16-15(18)17-13-7-3-1-5-11(13)9-10-12-6-2-4-8-14(12)17/h1-10H,(H2,16,18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FFGPTBGBLSHEPO-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1=CC=C2C(=C1)C=CC3=CC=CC=C3N2C(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C15H12N2O | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | Wikipedia | |
| URL | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbamazepine | |
| Description | Chemical information link to Wikipedia. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
85756-57-6 (di-hydrate) | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000298464 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4022731 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4022731 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
236.27 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
399.6±45.0 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Solubility |
>35.4 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), Sol in alcohol, acetone, propylene glycol; practically insol in water, Soluble in chloroform, dimethylformamide, ethylene glycol monomethyl ether, or methanol; only slightly soluble in ethanol or glacial acetic acid, 1.52e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855967 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Carbamazepine's mechanism of action is not fully elucidated and is widely debated. One major hypothesis is that carbamazepine inhibits sodium channel firing, treating seizure activity. Animal research studies have demonstrated that carbamazepine exerts its effects by lowering polysynaptic nerve response and inhibiting post-tetanic potentiation. In both cats and rats, carbamazepine was shown to decrease pain caused by infraorbital nerve stimulation. A decrease in the action potential in the nucleus ventralis of the thalamus in the brain and inhibition of the lingual mandibular reflex were observed in other studies after carbamazepine use. Carbamazepine causes the above effects by binding to voltage-dependent sodium channels and preventing action potentials, which normally lead to stimulatory effects on nerves. In bipolar disorder, carbamazepine is thought to increase dopamine turnover and increase GABA transmission, treating manic and depressive symptoms. A common issue that has arisen is resistance to this drug in up to 30% of epileptic patients, which may occur to altered metabolism in patients with variant genotypes. A potential therapeutic target to combat carbamazepine resistance has recently been identified as the EPHX1 gene promoter, potentially conferring resistance to carbamazepine through methylation., Anticonvulsant: Exact mechanism unknown; may act postsynaptically by limiting the ability of neurons to sustain high frequency repetitive firing of action potentials through enhancement of sodium channel inactivation; in addition to altering neuronal excitability, may act presynaptically to block the release of neurotransmitter by blocking presynaptic sodium channels and the firing of action potentials, which in turn decreases synaptic transmission., Antineuralgic: Exact mechanism unknown; may involve gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAB) receptors, which may be linked to calcium channels., Antimanic; antipsychotic: Exact mechanism is unknown; may be related to either the anticonvulsant or the antineuralgic effects of carbamazepine, or to tis effects on neurotransmitter modulator systems., Antidiuretic: Exact mechanism unknown; may exert a hypothalamic effect on the osmoreceptors mediated via secretion of antidiuretic hormone (ADH), or may have a direct effect on the renal tubule., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for CARBAMAZEPINE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals from absolute ethanol and benzene, White to off-white powder | |
CAS No. |
298-46-4 | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=298-46-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000298464 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=755920 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | carbamazepine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=169864 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4022731 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.005.512 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/33CM23913M | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
189-192, 190.2 °C | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00564 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | CARBAMAZEPINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3019 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Carbamazepine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014704 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details







Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
![S-[(2R,3S,4S,6S)-6-[[(2R,3S,4S,5R,6R)-5-[(2S,4S,5S)-5-(ethylamino)-4-methoxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-4-hydroxy-6-[[(2S,5Z,9R,13Z)-9-hydroxy-12-(methoxycarbonylamino)-13-[2-(methyltrisulfanyl)ethylidene]-11-oxo-2-bicyclo[7.3.1]trideca-1(12),5-dien-3,7-diynyl]oxy]-2-methyloxan-3-yl]amino]oxy-4-hydroxy-2-methyloxan-3-yl] 4-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6S)-3,5-dihydroxy-4-methoxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-5-iodo-2,3-dimethoxy-6-methylbenzenecarbothioate](/img/structure/B1668231.png)