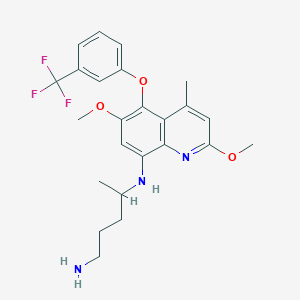
Tafenoquine
Overview
Description
Tafenoquine is an antimalarial medication used for both the prevention and treatment of malaria. It is particularly effective against Plasmodium vivax, a parasite responsible for relapsing malaria. This compound belongs to the 8-aminoquinoline class of compounds and was approved for medical use in Australia and the United States in 2018 . It is known for its long half-life, which allows for single-dose treatment, making it a convenient option for patients .
Mechanism of Action
Target of Action
Tafenoquine, an 8-aminoquinoline antimalarial drug, is primarily active against the liver stages, including the hypnozoite (dormant stage) of Plasmodium vivax . Hypnozoites are latent forms of the parasite that can reactivate the illness, a relapse, without any bite of an infected mosquito .
Mode of Action
It is believed that the active moiety of this compound, 5,6 ortho quinone this compound, seems to be redox cycled byP. falciparum which are upregulated in gametocytes and liver stages . This interaction with its targets leads to the death of the parasite, thereby preventing the relapse of malaria .
Biochemical Pathways
This compound affects the biochemical pathways of the Plasmodium species, including P. falciparum and P. vivax. It is active against pre-erythrocytic (liver) forms (including hypnozoite [dormant stage]) and erythrocytic (asexual) forms, as well as gametocytes . The interruption of these pathways leads to the death of the parasite and prevents the relapse of malaria .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is absorbed slowly, reaching peak plasma concentrations in 8–12 hours . It has a long half-life (2–3 weeks), which allows it to be given as a single dose for radical cure or as weekly chemoprophylaxis . This long half-life and slow absorption contribute to its high bioavailability and effectiveness in treating and preventing malaria .
Result of Action
The primary result of this compound’s action is the prevention of relapse in P. vivax malaria. By killing the dormant hypnozoites in the liver, this compound prevents the reactivation of the disease . It also has activity against P. vivax gametocytes and blood-stage schizonts .
Action Environment
Environmental factors such as the prevalence of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency in a population can influence the action and efficacy of this compound. This compound can cause hemolysis in individuals with G6PD deficiency, leading to severe anemia, kidney damage, and potentially death in cases of severe deficiency . Therefore, quantitative G6PD testing is required before administering this compound .
Biochemical Analysis
Biochemical Properties
Tafenoquine interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. The activation of this compound needs the activity of CYP 2D6 liver microsomal enzyme . It is metabolized by several metabolic pathways including O-demethylation, N-dealkylation, N-oxidation and oxidative deamination as well as C-hydroxylation of the 8-aminoalkylamino side chain .
Cellular Effects
This compound has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It is known to present dormant forms in the hepatocytes named hypnozoites which can remain dormant for weeks or even months . This dormant form produces ongoing relapses . In people with G6PD deficiency, red blood cell breakdown may occur .
Molecular Mechanism
The exact mechanism of action of this compound is not well established but studies have reported a longer and more effective action when compared to primaquine . The active moiety of this compound, 5,6 ortho quinone this compound, seems to be redox cycled by P. falciparum which are upregulated in gametocytes and liver stages .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound presents a high volume of distribution of approximately 2 560 L . The plasma protein binding of this compound in humans is very high and it represents about 99.5% . This compound is generally well tolerated in adults and there is no convincing evidence for neurologic, ophthalmic, and cardiac toxicities .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, this compound has shown to be highly effective against Babesia microti and Babesia duncani . It also exhibited an effective antimicrobial effect in a subcutaneous abscess model in vivo with a good toxicity profile .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in various metabolic pathways. It is metabolized by several metabolic pathways including O-demethylation, N-dealkylation, N-oxidation and oxidative deamination as well as C-hydroxylation of the 8-aminoalkylamino side chain .
Transport and Distribution
This compound presents a high volume of distribution of approximately 2 560 L . The plasma protein binding of this compound in humans is very high and it represents about 99.5% .
Subcellular Localization
The exact subcellular localization of this compound is not well established. Mechanistic studies by fluorescent probes of SYTOX Green/DiSC3 (5), molecular dynamic simulations, electron microscopy, and proteomic analysis revealed that this compound exerts antimicrobial activity mainly through selective bacterial cell membrane disruption .
Preparation Methods
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of tafenoquine involves several steps, starting with the preparation of key intermediates. One of the critical intermediates is 4-methyl-5-(3-trifluoromethylphenoxy)-6-methoxy-8-aminoquinoline. The synthesis typically involves the following steps:
Formation of the Quinoline Core: The quinoline core is synthesized through a series of reactions, including nitration, reduction, and cyclization.
Introduction of Functional Groups: Various functional groups, such as methoxy and trifluoromethylphenoxy, are introduced through substitution reactions.
Final Assembly: The final step involves coupling the intermediate with a suitable amine to form this compound.
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound follows similar synthetic routes but is optimized for large-scale manufacturing. This includes the use of efficient catalysts, high-yield reactions, and purification techniques to ensure the production of high-purity this compound .
Chemical Reactions Analysis
Types of Reactions: Tafenoquine undergoes several types of chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: this compound can be oxidized to form various metabolites.
Reduction: Reduction reactions can modify the quinoline core, affecting its antimalarial activity.
Substitution: Substitution reactions are used to introduce different functional groups during synthesis.
Common Reagents and Conditions:
Oxidizing Agents: Hydrogen peroxide, potassium permanganate.
Reducing Agents: Sodium borohydride, lithium aluminum hydride.
Substitution Reagents: Halogenated compounds, alkylating agents.
Major Products: The major products formed from these reactions include various this compound analogs and metabolites, which are studied for their antimalarial properties .
Scientific Research Applications
Tafenoquine has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound for studying the synthesis and reactivity of 8-aminoquinolines.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on Plasmodium species and other parasites.
Medicine: Primarily used for the treatment and prevention of malaria, especially relapsing malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax.
Industry: Employed in the development of new antimalarial drugs and formulations
Comparison with Similar Compounds
Primaquine: Another 8-aminoquinoline used for the treatment of malaria. Unlike tafenoquine, primaquine requires daily dosing for 14 days.
Chloroquine: A 4-aminoquinoline used for the treatment of malaria but less effective against relapsing malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax.
Uniqueness of this compound:
Long Half-Life: this compound’s long half-life allows for single-dose treatment, making it more convenient for patients.
Broad Spectrum: Effective against both liver and blood stages of Plasmodium parasites, providing a comprehensive treatment option
This compound represents a significant advancement in the treatment and prevention of malaria, offering a convenient and effective option for patients worldwide.
Properties
IUPAC Name |
4-N-[2,6-dimethoxy-4-methyl-5-[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy]quinolin-8-yl]pentane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H28F3N3O3/c1-14-11-20(32-4)30-22-18(29-15(2)7-6-10-28)13-19(31-3)23(21(14)22)33-17-9-5-8-16(12-17)24(25,26)27/h5,8-9,11-13,15,29H,6-7,10,28H2,1-4H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
LBHLFPGPEGDCJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=CC(=NC2=C1C(=C(C=C2NC(C)CCCN)OC)OC3=CC=CC(=C3)C(F)(F)F)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H28F3N3O3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
106635-81-8 (maleate) | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0106635807 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID90869466 | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90869466 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
463.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Insoluble | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
The mechanism of action of tafenoquine is not well established but studies have reported a longer and more effective action when compared to primaquine. The active moiety of tafenoquine, 5,6 ortho quinone tafenoquine, seems to be redox cycled by _P. falciparum_ which are upregulated in gametocytes and liver stages. Once inside, the oxidated metabolite produces hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals. It is thought that these radicals produce leads to the parasite death. On the other hand, tafenoquine inhibits heme polymerase in blood stage of parasites which explains the activity against blood stages of parasites. | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
106635-80-7 | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=106635-80-7 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0106635807 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06608 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Tafenoquine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID90869466 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | TAFENOQUINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/262P8GS9L9 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
ANone: Tafenoquine, an 8-aminoquinoline antimalarial drug, exerts its activity against Plasmodium species by targeting the parasite's liver stage hypnozoites, effectively preventing relapse in vivax and ovale malaria. While its exact mechanism is not fully elucidated, research suggests it involves the production of oxidative metabolites that are detrimental to the parasite. [] These metabolites are thought to disrupt essential parasite functions, ultimately leading to parasite death. [, ]
ANone: While primarily recognized for its anti-relapse properties against P. vivax and P. ovale, studies demonstrate that this compound also exhibits transmission blocking activity against P. falciparum. [] Low doses of this compound administered to infected individuals were shown to significantly reduce both oocyst and sporozoite positivity rates in mosquitoes feeding on these individuals, ultimately decreasing transmission rates. []
ANone: The molecular formula of this compound succinate, the salt form commonly used in pharmaceutical formulations, is C24H28F3N3O3∙C4H6O4. Its molecular weight is 581.6 g/mol. [, ]
ANone: Various analytical techniques have been utilized for this compound characterization, including nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, infrared (IR) spectroscopy, mass spectrometry (MS), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), and fluorimetry. [] These methods aid in confirming the drug's identity, purity, and stability.
ANone: Yes, computational chemistry studies have been performed on this compound, particularly in the context of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling. This modeling helps understand the relationship between drug concentration and its effects, allowing researchers to optimize dosing regimens and predict potential drug interactions. []
ANone: While the research papers don't delve into specific SAR studies, it is understood that even minor structural modifications to this compound or related 8-aminoquinolines could significantly influence their pharmacological properties, including their antimalarial activity, potency, and potential for side effects.
ANone: Population pharmacokinetic studies conducted on this compound administered as both capsules and tablets revealed no clinically significant difference in relative bioavailability between the two formulations. [] This suggests that this compound exhibits good stability in both these commonly used oral dosage forms.
ANone: this compound exhibits a long elimination half-life of approximately 12.7 days. [] The typical values for the first-order absorption rate constant (Ka), clearance (CL/F), and volume of distribution (V/F) were determined to be 0.243 h−1, 0.056 liters/h/kg, and 23.7 liters/kg, respectively. []
ANone: While not explicitly mentioned in the provided research papers, 8-aminoquinolines like this compound are primarily metabolized in the liver and subsequently eliminated through feces. []
ANone: While CYP2D6 is known to play a crucial role in the metabolism of primaquine, studies on this compound have yielded conflicting results. Some research suggests that CYP2D6 activity might influence this compound's effectiveness in preventing P. vivax relapses, while other studies indicate that CYP2D6 status does not significantly affect plasma this compound concentrations or its anti-relapse efficacy. [, ]
ANone: The in vitro activity of this compound has been evaluated using various methods, including the inhibition of schizont maturation assay, which measures the drug's ability to prevent the maturation of Plasmodium falciparum parasites in red blood cells. [, ]
ANone: this compound demonstrates promising in vitro activity against chloroquine-resistant strains of P. falciparum. Studies have shown that this compound maintains its efficacy even in regions where chloroquine resistance is prevalent, highlighting its potential as a valuable treatment option in such areas. [, ]
ANone: Mice infected with Babesia microti, a parasite causing babesiosis, have been successfully utilized as an animal model to investigate the efficacy and pharmacokinetics of this compound. Studies have shown that a single oral dose of this compound in these mice effectively reduces parasitemia, mimicking its activity against Plasmodium species in humans. []
ANone: Several clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy and safety of this compound for malaria prophylaxis. Notably, a Phase III trial involving Australian soldiers deployed to East Timor showed that weekly this compound prophylaxis was as effective as mefloquine in preventing malaria. [] Similarly, trials in Ghana, Kenya, and Thailand confirmed the efficacy of different weekly this compound regimens in preventing P. falciparum infection. [, , ]
ANone: Clinical trials have shown that a single dose of this compound (300 mg) is as effective as a 14-day course of primaquine (15 mg daily) in preventing P. vivax relapse. [, ] This finding highlights the potential of this compound to improve patient adherence and simplify treatment regimens for P. vivax malaria.
ANone: While there have been no documented cases of clinical resistance to this compound, the potential for resistance development remains a concern. This concern is particularly relevant given the drug's long half-life, which could allow parasites prolonged exposure to subtherapeutic drug concentrations, potentially favoring the selection of resistant strains. []
ANone: this compound administration has been associated with generally mild and transient side effects. The most common ones include gastrointestinal disturbances such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. [, ]
ANone: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study assessed the long-term ophthalmic and renal effects of this compound. The study found no clinically significant differences in night vision or other ophthalmic indices between the this compound and placebo groups after six months of treatment. [] Furthermore, no significant changes in glomerular filtration rate were observed, indicating that this compound did not adversely affect renal function in the study population. []
ANone: Currently, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency status is the most crucial biomarker used before this compound administration. G6PD deficiency testing is mandatory because the drug can cause hemolysis in individuals with this condition. [, ]
ANone: this compound concentrations in biological samples like plasma are typically measured using sophisticated analytical techniques like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS). [, ] These methods offer the sensitivity and specificity required to quantify this compound levels accurately.
ANone: Primaquine remains the mainstay drug for P. vivax radical cure and is the primary alternative to this compound. [, ] While both drugs belong to the 8-aminoquinoline class and effectively eliminate liver-stage hypnozoites, they differ significantly in their dosing regimens and potential for side effects.
Disclaimer and Information on In-Vitro Research Products
Please be aware that all articles and product information presented on BenchChem are intended solely for informational purposes. The products available for purchase on BenchChem are specifically designed for in-vitro studies, which are conducted outside of living organisms. In-vitro studies, derived from the Latin term "in glass," involve experiments performed in controlled laboratory settings using cells or tissues. It is important to note that these products are not categorized as medicines or drugs, and they have not received approval from the FDA for the prevention, treatment, or cure of any medical condition, ailment, or disease. We must emphasize that any form of bodily introduction of these products into humans or animals is strictly prohibited by law. It is essential to adhere to these guidelines to ensure compliance with legal and ethical standards in research and experimentation.


![4-Methylthieno[2,3-d]pyrimidine](/img/structure/B11840.png)
![4-[1-Methyl-3-[4-(phenoxymethyl)phenyl]propyl]morpholine](/img/structure/B11842.png)
![2-(carboxymethyl)-2,4-dihydroxy-4-oxobutanoate;(Z)-4-phenyl-3-[2-(3-piperidin-1-ium-1-ylpropoxy)phenoxy]but-3-en-2-one](/img/structure/B11853.png)
![4-[(2-Phenoxyethyl)sulfanyl]phenol](/img/structure/B11864.png)
