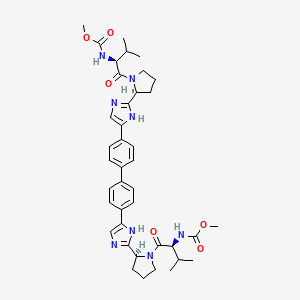
Daclatasvir
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Daclatasvir is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections. It is marketed under the brand name Daklinza. This compound works by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A, which is essential for viral replication . This compound is particularly effective against HCV genotypes 1, 3, and 4 .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Daclatasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent that primarily targets the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . It specifically binds to NS5A , a nonstructural phosphoprotein encoded by HCV . NS5A is part of a functional replication complex responsible for viral RNA genome amplification .
Mode of Action
This compound exerts its antiviral action by preventing RNA replication and virion assembly . It binds to the N-terminus of the D1 domain of NS5A, which prevents its interaction with host cell proteins and membranes required for virion replication complex assembly . This compound targets both the cis- and trans-acting functions of NS5A and disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound is the HCV RNA replication process . By binding to NS5A, this compound disrupts the replication of the HCV RNA genome, thereby inhibiting the assembly of new virions .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound undergoes rapid absorption, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration of 1–2 hours and an elimination half-life of approximately 10 to 14 hours . Steady state is achieved by day 4 in multiple-ascending dose studies . This compound has low-to-moderate clearance with the predominant route of elimination via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion . Renal clearance is a minor route of elimination for this compound .
Result of Action
The primary result of this compound’s action is the inhibition of HCV replication, leading to a reduction in the viral load . This can lead to significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Daclatasvir hat eine große Bandbreite an Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Es dient als Modellverbindung für die Erforschung des Designs und der Synthese von antiviralen Medikamenten.
Biologie: this compound wird verwendet, um die Mechanismen der viralen Replikation und die Rolle von NS5A bei HCV zu untersuchen.
Medizin: Es ist ein wichtiger Bestandteil von Kombinationstherapien zur Behandlung chronischer HCV-Infektionen, die zu hohen anhaltenden virologischen Ansprechraten führen.
Industrie: Die Produktion und Formulierung von this compound wird untersucht, um die Herstellungsprozesse und die Wirkstofffreigabe zu verbessern
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine antivirale Wirkung, indem es an den N-Terminus innerhalb der Domäne 1 des HCV-Nicht-strukturellen Proteins 5A (NS5A) bindet. Diese Bindung hemmt die virale RNA-Replikation und die Virion-Assemblierung, wodurch die Vermehrung und Verbreitung des Virus effektiv verhindert wird . Die Hemmung von NS5A stört die Bildung des viralen Replikationskomplexes, was zu einem Rückgang der Viruslast und einer letztendlich vollständigen Ausheilung der Infektion führt .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Sofosbuvir: Ein weiteres antivirales Medikament, das in Kombination mit this compound zur Behandlung von HCV eingesetzt wird. Es hemmt die HCV-RNA-Polymerase NS5B.
Ledipasvir: Ähnlich wie this compound hemmt es das NS5A-Protein, hat aber unterschiedliche pharmakokinetische Eigenschaften.
Velpatasvir: Ein weiterer NS5A-Inhibitor mit einem breiteren Wirkungsspektrum gegen verschiedene HCV-Genotypen.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound: this compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seiner hohen Selektivität und Potenz gegen HCV NS5A. Es verfügt über ein gut charakterisiertes pharmakokinetisches Profil, das eine einmalige tägliche orale Verabreichung ermöglicht. Zusätzlich hat this compound bei Patienten mit fortgeschrittener Lebererkrankung und Patienten, die mit HIV koinfiziert sind, Wirksamkeit gezeigt .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Daclatasvir exerts its antiviral action by preventing RNA replication and virion assembly via binding to NS5A, a nonstructural phosphoprotein encoded by HCV . Binding to the N-terminus of the D1 domain of NS5A prevents its interaction with host cell proteins and membranes required for virion replication complex assembly .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a profound effect on viral load with onset that is more rapid than had been seen previously with either NS3 protease or NS5B polymerase inhibitors . It disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound works by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A . It targets both the cis- and trans-acting functions of NS5A and disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound undergoes rapid absorption, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration of 1–2 h and an elimination half-life of 10 to 14 h observed in single-ascending dose studies . Steady state was achieved by day 4 in multiple-ascending dose studies .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In-vivo animal studies suggested that this compound concentrates in livers (mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys), with liver-to-serum or liver-to-plasma area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) ratios ranging from 1.9 to 17 in the different animal species tested .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound has low-to-moderate clearance with the predominant route of elimination via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion . Renal clearance is a minor route of elimination for this compound .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely to be found in close proximity to the HCV NS5A protein, which is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane where the HCV replication complex is located .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of daclatasvir involves multiple steps, starting from commercially available starting materials. . The reaction conditions typically involve the use of organic solvents, catalysts, and controlled temperatures to ensure high yield and purity.
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound follows a similar synthetic route but is optimized for large-scale production. This involves the use of high-efficiency reactors, continuous flow processes, and stringent quality control measures to ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory standards .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Daclatasvir unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden, was zur Bildung oxidierter Derivate führt.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können die Imidazolringe oder andere funktionelle Gruppen innerhalb des Moleküls modifizieren.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können am Biphenylkern oder den Imidazolringen auftreten, was zur Bildung verschiedener Analoga führt.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid und Lithiumaluminiumhydrid werden verwendet.
Substitution: Verschiedene Halogenierungsmittel und Nukleophile werden für Substitutionsreaktionen eingesetzt.
Hauptsächlich gebildete Produkte: Zu den Hauptprodukten, die bei diesen Reaktionen entstehen, gehören oxidierte Derivate, reduzierte Analoga und substituierte Verbindungen mit modifizierten pharmakologischen Eigenschaften .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Sofosbuvir: Another antiviral medication used in combination with daclatasvir for treating HCV. It inhibits the HCV RNA polymerase NS5B.
Ledipasvir: Similar to this compound, it inhibits the NS5A protein but has different pharmacokinetic properties.
Velpatasvir: Another NS5A inhibitor with a broader spectrum of activity against various HCV genotypes.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique due to its high selectivity and potency against HCV NS5A. It has a well-characterized pharmacokinetic profile, allowing for once-daily oral administration. Additionally, this compound has shown efficacy in patients with advanced liver disease and those co-infected with HIV .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C40H50N8O6/c1-23(2)33(45-39(51)53-5)37(49)47-19-7-9-31(47)35-41-21-29(43-35)27-15-11-25(12-16-27)26-13-17-28(18-14-26)30-22-42-36(44-30)32-10-8-20-48(32)38(50)34(24(3)4)46-40(52)54-6/h11-18,21-24,31-34H,7-10,19-20H2,1-6H3,(H,41,43)(H,42,44)(H,45,51)(H,46,52)/t31-,32-,33-,34-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FKRSSPOQAMALKA-CUPIEXAXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C40H50N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID901026404 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
738.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Freely soluble (>700 mg/mL) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
NS5A is a viral nonstructural phospoprotein that is part of a functional replication complex in charge of viral RNA genome amplification on endoplasmic reticulum membranes. It has the ability to bind to HCV RNA. It is shown to have two distinct functions in HCV RNA replication based on phosphorylated states. Maintaining the HCV replication complex is mediated by the cis-acting function of basally phosphorylated NS5A and the trans-acting function of hyperphosphorylated NS5A modulates HCV assembly and infectious particle formation. Daclatasvir is shown to disrupt hyperphosphorylated NS5A proteins thus interfere with the function of new HCV replication complexes. It is also reported that daclatasvir also blocks both intracellular viral RNA synthesis and virion assembly/secretion in vivo. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1009119-64-5 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1009119-64-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DACLATASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/LI2427F9CI | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.


![7,8-Dihydro-2-methyl-1H-thiopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4(5H)-one](/img/structure/B1662944.png)