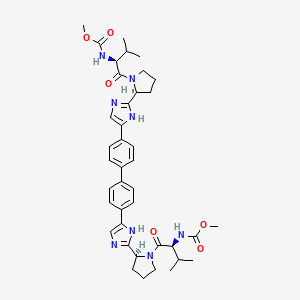
Daclatasvir
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le Daclatasvir est un médicament antiviral utilisé en association avec d'autres médicaments pour traiter les infections par le virus de l'hépatite C (VHC). Il est commercialisé sous le nom de marque Daklinza. Le this compound agit en inhibant la protéine NS5A du VHC, qui est essentielle à la réplication virale . Ce composé est particulièrement efficace contre les génotypes 1, 3 et 4 du VHC .
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Daclatasvir is a direct-acting antiviral agent that primarily targets the Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) . It specifically binds to NS5A , a nonstructural phosphoprotein encoded by HCV . NS5A is part of a functional replication complex responsible for viral RNA genome amplification .
Mode of Action
This compound exerts its antiviral action by preventing RNA replication and virion assembly . It binds to the N-terminus of the D1 domain of NS5A, which prevents its interaction with host cell proteins and membranes required for virion replication complex assembly . This compound targets both the cis- and trans-acting functions of NS5A and disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound is the HCV RNA replication process . By binding to NS5A, this compound disrupts the replication of the HCV RNA genome, thereby inhibiting the assembly of new virions .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound undergoes rapid absorption, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration of 1–2 hours and an elimination half-life of approximately 10 to 14 hours . Steady state is achieved by day 4 in multiple-ascending dose studies . This compound has low-to-moderate clearance with the predominant route of elimination via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion . Renal clearance is a minor route of elimination for this compound .
Result of Action
The primary result of this compound’s action is the inhibition of HCV replication, leading to a reduction in the viral load . This can lead to significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Daclatasvir has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: It serves as a model compound for studying antiviral drug design and synthesis.
Biology: this compound is used to study the mechanisms of viral replication and the role of NS5A in HCV.
Medicine: It is a crucial component of combination therapies for treating chronic HCV infections, leading to high sustained virological response rates.
Industry: this compound’s production and formulation are studied to improve manufacturing processes and drug delivery systems
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Daclatasvir exerts its antiviral action by preventing RNA replication and virion assembly via binding to NS5A, a nonstructural phosphoprotein encoded by HCV . Binding to the N-terminus of the D1 domain of NS5A prevents its interaction with host cell proteins and membranes required for virion replication complex assembly .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a profound effect on viral load with onset that is more rapid than had been seen previously with either NS3 protease or NS5B polymerase inhibitors . It disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound works by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A . It targets both the cis- and trans-acting functions of NS5A and disrupts the function of new HCV replication complexes by modulating the NS5A phosphorylation status .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound undergoes rapid absorption, with a time to reach maximum plasma concentration of 1–2 h and an elimination half-life of 10 to 14 h observed in single-ascending dose studies . Steady state was achieved by day 4 in multiple-ascending dose studies .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In-vivo animal studies suggested that this compound concentrates in livers (mice, rats, dogs, and monkeys), with liver-to-serum or liver-to-plasma area under the concentration–time curve (AUC) ratios ranging from 1.9 to 17 in the different animal species tested .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound has low-to-moderate clearance with the predominant route of elimination via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion . Renal clearance is a minor route of elimination for this compound .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues via cytochrome P450 3A4-mediated metabolism and P-glycoprotein excretion and intestinal secretion .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely to be found in close proximity to the HCV NS5A protein, which is associated with the endoplasmic reticulum membrane where the HCV replication complex is located .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions de réaction : La synthèse du Daclatasvir implique plusieurs étapes, à partir de matières premières disponibles dans le commerce. . Les conditions de réaction impliquent généralement l'utilisation de solvants organiques, de catalyseurs et de températures contrôlées pour assurer un rendement et une pureté élevés.
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle du this compound suit une voie de synthèse similaire, mais elle est optimisée pour la production à grande échelle. Cela implique l'utilisation de réacteurs à haut rendement, de procédés en continu et de mesures strictes de contrôle qualité pour assurer la cohérence et la conformité aux normes réglementaires .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : Le Daclatasvir subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le this compound peut être oxydé dans des conditions spécifiques, conduisant à la formation de dérivés oxydés.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent modifier les cycles imidazole ou d'autres groupes fonctionnels dans la molécule.
Réactifs et conditions courantes :
Oxydation : Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le peroxyde d'hydrogène et le permanganate de potassium.
Réduction : Des agents réducteurs tels que le borohydrure de sodium et l'hydrure de lithium et d'aluminium sont utilisés.
Substitution : Divers agents halogénants et nucléophiles sont utilisés pour les réactions de substitution.
Principaux produits formés : Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent des dérivés oxydés, des analogues réduits et des composés substitués avec des propriétés pharmacologiques modifiées .
4. Applications de la recherche scientifique
Le this compound a un large éventail d'applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Il sert de composé modèle pour l'étude de la conception et de la synthèse de médicaments antiviraux.
Biologie : Le this compound est utilisé pour étudier les mécanismes de la réplication virale et le rôle de la NS5A dans le VHC.
Médecine : Il est un composant crucial des thérapies combinées pour le traitement des infections chroniques par le VHC, conduisant à des taux élevés de réponse virologique soutenue.
Industrie : La production et la formulation du this compound sont étudiées pour améliorer les procédés de fabrication et les systèmes d'administration des médicaments
5. Mécanisme d'action
Le this compound exerce ses effets antiviraux en se liant à l'extrémité N-terminale dans le domaine 1 de la protéine non structurale 5A (NS5A) du VHC. Cette liaison inhibe la réplication de l'ARN viral et l'assemblage des virions, empêchant efficacement le virus de se multiplier et de se propager . L'inhibition de la NS5A perturbe la formation du complexe de réplication viral, entraînant une diminution de la charge virale et l'élimination finale de l'infection .
Composés similaires :
Sofosbuvir : Un autre médicament antiviral utilisé en association avec le this compound pour le traitement du VHC. Il inhibe l'ARN polymérase NS5B du VHC.
Ledipasvir : Similaire au this compound, il inhibe la protéine NS5A mais possède des propriétés pharmacocinétiques différentes.
Velpatasvir : Un autre inhibiteur de la NS5A avec un spectre d'activité plus large contre divers génotypes du VHC.
Unicité du this compound : Le this compound est unique en raison de sa grande sélectivité et de sa puissance contre la NS5A du VHC. Il possède un profil pharmacocinétique bien caractérisé, ce qui permet une administration orale une fois par jour. De plus, le this compound a montré son efficacité chez les patients atteints de maladie hépatique avancée et chez les patients co-infectés par le VIH .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Sofosbuvir: Another antiviral medication used in combination with daclatasvir for treating HCV. It inhibits the HCV RNA polymerase NS5B.
Ledipasvir: Similar to this compound, it inhibits the NS5A protein but has different pharmacokinetic properties.
Velpatasvir: Another NS5A inhibitor with a broader spectrum of activity against various HCV genotypes.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique due to its high selectivity and potency against HCV NS5A. It has a well-characterized pharmacokinetic profile, allowing for once-daily oral administration. Additionally, this compound has shown efficacy in patients with advanced liver disease and those co-infected with HIV .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
methyl N-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-[5-[4-[4-[2-[(2S)-1-[(2S)-2-(methoxycarbonylamino)-3-methylbutanoyl]pyrrolidin-2-yl]-1H-imidazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]-1H-imidazol-2-yl]pyrrolidin-1-yl]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C40H50N8O6/c1-23(2)33(45-39(51)53-5)37(49)47-19-7-9-31(47)35-41-21-29(43-35)27-15-11-25(12-16-27)26-13-17-28(18-14-26)30-22-42-36(44-30)32-10-8-20-48(32)38(50)34(24(3)4)46-40(52)54-6/h11-18,21-24,31-34H,7-10,19-20H2,1-6H3,(H,41,43)(H,42,44)(H,45,51)(H,46,52)/t31-,32-,33-,34-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FKRSSPOQAMALKA-CUPIEXAXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C(C(=O)N1CCCC1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)C6CCCN6C(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)[C@@H](C(=O)N1CCC[C@H]1C2=NC=C(N2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=C(C=C4)C5=CN=C(N5)[C@@H]6CCCN6C(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)OC)NC(=O)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C40H50N8O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID901026404 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
738.9 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Freely soluble (>700 mg/mL) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
NS5A is a viral nonstructural phospoprotein that is part of a functional replication complex in charge of viral RNA genome amplification on endoplasmic reticulum membranes. It has the ability to bind to HCV RNA. It is shown to have two distinct functions in HCV RNA replication based on phosphorylated states. Maintaining the HCV replication complex is mediated by the cis-acting function of basally phosphorylated NS5A and the trans-acting function of hyperphosphorylated NS5A modulates HCV assembly and infectious particle formation. Daclatasvir is shown to disrupt hyperphosphorylated NS5A proteins thus interfere with the function of new HCV replication complexes. It is also reported that daclatasvir also blocks both intracellular viral RNA synthesis and virion assembly/secretion in vivo. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
1009119-64-5 | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=1009119-64-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB09102 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID901026404 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Daclatasvir | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DACLATASVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/LI2427F9CI | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![7-[3-(4-Acetyl-3-hydroxy-2-propylphenoxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]-4-oxo-8-propylchromene-2-carboxylic acid](/img/structure/B1662943.png)
![2-pyridin-3-yl-1-azabicyclo[3.2.2]nonane;dihydrochloride](/img/structure/B1662946.png)
![N-[9-[4-(dimethylamino)anilino]-6-(3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropanoylamino)acridin-3-yl]-3-pyrrolidin-1-ylpropanamide;trihydrochloride](/img/structure/B1662963.png)
