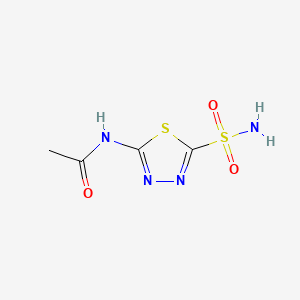
Acetazolamid
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Acetazolamid ist ein Carboanhydrase-Hemmer, der in der Medizin weit verbreitet ist. Es ist bekannt für seine Anwendungen bei der Behandlung von Glaukom, Epilepsie, akuter Höhenkrankheit, periodischer Paralyse, idiopathischer intrakranieller Hypertension und Herzinsuffizienz. Die Verbindung wird auch verwendet, um den Urin zu alkalisieren . This compound wurde erstmals 1952 eingeführt und ist als Generikum erhältlich .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Acetazolamide primarily targets carbonic anhydrase , an enzyme found in many tissues of the body, including the eye and the kidneys . This enzyme plays a crucial role in the regulation of pH and fluid balance .
Mode of Action
Acetazolamide works by inhibiting the activity of carbonic anhydrase . This inhibition decreases the formation of hydrogen ions and bicarbonate from carbon dioxide and water . The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension .
Pharmacokinetics
Acetazolamide is well absorbed orally, with a bioavailability of over 90% . It has a volume of distribution of 0.3 L/kg, and plasma protein binding is 90–95% . An increase in urine pH from bicarbonate diuresis occurs within 30 minutes, is maximal at 2 hours, and persists for 12 hours after a single dose . It is excreted by secretion in the proximal convoluted tubule of the kidney, therefore dosing must be reduced in renal failure .
Action Environment
The efficacy of Acetazolamide can be influenced by environmental factors such as altitude. It is firmly established as a first-line prevention for altitude sickness .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Acetazolamid hat eine breite Palette von Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Wird als Carboanhydrase-Hemmer in verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen eingesetzt.
Biologie: Untersucht auf seine Auswirkungen auf die Aktivität von Zellmembran-Ionen-/Wasserkanälen.
Medizin: Wird zur Behandlung von Glaukom, Epilepsie, akuter Höhenkrankheit, periodischer Paralyse, idiopathischer intrakranieller Hypertension und Herzinsuffizienz eingesetzt.
Industrie: Wird bei der Herstellung von Arzneimitteln und als antibakterielles und antioxidatives Mittel eingesetzt.
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound wirkt, indem es das Enzym Carboanhydrase hemmt, wodurch die Bildung von Wasserstoffionen und Bicarbonat aus Kohlendioxid und Wasser verringert wird . Diese Hemmung führt zu einer Verringerung der Rückresorption von Bicarbonat-, Natrium- und Chlorid-Ionen im proximalen Tubulus der Niere, was zu einer erhöhten Ausscheidung dieser Ionen zusammen mit überschüssigem Wasser führt . Dieser Mechanismus hilft, den Blutdruck, den intrakraniellen Druck und den Augeninnendruck zu senken .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Sulfanilamid: Eine früher entdeckte Verbindung mit ähnlicher enzymatischer Hemmwirkung, aber viel weniger potent als this compound.
Andere Sulfonamid-Derivate: Verschiedene Diuretika und Antikonvulsiva mit schwacher bis mittelschwerer Carboanhydrase-Aktivität.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound: this compound zeichnet sich durch seine potente hemmende Wirkung auf die Carboanhydrase aus, wodurch es bei der Behandlung einer Vielzahl von Erkrankungen hochwirksam ist. Seine Fähigkeit, als Diuretikum, Antikonvulsivum und Glaukom-Medikament zu wirken, unterstreicht seine Vielseitigkeit und Bedeutung sowohl in klinischen als auch in Forschungsumgebungen .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Acetazolamide’s major biochemical and pharmacological effect is deemed to be carbonic anhydrase inhibition . It interacts with this enzyme, inhibiting its activity . This interaction plays a significant role in the biochemical reactions involving Acetazolamide .
Cellular Effects
Acetazolamide has a profound impact on cellular membrane ion/water channel activity . It influences cell function by modulating these channels, which can affect cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Acetazolamide is primarily based on its inhibition of carbonic anhydrase . This inhibition leads to changes in ion/water channel activity at the cellular membrane, which can result in changes in gene expression .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of Acetazolamide can change over time in laboratory settings . Information on the product’s stability, degradation, and any long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies is currently being researched .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Acetazolamide can vary with different dosages in animal models . Studies are ongoing to determine any threshold effects observed in these studies, as well as any toxic or adverse effects at high doses .
Metabolic Pathways
Acetazolamide is involved in metabolic pathways through its interaction with carbonic anhydrase . This interaction can affect metabolic flux or metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
It is believed to interact with certain transporters or binding proteins, which could affect its localization or accumulation .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of Acetazolamide and its effects on its activity or function are areas of active research . It is possible that certain targeting signals or post-translational modifications direct it to specific compartments or organelles .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen: Die Synthese von Acetazolamid beinhaltet die Oxidation eines Thiol-Derivats unter Bildung eines Sulfonylchlorid-Zwischenprodukts. Dieses Zwischenprodukt reagiert dann mit verschiedenen Aminen, Hydrazenen und Bis-Amin-Vorläufern unter Bildung neuer Sulfonamid-Derivate . Der Oxidationsprozess kann durch Ersetzen von Chlorgas durch Natriumhypochlorit (handelsübliche Bleiche) verbessert werden, was die Sicherheit und die Umweltbedingungen verbessert .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden: In industriellen Umgebungen wird this compound durch Mischen von this compound mit Laktose, Maisstärke, vorgelierter Stärke, PVP, Saccharose und Carboxymethylstärke-Natrium hergestellt. Die Mischung wird dann verpelletiert, getrocknet und tabletiert, um this compound-Tabletten zu erhalten .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Acetazolamid durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution. Die Verbindung ist bekannt für ihre hemmende Wirkung auf die Carboanhydrase, was zu einer Verringerung der Bildung von Wasserstoffionen und Bicarbonat aus Kohlendioxid und Wasser führt .
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Natriumhypochlorit (handelsübliche Bleiche) wird als Oxidationsmittel verwendet.
Reduktion und Substitution: Verschiedene Amine, Hydrazone und Bis-Amin-Vorläufer werden bei der Synthese neuer Sulfonamid-Derivate verwendet.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden: Zu den Hauptprodukten, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, gehören neuartige Sulfonamid-Derivate mit verbesserten antibakteriellen und antioxidativen Eigenschaften .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Sulfanilamide: An earlier discovered compound with similar enzymatic inhibitory activity but much less potent than acetazolamide.
Other Sulfonamide Derivatives: Various diuretics and anticonvulsants with minor to moderate carbonic anhydrase activity.
Uniqueness of Acetazolamide: Acetazolamide stands out due to its potent inhibitory effect on carbonic anhydrase, making it highly effective in treating a wide range of medical conditions. Its ability to act as a diuretic, anticonvulsant, and glaucoma medication highlights its versatility and importance in both clinical and research settings .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
N-(5-sulfamoyl-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl)acetamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C4H6N4O3S2/c1-2(9)6-3-7-8-4(12-3)13(5,10)11/h1H3,(H2,5,10,11)(H,6,7,9) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BZKPWHYZMXOIDC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(=O)NC1=NN=C(S1)S(=O)(=O)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C4H6N4O3S2 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
1424-27-7 (mono-hydrochloride salt) | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000059665 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7022544 | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022544 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
222.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Acetazolamide appears as white to yellowish-white fine crystalline powder. No odor or taste. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
>33.3 [ug/mL] (The mean of the results at pH 7.4), less than 1 mg/mL at 72 °F (NTP, 1992), SPARINGLY SOL IN COLD WATER, SLIGHTLY SOL IN ALCOHOL, INSOL IN CHLOROFORM, DIETHYL ETHER, CARBON TETRACHLORIDE; SLIGHTLY SOL IN ACETONE, Readily soluble in 1 N sodium carbonate solution., In water= 980 mg/l at 30 °C., 2.79e+00 g/L | |
| Record name | SID855900 | |
| Source | Burnham Center for Chemical Genomics | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/1996#section=Data-Table | |
| Description | Aqueous solubility in buffer at pH 7.4 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The anticonvulsant activity of Acetazolamide may depend on a direct inhibition of carbonic anhydrase in the CNS, which decreases carbon dioxide tension in the pulmonary alveoli, thus increasing arterial oxygen tension. The diuretic effect depends on the inhibition of carbonic anhydrase, causing a reduction in the availability of hydrogen ions for active transport in the renal tubule lumen. This leads to alkaline urine and an increase in the excretion of bicarbonate, sodium, potassium, and water., Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors potently inhibit (IC50 for acetazolamide is 10 nM) both the membrane bound and cytoplasmic forms of carbonic anhydrase, resulting in nearly complete abolition of NaHCO3 reabsorption in the proximal tubule. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, Although the proximal tubule is the major site of action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, carbonic anhydrase also is involved in secretion of titratable acid in the collecting duct system (a process which involves a proton pump), and therefore the collecting duct system is a secondary site of action for this class of drugs. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, Acetazolamide frequently causes paresthesias and somnolence, suggesting an action of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors in the CNS. The efficacy of acetazolamide in epilepsy is in part due to the production of metabolic acidosis; however, direct actions of acetazolamide in the CNS also contribute to its anticonvulsant action., ... Inhibition of carbonic anhydrase decreases the rate of formation of aqueous humor and consequently reduce intraocular pressure. /Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors/, For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for ACETAZOLAMIDE (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
CRYSTALS FROM WATER, WHITE TO FAINTLY YELLOWISH WHITE, CRYSTALLINE, POWDER | |
CAS No. |
59-66-5 | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59-66-5 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide [USP:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000059665 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | acetazolamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=755854 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | acetazolamide | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=145177 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Acetamide, N-[5-(aminosulfonyl)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-2-yl]- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022544 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.400 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/O3FX965V0I | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
496 to 498 °F (effervescence) (NTP, 1992), 258-259 °C (EFFERVESCENCE), 260.5 °C | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/19702 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00819 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | ACETAZOLAMIDE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3002 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Acetazolamide | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014957 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details








Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![triethyl-[3-[4-(triethylazaniumyl)phenyl]propyl]azanium;diiodide](/img/structure/B1664915.png)
![trimethyl-[3-[4-(trimethylazaniumyl)phenyl]propyl]azanium;diiodide](/img/structure/B1664916.png)
![ethyl-[4-[4-[ethyl(dimethyl)azaniumyl]butyl]phenyl]-dimethylazanium;diiodide](/img/structure/B1664917.png)
![trimethyl-[4-[4-(trimethylazaniumyl)butyl]phenyl]azanium;diiodide](/img/structure/B1664918.png)