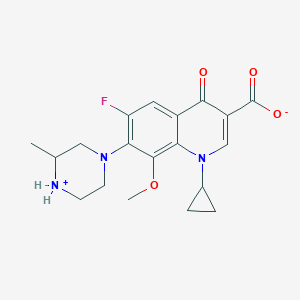
Gatifloxacin
Descripción general
Descripción
- El fumarato de quetiapina, también conocido por sus nombres comerciales Seroquel y Seroquel XR, pertenece a la clase de medicamentos llamados antipsicóticos atípicos.
- Se utiliza principalmente para tratar varios trastornos mentales y del estado de ánimo, incluida la esquizofrenia, el trastorno bipolar y el trastorno depresivo mayor.
- La quetiapina funciona modulando la actividad de ciertos neurotransmisores en el cerebro, específicamente la serotonina y la dopamina .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
- En química, la quetiapina sirve como una herramienta valiosa para estudiar las interacciones de los neurotransmisores y la unión a los receptores.
- En biología, ayuda a comprender el funcionamiento del cerebro y el papel de los neurotransmisores en la salud mental.
- En medicina, es crucial para el manejo de la esquizofrenia, el trastorno bipolar y la depresión.
- En la industria, la quetiapina contribuye al desarrollo de medicamentos antipsicóticos.
Mecanismo De Acción
- Los efectos de la quetiapina resultan de su interacción con receptores específicos, incluidos los receptores de serotonina (5-HT2A y 5-HT2C) y dopamina (D2).
- Al modular estos receptores, ayuda a restaurar el equilibrio de los neurotransmisores y aliviar los síntomas de los trastornos mentales.
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Gatifloxacin works by inhibiting the bacterial enzymes DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV . These enzymes are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination . By inhibiting these enzymes, this compound prevents bacteria from replicating, thereby stopping the infection.
Cellular Effects
This compound’s primary cellular effect is the inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV enzymes . This inhibition disrupts the bacterial DNA replication process, leading to cell death . This compound is effective against a broad spectrum of bacteria, including Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and anaerobic bacteria .
Molecular Mechanism
The bactericidal action of this compound results from the inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV . These enzymes are essential for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination . By inhibiting these enzymes, this compound prevents the bacteria from replicating their DNA, leading to cell death .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound demonstrates improved in vitro activity against gram-positive organisms, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics when compared with levofloxacin and ciprofloxacin
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
It’s primarily excreted unchanged in the urine .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound undergoes limited biotransformation in humans with less than 1% of the dose excreted in the urine as ethylenediamine and methylethylenediamine metabolites . It does not inhibit the cytochrome P450 (CYP) system and thus is not expected to interfere with CYP-dependent metabolism of drugs .
Transport and Distribution
This compound has a large volume of distribution, low protein binding, and broad tissue distribution . It’s primarily excreted unchanged in the urine
Métodos De Preparación
- El fumarato de quetiapina se puede sintetizar a través de varias rutas, pero un método común implica la reacción de la base de quetiapina con ácido fumárico.
- Los métodos de producción industrial normalmente implican la síntesis química a gran escala, asegurando una alta pureza y rendimiento.
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
- La quetiapina experimenta varias reacciones, incluyendo oxidación, reducción y sustitución.
- Los reactivos y condiciones comunes utilizados en estas reacciones incluyen ácidos fuertes, bases y agentes reductores.
- Los principales productos formados incluyen el propio fumarato de quetiapina y sus metabolitos.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
- La quetiapina destaca por su doble acción sobre los receptores de serotonina y dopamina.
- Compuestos similares incluyen otros antipsicóticos atípicos como la risperidona y la olanzapina.
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-8-methoxy-7-(3-methylpiperazin-4-ium-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylate | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H22FN3O4/c1-10-8-22(6-5-21-10)16-14(20)7-12-15(18(16)27-2)23(11-3-4-11)9-13(17(12)24)19(25)26/h7,9-11,21H,3-6,8H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XUBOMFCQGDBHNK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1CN(CC[NH2+]1)C2=C(C=C3C(=C2OC)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)[O-])C4CC4)F | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C19H22FN3O4 | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
375.4 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Gatifloxacin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015178 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
6.31e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Gatifloxacin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015178 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
CAS No. |
112811-59-3 | |
| Record name | Gatifloxacin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=112811-59-3 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Gatifloxacin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015178 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
182 - 185 °C | |
| Record name | Gatifloxacin | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015178 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of gatifloxacin?
A1: this compound, an 8-methoxyfluoroquinolone, primarily targets bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV. [] These enzymes are essential for bacterial DNA replication and repair. This compound inhibits these enzymes, leading to bacterial cell death. []
Q2: How does the presence of the 8-methoxy group in this compound impact its activity compared to other fluoroquinolones?
A2: The 8-methoxy group enhances this compound's activity against Gram-positive bacteria, including those resistant to other fluoroquinolones. [] It requires mutations in both topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase for resistance to develop, unlike some other fluoroquinolones. []
Q3: What makes this compound effective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)?
A3: this compound, particularly when combined with benzalkonium chloride (BAK), exhibits potent activity against MRSA, even at low concentrations. [] The addition of BAK significantly lowers the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and mutant prevention concentration (MPC) of this compound against MRSA. [] This suggests a synergistic effect between these compounds.
Q4: What is the chemical formula and molecular weight of this compound?
A4: Unfortunately, the provided research abstracts do not explicitly state the chemical formula and molecular weight of this compound. This information would need to be sourced from a drug database or chemical reference.
Q5: How does the stability of this compound for injection vary between different manufacturers?
A5: A study evaluating four different manufacturers of this compound for injection found that all products remained stable for at least two years, meeting the requirements outlined in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. [] This suggests consistent manufacturing processes and adherence to quality standards across different manufacturers.
Q6: How does the formulation of this compound as an ophthalmic gel affect its bioavailability compared to eye drops?
A6: this compound ophthalmic gel demonstrates significantly increased bioavailability and a longer duration of action in the eye compared to this compound eye drops. [] The gel formulation likely enhances drug retention on the ocular surface, resulting in prolonged drug exposure.
Q7: What are the pharmacokinetic properties of this compound in infants and children?
A7: Studies in pediatric patients aged 6 months to 16 years showed that this compound, administered as an oral suspension, exhibits age-dependent pharmacokinetics. [] The apparent clearance of this compound decreases with increasing age. [] A dose of 10 mg/kg every 24 hours is expected to achieve therapeutic concentrations in this population. []
Q8: How does the co-administration of this compound with rifampicin affect its pharmacokinetics?
A8: When administered with rifampicin, isoniazid, and pyrazinamide in a tuberculosis treatment regimen, this compound's exposure initially increases due to drug interactions, but then decreases with repeated daily dosing. [] This decline in exposure with multiple doses might necessitate dose adjustments to maintain therapeutic levels.
Q9: How does the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) relate to the development of resistance to this compound in Streptococcus pneumoniae?
A9: In vitro studies using S. pneumoniae showed a clear relationship between the ratio of the free AUC to the MIC (fAUC/MIC) and the emergence of resistance. [] Higher fAUC/MIC ratios were associated with delayed development of resistance mutations in topoisomerase genes. [] Levofloxacin, at clinical doses, showed a higher likelihood of resistance development compared to the newer fluoroquinolones like this compound, gemifloxacin, and moxifloxacin. []
Q10: What are some reported adverse effects associated with this compound administration?
A11: this compound has been associated with dysglycemic events, including both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. [, , , ] These effects are thought to be related to this compound potentially influencing insulin secretion. [] Other reported side effects include gastrointestinal disturbances, dizziness, and skin reactions. [, ]
Q11: What analytical techniques are commonly used to quantify this compound in biological samples?
A13: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a widely employed technique for quantifying this compound concentrations in various matrices, including serum, vitreous humor, and aqueous humor. [, , ] The combination of HPLC with mass spectrometry (LC-MS) further enhances the sensitivity and specificity of this compound detection. []
Q12: What is the potential impact of hexavalent chromium (Cr6+) on the interaction between this compound and DNA?
A14: Studies suggest that Cr6+ can hinder the binding of this compound to DNA. [] This interference might be due to Cr6+ competing with this compound for binding sites on DNA or forming complexes with this compound, thereby reducing its availability for DNA interaction. []
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.