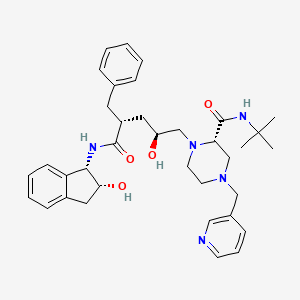
Indinavir
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Indinavir, connu sous le nom commercial de Crixivan, est un inhibiteur de protéase utilisé comme composant d’un traitement antirétroviral hautement actif pour traiter le VIH/SIDA . C’est une poudre blanche, soluble, administrée par voie orale en association avec d’autres médicaments antiviraux. This compound a été synthétisé pour inhiber l’enzyme protéase du virus VIH, empêchant le virus de se reproduire et réduisant ainsi la charge virale chez les patients .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Indinavir has a wide range of scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: this compound is used as a model compound in studies of protease inhibitors and their interactions with enzymes.
Biology: It is used to study the mechanisms of viral replication and the role of proteases in viral life cycles.
Medicine: this compound is a critical component of antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS, helping to manage the disease and improve patient outcomes.
Mécanisme D'action
Indinavir inhibe l’enzyme protéase virale du VIH, qui est essentielle à la coupure protéolytique des précurseurs polyprotéiques viraux en protéines fonctionnelles individuelles. En se liant au site actif de la protéase, l’this compound empêche la coupure de ces polyprotéines, ce qui entraîne la formation de particules virales immatures et non infectieuses. Cette inhibition réduit la charge virale chez les patients et ralentit la progression du VIH/SIDA .
Composés Similaires :
- Ritonavir
- Saquinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Lopinavir
Comparaison : this compound est unique parmi les inhibiteurs de protéase en raison de son affinité de liaison spécifique et de son mécanisme d’inhibition. Alors que d’autres inhibiteurs de protéase comme le ritonavir et le saquinavir ciblent également l’enzyme protéase du VIH, la structure moléculaire d’this compound permet des interactions distinctes avec le site actif de l’enzyme, conduisant à des profils pharmacocinétiques et pharmacodynamiques différents. De plus, la solubilité et la biodisponibilité d’this compound sont améliorées par ses modifications chimiques spécifiques .
Les propriétés uniques d’this compound en font un outil précieux dans le traitement du VIH/SIDA, malgré ses effets secondaires et le développement d’une résistance dans certains cas. Sa comparaison avec d’autres inhibiteurs de protéase met en évidence l’importance de la diversité structurelle dans le développement de thérapies antirétrovirales efficaces .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Indinavir interacts with HIV-1 protease, an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of the viral polyprotein precursors into the individual functional proteins found in infectious HIV-1 . The interaction between this compound and HIV-1 protease inhibits the activity of the enzyme .
Cellular Effects
This compound influences cell function by preventing the cleavage of the viral polyproteins, resulting in the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles . This impacts cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism.
Molecular Mechanism
This compound exerts its effects at the molecular level by binding to the protease active site, inhibiting the enzyme’s activity . This inhibition prevents the cleavage of the viral polyproteins, leading to the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that this compound is a potent and specific HIV protease inhibitor .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is metabolized in the body, with seven metabolites identified, one glucuronide conjugate and six oxidative metabolites . Cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP3A4) is the major enzyme responsible for the formation of these oxidative metabolites .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de Synthèse et Conditions de Réaction : Indinavir est synthétisé par un processus en plusieurs étapes impliquant la formation de plusieurs intermédiairesLes conditions de réaction impliquent généralement l’utilisation de solvants organiques, de catalyseurs et de températures contrôlées pour garantir que les transformations chimiques souhaitées se produisent efficacement .
Méthodes de Production Industrielle : La production industrielle d’this compound implique une synthèse à grande échelle utilisant des conditions de réaction optimisées pour maximiser le rendement et la pureté. Le processus comprend des étapes de purification rigoureuses telles que la cristallisation et la chromatographie pour obtenir le produit final sous sa forme pure. La production est effectuée sous des mesures strictes de contrôle de la qualité pour garantir la cohérence et la sécurité .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de Réactions : Indinavir subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : this compound peut être oxydé dans des conditions spécifiques, conduisant à la formation de dérivés oxydés.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent modifier les groupes fonctionnels présents dans l’this compound, modifiant potentiellement son activité.
Réactifs et Conditions Courants :
Oxydation : Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le peroxyde d’hydrogène et le permanganate de potassium.
Réduction : Des agents réducteurs tels que le borohydrure de sodium et l’hydrure de lithium et d’aluminium sont utilisés.
Substitution : Différents nucléophiles et électrophiles peuvent être utilisés dans les réactions de substitution, en fonction de la modification souhaitée.
Principaux Produits Formés : Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions dépendent des réactifs et des conditions spécifiques utilisés. Par exemple, l’oxydation peut conduire à la formation de dérivés hydroxylés ou cétoniques, tandis que la réduction peut produire des alcools ou des amines .
4. Applications de la Recherche Scientifique
This compound a un large éventail d’applications de recherche scientifique, notamment :
Chimie : this compound est utilisé comme composé modèle dans les études sur les inhibiteurs de protéase et leurs interactions avec les enzymes.
Biologie : Il est utilisé pour étudier les mécanismes de réplication virale et le rôle des protéases dans les cycles de vie viraux.
Médecine : this compound est un composant essentiel du traitement antirétroviral du VIH/SIDA, aidant à gérer la maladie et à améliorer les résultats des patients.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
- Ritonavir
- Saquinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Lopinavir
Comparison: Indinavir is unique among protease inhibitors due to its specific binding affinity and inhibition mechanism. While other protease inhibitors like ritonavir and saquinavir also target the HIV protease enzyme, this compound’s molecular structure allows for distinct interactions with the enzyme’s active site, leading to different pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. Additionally, this compound’s solubility and bioavailability are enhanced by its specific chemical modifications .
This compound’s unique properties make it a valuable tool in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, despite its side effects and the development of resistance in some cases. Its comparison with other protease inhibitors highlights the importance of structural diversity in developing effective antiretroviral therapies .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(2S)-1-[(2S,4R)-4-benzyl-2-hydroxy-5-[[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]amino]-5-oxopentyl]-N-tert-butyl-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)piperazine-2-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C36H47N5O4/c1-36(2,3)39-35(45)31-24-40(22-26-12-9-15-37-21-26)16-17-41(31)23-29(42)19-28(18-25-10-5-4-6-11-25)34(44)38-33-30-14-8-7-13-27(30)20-32(33)43/h4-15,21,28-29,31-33,42-43H,16-20,22-24H2,1-3H3,(H,38,44)(H,39,45)/t28-,29+,31+,32-,33+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CBVCZFGXHXORBI-PXQQMZJSSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)C1CN(CCN1CC(CC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)NC3C(CC4=CC=CC=C34)O)O)CC5=CN=CC=C5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)[C@@H]1CN(CCN1C[C@H](C[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N[C@@H]3[C@@H](CC4=CC=CC=C34)O)O)CC5=CN=CC=C5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C36H47N5O4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
157810-81-6 (sulfate (1:1) (salt)) | |
| Record name | Indinavir [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0150378179 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4043802 | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4043802 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
613.8 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
4.82e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Indinavir inhibits the HIV viral protease enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
150378-17-9 | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=150378-17-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Indinavir [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0150378179 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4043802 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | INDINAVIR ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/9MG78X43ZT | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
167.5-168 °C, 167.5 - 168 °C | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![manganese(2+);(4R,9R,14R,19R)-3,10,13,20,26-pentazatetracyclo[20.3.1.04,9.014,19]hexacosa-1(26),22,24-triene;dichloride](/img/structure/B1671796.png)
![9,10-Dihydro-9,10[1',2']-benzenoanthracene-1,4-dione](/img/structure/B1671815.png)
