Fexinidazole
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le Fexinidazole est un dérivé du 5-nitroimidazole utilisé principalement comme médicament antiparasitaire. Il est efficace contre la trypanosomiase africaine (maladie du sommeil) causée par Trypanosoma brucei gambiense et a montré un potentiel dans le traitement de la maladie de Chagas . Ce composé est remarquable pour être le premier traitement entièrement oral pour les stades précoces et tardifs de la maladie du sommeil .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Fexinidazole has a wide range of applications in scientific research:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound to study nitroimidazole chemistry and its reactivity.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on cellular processes and its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Medicine: Primarily used to treat African trypanosomiasis and being explored for Chagas disease treatment.
Industry: Potential applications in developing new antiparasitic drugs and studying drug resistance mechanisms
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Fexinidazole is primarily targeted against the parasite Trypanosoma brucei gambiense , which is responsible for causing human African trypanosomiasis (HAT), also known as sleeping sickness .
Mode of Action
This compound is a 2-substituted 5-nitroimidazole that is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species . This activation leads to DNA and protein damage and eventually results in the death of the parasite .
Biochemical Pathways
It is known that the drug is metabolized by the host’s cytochrome p450 and flavin-containing monooxygenase into two active metabolites, sulfoxide and sulfone . These metabolites are believed to cause damage to the DNA and proteins of the parasite, leading to its death .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is orally bioavailable and is extensively metabolized by the liver . The drug and its metabolites, M1 and M2, have mean day 10 half-lives of 15 ± 6, 16 ± 6, and 23 ± 4 hours, respectively . Elimination is almost entirely extra-renal, with roughly 0.75-3.15% of a this compound dose being recovered in urine over 168 hours, primarily as M1 and M2 metabolites . The pharmacokinetics of this compound in patients with hepatic impairment is unknown .
Result of Action
The action of this compound results in the death of the Trypanosoma brucei gambiense parasite, effectively treating both the first (hemolymphatic) and second (meningoencephalitic) stages of HAT . In cell culture, this compound has an IC50 of around 1–4 μM against Trypanosoma brucei .
Action Environment
This compound is taken orally, and its efficacy can be influenced by factors such as the patient’s diet and the presence of other medications . It is practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in acetone and acetonitrile, very slightly soluble in ethanol, and slightly soluble in methanol . This suggests that the drug’s solubility and stability could be influenced by the pH and composition of the gastrointestinal tract.
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Fexinidazole is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death . It interacts with enzymes within the parasites that result in their death .
Cellular Effects
This compound has a broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6 . Therefore, it is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . It has been shown to be non-inferior to existing nifurtimox / eflornithine combination therapy in late-stage T. brucei gambiense infection .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound is believed to work by turning on certain enzymes within the parasites that result in their death . It is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
This compound is well absorbed, although the rate and extent of absorption are less than dose-proportional . After a 14-day administration schedule, the mean C max and AUC last increased by 1.17 and 1.34, or by 1.5 and 1.61, when the dose was either doubled or tripled .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In the mouse model, this compound cures both the first, hemolymphatic, and the second, meningoencephalitic stage of the infection, the latter at 100 mg/kg twice daily for 5 days . The dosage effects of this compound were found to be dose-dependent in a mouse model of human African trypanosomiasis .
Metabolic Pathways
Following absorption, this compound is rapidly converted to its M1 metabolite, which undergoes a slower transformation to M2 over time . These metabolites have equivalent biological activity to the parent and contribute significantly to the in vivo efficacy .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is well-absorbed and readily distributes throughout the body, including the brain . Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled this compound in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues .
Subcellular Localization
This compound is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . This suggests that it can localize to various subcellular compartments where the parasites reside.
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions réactionnelles : Le Fexinidazole est synthétisé par un processus en plusieurs étapes à partir de précurseurs disponibles dans le commerce. Les étapes clés impliquent la nitration de l'imidazole, suivie de l'alkylation et de réactions ultérieures pour introduire le groupe méthylsulfanylphénoxy. Les conditions réactionnelles impliquent généralement des températures contrôlées et l'utilisation de catalyseurs spécifiques pour assurer un rendement et une pureté élevés .
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle de this compound implique la mise à l'échelle du processus de synthèse en laboratoire. Cela inclut l'optimisation des conditions réactionnelles pour maximiser le rendement et minimiser les impuretés. Le processus est effectué dans de grands réacteurs avec un contrôle précis de la température, de la pression et du temps de réaction. Des étapes de purification telles que la cristallisation et la filtration sont utilisées pour obtenir le produit final .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : Le Fexinidazole subit plusieurs types de réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le groupe nitro peut être réduit en amine dans des conditions spécifiques.
Substitution : Le cycle imidazole peut subir des réactions de substitution nucléophile.
Hydrolyse : Le composé peut être hydrolysé en milieu acide ou basique.
Réactifs et conditions courants :
Oxydation : Les réactifs courants comprennent le peroxyde d'hydrogène et les catalyseurs métalliques.
Substitution : Des nucléophiles tels que les amines ou les thiols sont utilisés.
Hydrolyse : Des solutions acides ou basiques sont utilisées.
Principaux produits :
Réduction du groupe nitro : conduit à la formation d'un dérivé amine.
Réactions de substitution : donnent divers dérivés imidazole substitués.
Hydrolyse : peut conduire à la dégradation du composé en molécules plus simples.
4. Applications de la recherche scientifique
Le this compound a une large gamme d'applications dans la recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme composé modèle pour étudier la chimie du nitroimidazole et sa réactivité.
Biologie : Investigated for its effects on cellular processes and its potential as a therapeutic agent.
Médecine : Principalement utilisé pour traiter la trypanosomiase africaine et exploré pour le traitement de la maladie de Chagas.
Industrie : Applications potentielles dans le développement de nouveaux médicaments antiparasitaires et l'étude des mécanismes de résistance aux médicaments
5. Mécanisme d'action
Le this compound exerce ses effets en étant métabolisé en métabolites actifs qui interfèrent avec la synthèse de l'ADN du parasite. On pense que le composé active certaines enzymes dans les parasites, ce qui conduit à la production d'espèces réactives de l'oxygène qui endommagent les structures cellulaires du parasite. Cela conduit finalement à la mort du parasite .
Composés similaires :
Nifurtimox : Autre nitroimidazole utilisé pour traiter la maladie de Chagas.
Benznidazole : Utilisé pour la maladie de Chagas, similaire en structure et en fonction au this compound.
Métronidazole : Un nitroimidazole largement utilisé pour les infections bactériennes et protozoaires.
Unicité du this compound : Le this compound se distingue par sa biodisponibilité orale et son efficacité contre les stades précoces et tardifs de la trypanosomiase africaine. Contrairement aux autres traitements qui nécessitent une administration intraveineuse, le this compound peut être pris par voie orale, ce qui le rend plus accessible et plus facile à administrer dans les milieux à ressources limitées .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Nifurtimox: Another nitroimidazole used to treat Chagas disease.
Benznidazole: Used for Chagas disease, similar in structure and function to fexinidazole.
Metronidazole: A widely used nitroimidazole for bacterial and protozoal infections.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound stands out due to its oral bioavailability and effectiveness against both early and late stages of African trypanosomiasis. Unlike other treatments that require intravenous administration, this compound can be taken orally, making it more accessible and easier to administer in resource-limited settings .
Propriétés
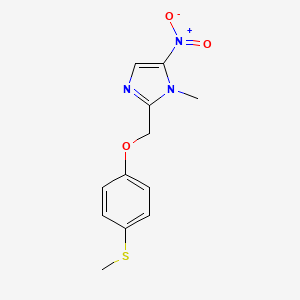
IUPAC Name |
1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H13N3O3S/c1-14-11(13-7-12(14)15(16)17)8-18-9-3-5-10(19-2)6-4-9/h3-7H,8H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MIWWSGDADVMLTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1C(=CN=C1COC2=CC=C(C=C2)SC)[N+](=O)[O-] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H13N3O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID00208448 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
279.32 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is caused by two subspecies of _Trypanosoma brucei_, _T. brucei gambiense_ and _T. brucei rhodesiense_, with _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT accounting for ~97% of the total disease burden. Transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly, HAT begins as a local infection at the bite site before disseminating throughout the blood and reticuloendothelial system (first or hemolymphatic stage) and eventually crossing the blood-brain barrier (second or meningoencephalitic stage). First stage _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT is characterized by fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, pruritus, and other non-specific symptoms. Progression to the second stage results in progressive deterioration of neurological function, including sleep disturbances (HAT is also referred to as sleeping sickness), tremors, ataxia, abnormal behaviour, confusion, and coma; myocarditis and endocrine hypothalamic-hypophyseal dysfunction may also be present. If left untreated, HAT is fatal. Fexinidazole is the first all-oral treatment for _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT. Both fexinidazole and its two main metabolites, a sulfoxide (M1) and sulfone (M2) metabolite, possess _in vitro_ activity against _T. brucei gambiense_, _T. brucei rhodesiense_, and _T. brucei brucei_ in the 0.2-0.9 μg/mL range. Further studies revealed _in vivo_ efficacy in HAT animal models and acceptable toxicity profiles, both in animal and human subjects. Crucially, fexinidazole was shown to be non-inferior to existing [nifurtimox]/[eflornithine] combination therapy (NECT) in late-stage _T. brucei gambiense_ infection. The precise mechanism of action of fexinidazole remains unknown. However, it is suggested that bacterial-like nitroreductases encoded by trypanosomes activate fexinidazole and its M1/M2 metabolites through reduction to form reactive intermediates capable of damaging DNA and proteins. Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled fexinidazole in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6. Therefore, fexinidazole is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain, which is consistent with its efficacy against both early and late-stage infections. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
59729-37-2 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59729-37-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0059729372 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | FEXINIDAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/306ERL82IR | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
![3-Chloro-2,6-Dimethyl-5-{4-[4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]phenyl}pyridin-4-Ol](/img/structure/B1672545.png)
![(2R)-methyl-1-{3-[2-(3-pyridinyloxy)ethoxy]-2-pyrazinyl}piperazine](/img/structure/B1672550.png)