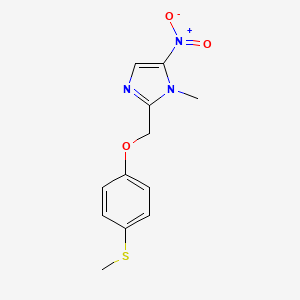
Fexinidazol
Descripción general
Descripción
Fexinidazol es un derivado del 5-nitroimidazol que se utiliza principalmente como medicamento antiparasitario. Es eficaz contra la tripanosomiasis africana (enfermedad del sueño) causada por Trypanosoma brucei gambiense y ha mostrado potencial en el tratamiento de la enfermedad de Chagas . Este compuesto es notable por ser el primer tratamiento totalmente oral para las etapas temprana y tardía de la enfermedad del sueño .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Fexinidazol tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones en la investigación científica:
Química: Se utiliza como compuesto modelo para estudiar la química del nitroimidazol y su reactividad.
Biología: Se ha investigado por sus efectos sobre los procesos celulares y su potencial como agente terapéutico.
Medicina: Se utiliza principalmente para tratar la tripanosomiasis africana y se está explorando para el tratamiento de la enfermedad de Chagas.
Industria: Aplicaciones potenciales en el desarrollo de nuevos fármacos antiparasitarios y el estudio de los mecanismos de resistencia a los fármacos
Mecanismo De Acción
Fexinidazol ejerce sus efectos al metabolizarse en metabolitos activos que interfieren con la síntesis de ADN del parásito. Se cree que el compuesto activa ciertas enzimas dentro de los parásitos, lo que lleva a la producción de especies reactivas de oxígeno que dañan las estructuras celulares del parásito. Esto finalmente resulta en la muerte del parásito .
Compuestos similares:
Nifurtimox: Otro nitroimidazol que se utiliza para tratar la enfermedad de Chagas.
Benznidazol: Utilizado para la enfermedad de Chagas, similar en estructura y función a this compound.
Metronidazol: Un nitroimidazol ampliamente utilizado para infecciones bacterianas y protozoarias.
Singularidad de this compound: this compound destaca por su biodisponibilidad oral y su eficacia contra las etapas temprana y tardía de la tripanosomiasis africana. A diferencia de otros tratamientos que requieren administración intravenosa, this compound se puede tomar por vía oral, lo que lo hace más accesible y fácil de administrar en entornos con recursos limitados .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Fexinidazole is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death . It interacts with enzymes within the parasites that result in their death .
Cellular Effects
Fexinidazole has a broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6 . Therefore, it is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . It has been shown to be non-inferior to existing nifurtimox / eflornithine combination therapy in late-stage T. brucei gambiense infection .
Molecular Mechanism
Fexinidazole is believed to work by turning on certain enzymes within the parasites that result in their death . It is likely activated by parasitic nitroreductases to highly reactive species, leading to DNA and protein damage and eventual parasite death .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Fexinidazole is well absorbed, although the rate and extent of absorption are less than dose-proportional . After a 14-day administration schedule, the mean C max and AUC last increased by 1.17 and 1.34, or by 1.5 and 1.61, when the dose was either doubled or tripled .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In the mouse model, fexinidazole cures both the first, hemolymphatic, and the second, meningoencephalitic stage of the infection, the latter at 100 mg/kg twice daily for 5 days . The dosage effects of fexinidazole were found to be dose-dependent in a mouse model of human African trypanosomiasis .
Metabolic Pathways
Following absorption, fexinidazole is rapidly converted to its M1 metabolite, which undergoes a slower transformation to M2 over time . These metabolites have equivalent biological activity to the parent and contribute significantly to the in vivo efficacy .
Transport and Distribution
Fexinidazole is well-absorbed and readily distributes throughout the body, including the brain . Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled fexinidazole in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues .
Subcellular Localization
Fexinidazole is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain . This suggests that it can localize to various subcellular compartments where the parasites reside.
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas sintéticas y condiciones de reacción: Fexinidazol se sintetiza a través de un proceso de múltiples pasos que comienza con precursores disponibles comercialmente. Los pasos clave incluyen la nitración del imidazol, seguida de alquilación y reacciones posteriores para introducir el grupo metilsulfanilfenoxi. Las condiciones de reacción suelen implicar temperaturas controladas y el uso de catalizadores específicos para garantizar un alto rendimiento y pureza .
Métodos de producción industrial: La producción industrial de this compound implica la ampliación del proceso de síntesis de laboratorio. Esto incluye la optimización de las condiciones de reacción para maximizar el rendimiento y minimizar las impurezas. El proceso se lleva a cabo en grandes reactores con un control preciso de la temperatura, la presión y el tiempo de reacción. Se emplean pasos de purificación como la cristalización y la filtración para obtener el producto final .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de reacciones: Fexinidazol experimenta varios tipos de reacciones químicas, que incluyen:
Oxidación: El grupo nitro puede reducirse a una amina en condiciones específicas.
Sustitución: El anillo de imidazol puede experimentar reacciones de sustitución nucleofílica.
Hidrólisis: El compuesto puede hidrolizarse en condiciones ácidas o básicas.
Reactivos y condiciones comunes:
Oxidación: Los reactivos comunes incluyen peróxido de hidrógeno y catalizadores metálicos.
Sustitución: Se utilizan nucleófilos como aminas o tioles.
Hidrólisis: Se emplean soluciones ácidas o básicas.
Productos principales:
Reducción del grupo nitro: da como resultado la formación de un derivado de amina.
Reacciones de sustitución: producen varios derivados de imidazol sustituidos.
Hidrólisis: puede conducir a la descomposición del compuesto en moléculas más simples.
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Nifurtimox: Another nitroimidazole used to treat Chagas disease.
Benznidazole: Used for Chagas disease, similar in structure and function to fexinidazole.
Metronidazole: A widely used nitroimidazole for bacterial and protozoal infections.
Uniqueness of Fexinidazole: Fexinidazole stands out due to its oral bioavailability and effectiveness against both early and late stages of African trypanosomiasis. Unlike other treatments that require intravenous administration, fexinidazole can be taken orally, making it more accessible and easier to administer in resource-limited settings .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H13N3O3S/c1-14-11(13-7-12(14)15(16)17)8-18-9-3-5-10(19-2)6-4-9/h3-7H,8H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
MIWWSGDADVMLTG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1C(=CN=C1COC2=CC=C(C=C2)SC)[N+](=O)[O-] | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H13N3O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID00208448 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
279.32 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Human African trypanosomiasis (HAT) is caused by two subspecies of _Trypanosoma brucei_, _T. brucei gambiense_ and _T. brucei rhodesiense_, with _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT accounting for ~97% of the total disease burden. Transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly, HAT begins as a local infection at the bite site before disseminating throughout the blood and reticuloendothelial system (first or hemolymphatic stage) and eventually crossing the blood-brain barrier (second or meningoencephalitic stage). First stage _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT is characterized by fever, headache, swollen lymph nodes, pruritus, and other non-specific symptoms. Progression to the second stage results in progressive deterioration of neurological function, including sleep disturbances (HAT is also referred to as sleeping sickness), tremors, ataxia, abnormal behaviour, confusion, and coma; myocarditis and endocrine hypothalamic-hypophyseal dysfunction may also be present. If left untreated, HAT is fatal. Fexinidazole is the first all-oral treatment for _T. brucei gambiense_ HAT. Both fexinidazole and its two main metabolites, a sulfoxide (M1) and sulfone (M2) metabolite, possess _in vitro_ activity against _T. brucei gambiense_, _T. brucei rhodesiense_, and _T. brucei brucei_ in the 0.2-0.9 μg/mL range. Further studies revealed _in vivo_ efficacy in HAT animal models and acceptable toxicity profiles, both in animal and human subjects. Crucially, fexinidazole was shown to be non-inferior to existing [nifurtimox]/[eflornithine] combination therapy (NECT) in late-stage _T. brucei gambiense_ infection. The precise mechanism of action of fexinidazole remains unknown. However, it is suggested that bacterial-like nitroreductases encoded by trypanosomes activate fexinidazole and its M1/M2 metabolites through reduction to form reactive intermediates capable of damaging DNA and proteins. Whole-body autoradiography of [14C]-labelled fexinidazole in rats revealed broad distribution into all tissues, including an observed brain-to-blood concentration ratio of 0.4-0.6. Therefore, fexinidazole is capable of direct toxicity against trypanosomes throughout the body and in the brain, which is consistent with its efficacy against both early and late-stage infections. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
59729-37-2 | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=59729-37-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0059729372 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB12265 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Fexinidazole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID00208448 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 1-methyl-2-[(4-methylsulfanylphenoxy)methyl]-5-nitroimidazole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | FEXINIDAZOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/306ERL82IR | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.
![3-Chloro-2,6-Dimethyl-5-{4-[4-(Trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]phenyl}pyridin-4-Ol](/img/structure/B1672545.png)
![1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-[4-[2-chloroethylcarbamoyl(nitroso)amino]-2,3-dihydroxybutyl]-1-nitrosourea](/img/structure/B1672557.png)
