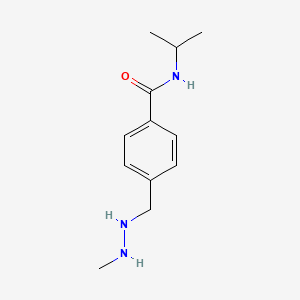
Procarbazine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Procarbazine est un médicament de chimiothérapie principalement utilisé pour le traitement de la maladie de Hodgkin et de certains types de cancers du cerveau, comme le glioblastome multiforme . Il appartient à la classe des agents alkylants, qui agissent en ajoutant des groupes alkyles à de nombreux groupes électronégatifs dans les conditions présentes dans les cellules . This compound a été approuvé pour un usage médical aux États-Unis en 1969 et est inclus dans la Liste des médicaments essentiels de l'Organisation mondiale de la santé .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions réactionnelles : La synthèse de la procarbazine implique plusieurs étapes à partir du p-tolualdéhyde. Le processus comprend l'addition d'acide cyanurique dibromé et d'isopropylamine pour obtenir la toluylisopropylamine. Ce composé intermédiaire est ensuite dissous dans un réactif organique, suivi de l'addition de N-bromo-succinimide et d'un initiateur. Le mélange est porté à reflux et le solvant est éliminé. De l'acétonitrile et un agent accélérateur d'hydrolyse sont ajoutés et le mélange est porté à reflux pour former la formoxylbenzoyl isopropylamine. Finalement, la formoxylbenzoyl isopropylamine est mise à réagir avec du sulfate de méthylhydrazinium et de la triéthylamine, suivie de l'ajout de cyanoborohydrure de sodium, ce qui entraîne la formation de this compound .
Méthodes de production industrielle : La production industrielle de this compound suit des voies de synthèse similaires, mais est optimisée pour des rendements et une efficacité plus élevés. Le processus évite l'utilisation d'oxydants forts et d'acides forts, ce qui le rend plus respectueux de l'environnement. Le taux de récupération total de la méthode industrielle est d'environ 52,9% .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : La procarbazine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment l'oxydation, la réduction et la substitution. Une réaction notable est son auto-oxydation pour former un dérivé azoïque, qui s'isomérise ensuite en une hydrazone. Cette hydrazone subit une hydrolyse pour produire un dérivé de benzaldéhyde et de la méthylhydrazine .
Réactifs et conditions courants : Les réactifs courants utilisés dans les réactions impliquant la this compound comprennent la N-bromo-succinimide, l'acétonitrile, les agents accélérateurs d'hydrolyse, le sulfate de méthylhydrazinium et le cyanoborohydrure de sodium . Les conditions réactionnelles impliquent généralement un chauffage à reflux et l'utilisation de solvants organiques.
Produits principaux : Les principaux produits formés à partir des réactions de la this compound comprennent les dérivés de benzaldéhyde et la méthylhydrazine .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
La this compound a un large éventail d'applications de recherche scientifique, en particulier dans les domaines de la chimie, de la biologie, de la médecine et de l'industrie. En médecine, elle est utilisée dans le cadre de schémas de chimiothérapie combinée pour le traitement de la maladie de Hodgkin et des cancers du cerveau . En chimie, la this compound est étudiée pour ses propriétés alkylants uniques et ses interactions avec diverses nanostructures pour les systèmes d'administration de médicaments . En biologie, elle est utilisée pour étudier les effets des agents alkylants sur les processus cellulaires et la synthèse de l'ADN . Les applications industrielles comprennent son utilisation dans la synthèse d'autres composés pharmaceutiques et son rôle dans le développement de méthodes de production respectueuses de l'environnement .
Mécanisme d'action
Le mécanisme d'action précis de la this compound n'est pas entièrement compris. Il est connu pour inhiber la synthèse des protéines, de l'ARN et de l'ADN en interférant avec la transméthylation des groupes méthyles de la méthionine dans l'ARN de transfert . La this compound agit également comme un agent alkylant, méthylant la guanine en position O-6, ce qui conduit à la rupture de l'ADN et à l'inhibition de la synthèse de l'ARN et des protéines .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Procarbazine has a wide range of scientific research applications, particularly in the fields of chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry. In medicine, it is used as part of combination chemotherapy regimens for treating Hodgkin’s lymphoma and brain cancers . In chemistry, this compound is studied for its unique alkylating properties and its interactions with various nanostructures for drug delivery systems . In biology, it is used to study the effects of alkylating agents on cellular processes and DNA synthesis . Industrial applications include its use in the synthesis of other pharmaceutical compounds and its role in developing environmentally friendly production methods .
Mécanisme D'action
The precise mechanism of action of procarbazine is not fully understood. it is known to inhibit the synthesis of protein, RNA, and DNA by interfering with the transmethylation of methyl groups of methionine into transfer RNA . This compound also works as an alkylating agent, methylating guanine at the O-6 position, which leads to DNA breakage and inhibition of RNA and protein synthesis .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Composés similaires : Les composés similaires à la procarbazine comprennent la dacarbazine, la bléomycine et le nivolumab . Ces composés sont également utilisés dans le traitement de divers cancers et ont des mécanismes d'action similaires à ceux des agents alkylants ou des agents antinéoplasiques.
Unicité : La this compound est unique en sa capacité à être utilisée en association avec d'autres agents chimiothérapeutiques, tels que la chlormethine, la vincristine et la prednisone, pour le traitement de la maladie de Hodgkin . Elle se distingue également par son interaction avec les nanostructures pour les systèmes d'administration de médicaments, ce qui améliore son efficacité dans le ciblage des cellules cancéreuses .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
4-[(2-methylhydrazinyl)methyl]-N-propan-2-ylbenzamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C12H19N3O/c1-9(2)15-12(16)11-6-4-10(5-7-11)8-14-13-3/h4-7,9,13-14H,8H2,1-3H3,(H,15,16) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CPTBDICYNRMXFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)NC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)CNNC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C12H19N3O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
366-70-1 (mono-hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Procarbazine [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000671169 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4021189 | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4021189 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
221.30 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015299 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
In water, 1,400 mg/L @ 25 °C /Estimated/, 2.28e-01 g/L | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01168 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PROCARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3250 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015299 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Vapor Pressure |
8.4X10-7 mm Hg @ 25 °C /Estimated/ | |
| Record name | PROCARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3250 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The precise mode of cytotoxic action of procarbazine has not been clearly defined. There is evidence that the drug may act by inhibition of protein, RNA and DNA synthesis. Studies have suggested that procarbazine may inhibit transmethylation of methyl groups of methionine into t-RNA. The absence of functional t-RNA could cause the cessation of protein synthesis and consequently DNA and RNA synthesis. In addition, procarbazine may directly damage DNA. Hydrogen peroxide, formed during the auto-oxidation of the drug, may attack protein sulfhydryl groups contained in residual protein which is tightly bound to DNA., Procarbazine is an alkylating agent. The exact mechanism of antineoplastic action is unknown but is thought to resemble that of the alkylating agents; procarbazine is cell cycle-specific for the S phase of cell division. Procarbazine is thought to inhibit DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis., O-6-Methylguanine was measured in blood leukocyte DNA of seven patients with Hodgkin's or non-Hodgkin's lymphoma during therapeutic exposure to procarbazine involving three daily p.o. doses (50 mg each) for 10 days (corresponding to 2.1 mg/kg/day for a 70-kg human). Adduct accumulation was observed in all seven cases, reaching levels up to 0.28 fmol/microgram of DNA (0.45 umol/mol of guanine). In one individual, maximal levels of adduct were reached after 7 days of exposure, followed by a steady decline, whereas in all other individuals continuous accumulation was observed throughout the exposure period. In four individuals for which data were available for day 11 (12 to 16 hr after the final intake of procarbazine), decreased amounts of O-6-methylguanine were observed relative to the last previous measurements. The accumulation of O-6-methylguanine was linearly correlated with the cumulative dose of procarbazine, with a slope of 0.011 fmol of O-6-methylguanine/microgram of DNA per mg/kg of body weight or 2.68x10-4 fmol of O-6-methylguanine DNA per mg/sq m. Two hr after the administration of single p.o. doses of l to 10 mg/kg of procarbazine to rats, O-6-methylguanine formation in leukocyte DNA was just under half that in liver DNA and showed a linear relationship with dose with a slope of 0.017 fmol/microgram of DNA per mg/kg of body weight or 5.67x10-4 fmol of O-6-methylguanine/microgram of DNA per mg/sq m. A negative correlation between the rate of accumulation of O-6-methylguanine in different individuals and lymphocyte O-6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase was observed, demonstrating a probable protective effect of O-6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase against the accumulation of O-6-methylguanine during exposure to methylating agents. This observation supports the suggestion of a possible role of procarbazine-induced O-6-methylguanine in the pathogenesis of acute nonlymphocytic leukemia appearing after treatment with chemotherapeutic protocols which include procarbazine, based on the finding of low lymphocyte O-6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase levels in patients with such therapy-related neoplastic disease. Lymphocyte O-6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase levels were mainly in the range of 5 to 10 fmol/micrograms of DNA and showed no consistent variation during procarbazine exposure., Procarbazine causes weak inhibition of monoamine oxidase (MAO). MAO inhibitors prevent the inactivation of tyramine by hepatic and gastrointestinal monoamine oxidase. Tyramine in the bloodstream releases norepinephrine from the sympathetic nerve terminals and produces a sudden increase in blood pressure. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01168 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | PROCARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3250 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
671-16-9, 366-70-1 | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=671-16-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000671169 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01168 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Procarbazine hydrochloride | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=759626 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4021189 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.010.531 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | PROCARBAZINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/35S93Y190K | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | PROCARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3250 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015299 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
223 °C | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01168 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Procarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015299 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![[(11Z,13E)-6-[4-(dimethylamino)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-10-[5-(dimethylamino)-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-5-methoxy-9,16-dimethyl-2-oxo-7-(2-oxoethyl)-1-oxacyclohexadeca-11,13-dien-4-yl] propanoate](/img/structure/B1678178.png)