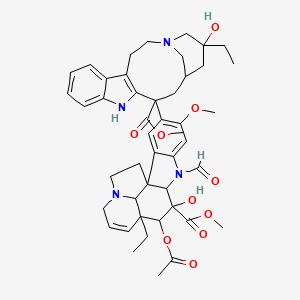
ビンクリスチン
概要
説明
Vincristine is a vinca alkaloid derived from the Madagascar periwinkle plant, Catharanthus roseus . It is a chemotherapy medication used to treat various types of cancer, including acute lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin’s disease, non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, neuroblastoma, and small cell lung cancer . Vincristine works by inhibiting cell division, making it a crucial component in cancer treatment regimens .
作用機序
Target of Action
Vincristine, a vinca alkaloid, primarily targets the protein tubulin, a key component of the microtubules in cells . Microtubules play a crucial role in maintaining cell structure and function, particularly during cell division .
Mode of Action
Vincristine binds to tubulin, inhibiting the polymerization of tubulin dimers and preventing the formation of microtubules . This interaction disrupts the formation of the mitotic spindle, a structure essential for chromosome separation during cell division . As a result, cells are arrested at metaphase, a stage in mitosis, leading to cell death .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by vincristine is the cell cycle, specifically the M and S phases . By disrupting microtubule dynamics, vincristine causes mitotic arrest, halting the cell cycle and leading to cell death . This disruption can also interfere with amino acid, cyclic AMP, and glutathione metabolism, as well as calmodulin-dependent Ca2±transport ATPase activity, and cellular respiration .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of vincristine involve its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Vincristine is administered intravenously, bypassing the absorption phase . It is metabolized primarily in the liver by the CYP3A5 enzyme . Vincristine’s neurotoxicity, a dose-limiting factor, is thought to be influenced by genetic variations in drug-metabolizing enzymes and transporters .
Result of Action
The molecular effect of vincristine’s action is the disruption of microtubule formation, leading to cell cycle arrest . On a cellular level, this results in the death of rapidly dividing cells, particularly cancer cells . This can also affect healthy cells, leading to side effects such as peripheral neuropathy .
Action Environment
Environmental factors can influence the action and efficacy of vincristine. For instance, the presence of other drugs used in combination therapies can impact vincristine’s effectiveness and toxicity profile . Additionally, genetic variations in patients can influence the drug’s metabolism and transport, potentially affecting its efficacy and toxicity .
科学的研究の応用
Vincristine has a wide range of scientific research applications, particularly in the fields of chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry . In chemistry, it is used as a model compound for studying the mechanisms of alkaloid biosynthesis and the development of new synthetic methodologies . In biology, vincristine is used to study cell division and the effects of microtubule inhibition on cellular processes . In medicine, it is a key component of chemotherapy regimens for various cancers, helping to inhibit the growth and spread of cancer cells . In industry, vincristine is used in the development of new drug formulations and delivery systems to improve its efficacy and reduce side effects .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Vincristine is a vinca alkaloid that binds to the microtubular proteins of the mitotic spindle . This interaction leads to the crystallization of the microtubule and mitotic arrest or cell death . Vincristine has some immunosuppressant effect . The vinca alkaloids are considered to be cell cycle phase-specific .
Cellular Effects
Vincristine works by stopping the cancer cells from separating into 2 new cells, thereby stopping the growth of the cancer . It achieves this through a process that disrupts the formation of microtubules, which affects cell division and eventually leads to apoptosis .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Vincristine involves its binding to the tubulin protein, stopping the tubulin dimers from polymerizing to form microtubules . This causes the cell to be unable to separate its chromosomes during the metaphase . The cell then undergoes apoptosis . The vincristine molecule inhibits leukocyte production and maturation .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that within 15 to 30 minutes after injection, over 90% of the drug is distributed from the blood into tissue, where it remains tightly, but not irreversibly, bound .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, vincristine has shown high efficiency (86.6%) for treatment of transmissible venereal tumor in canines at the dose of 0.5 mg/m^2 of body surface (IV), on 7-14 days intervals . One tumor (6.6%) was refractory to vincristine, while at the treatment beginning a mass reduction was observed .
Metabolic Pathways
Vincristine may interfere with amino acid, cyclic AMP, and glutathione metabolism . It may also interfere with calmodulin-dependent Ca^2+ -transport ATPase activity, cellular respiration, and nucleic acid and lipid biosynthesis .
Transport and Distribution
Vincristine is transported and distributed within cells and tissues primarily through the bloodstream . It is given intravenously and can be administered through a drip into the arm or hand . Over 90% of the drug is distributed from the blood into tissue within 15 to 30 minutes after injection .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of Vincristine is primarily at the mitotic spindle, where it binds to the microtubular proteins . This binding leads to the crystallization of the microtubule and mitotic arrest or cell death .
準備方法
Vincristine is primarily obtained from the natural alkaloid plant source, Catharanthus roseus . The extraction process involves isolating the compound from the plant material, followed by purification steps to obtain the active ingredient . Industrial production methods often involve the use of advanced extraction techniques and purification processes to ensure the compound’s efficacy and safety .
化学反応の分析
Vincristine undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution . Common reagents used in these reactions include oxidizing agents, reducing agents, and nucleophiles . The major products formed from these reactions depend on the specific conditions and reagents used . For example, oxidation of vincristine can lead to the formation of different oxidized derivatives, while reduction can yield reduced forms of the compound .
類似化合物との比較
These compounds share a similar mechanism of action, targeting microtubule formation and inhibiting cell division . vincristine is unique in its specific clinical applications and its relatively lower bone marrow suppression compared to other vinca alkaloids . Vinblastine, for example, is used to treat different types of cancer and has a different toxicity profile . Vindesine and vinflunine are also used in cancer treatment but have distinct pharmacokinetic properties and clinical uses .
特性
CAS番号 |
57-22-7 |
|---|---|
分子式 |
C46H56N4O10 |
分子量 |
825.0 g/mol |
IUPAC名 |
methyl (10S,11R,12R)-11-acetyloxy-12-ethyl-4-[(13S,15S,17S)-17-ethyl-17-hydroxy-13-methoxycarbonyl-1,11-diazatetracyclo[13.3.1.04,12.05,10]nonadeca-4(12),5,7,9-tetraen-13-yl]-8-formyl-10-hydroxy-5-methoxy-8,16-diazapentacyclo[10.6.1.01,9.02,7.016,19]nonadeca-2,4,6,13-tetraene-10-carboxylate |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C46H56N4O10/c1-7-42(55)22-28-23-45(40(53)58-5,36-30(14-18-48(24-28)25-42)29-12-9-10-13-33(29)47-36)32-20-31-34(21-35(32)57-4)50(26-51)38-44(31)16-19-49-17-11-15-43(8-2,37(44)49)39(60-27(3)52)46(38,56)41(54)59-6/h9-13,15,20-21,26,28,37-39,47,55-56H,7-8,14,16-19,22-25H2,1-6H3/t28-,37?,38?,39-,42+,43-,44?,45+,46+/m1/s1 |
InChIキー |
OGWKCGZFUXNPDA-DLBZMDDPSA-N |
不純物 |
3'-hydroxyvincristine; 4'-deoxyvincristine; N-desmethylvinblastine; deacetylvincristine; deacetylvinblastine; vinblastine; leurosine; formylleurosine |
SMILES |
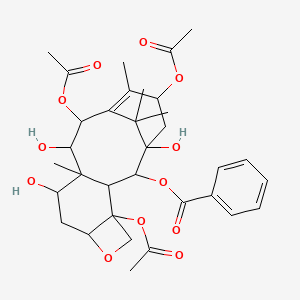
CCC1(CC2CC(C3=C(CCN(C2)C1)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)(C5=C(C=C6C(=C5)C78CCN9C7C(C=CC9)(C(C(C8N6C=O)(C(=O)OC)O)OC(=O)C)CC)OC)C(=O)OC)O |
異性体SMILES |
CC[C@@]1(C[C@@H]2C[C@@](C3=C(CCN(C2)C1)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)(C5=C(C=C6C(=C5)C78CCN9C7[C@@](C=CC9)([C@H]([C@@](C8N6C=O)(C(=O)OC)O)OC(=O)C)CC)OC)C(=O)OC)O |
正規SMILES |
CCC1(CC2CC(C3=C(CCN(C2)C1)C4=CC=CC=C4N3)(C5=C(C=C6C(=C5)C78CCN9C7C(C=CC9)(C(C(C8N6C=O)(C(=O)OC)O)OC(=O)C)CC)OC)C(=O)OC)O |
外観 |
White to off-white, odorless amorphous or crystalline powder |
Color/Form |
Blades from methanol |
melting_point |
424 to 428 °F (NTP, 1992) 218-220 °C |
| 57-22-7 | |
物理的記述 |
Vincristine appears as a white crystalline solid. Melting point 218 °C. Used as an antineoplastic. |
賞味期限 |
STERILE SOLN IN EITHER H2O OR PHYSIOLOGICAL SALINE STORED IN REFRIGERATOR FOR UP TO 2 WK WITHOUT SIGNIFICANT LOSS OF POTENCY |
溶解性 |
WHITE TO SLIGHTLY YELLOW, AMORPHOUS OR CRYSTALLINE POWDER; ODORLESS, HYGROSCOPIC; FREELY SOL IN WATER /VINCRISTINE SULFATE USP/ |
同義語 |
cellcristin Citomid Farmistin Leurocristine Oncovin Oncovine Onkocristin PFS, Vincasar Sulfate, Vincristine Vincasar Vincasar PFS Vincristin Bristol Vincristin medac Vincristine Vincristine Sulfate Vincrisul Vintec |
製品の起源 |
United States |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。


![3-[4-[2-[[6-amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5S)-5-(ethylcarbamoyl)-3,4-dihydroxyoxolan-2-yl]purin-2-yl]amino]ethyl]phenyl]propanoic acid;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B1662843.png)
![(E)-N-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-N-[[3-[(4-thiophen-3-ylthiophen-2-yl)methoxy]phenyl]methyl]hept-2-en-4-yn-1-amine;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B1662855.png)