インジナビル
概要
説明
インジナビルは、クリキシバンという商品名で知られており、HIV/エイズの治療に用いられる、高活性抗レトロウイルス療法の成分として使用されるプロテアーゼ阻害剤です 。白色の可溶性粉末で、他の抗ウイルス薬と組み合わせて経口投与されます。 インジナビルは、HIVウイルスのプロテアーゼ酵素を阻害するように合成的に生産され、ウイルスが複製することを阻止し、それにより患者のウイルス量を減少させます .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: インジナビルは、いくつかの中間体を形成する多段階プロセスによって合成されます反応条件は通常、有機溶媒、触媒、および制御された温度の使用を含み、目的の化学変換が効率的に行われるようにします .
工業的生産方法: インジナビルの工業的生産には、収率と純度を最大限に高めるための最適化された反応条件を用いた大規模合成が含まれます。このプロセスには、結晶化やクロマトグラフィーなどの厳密な精製手順が含まれ、最終製品を純粋な形で得ることができます。 生産は、一貫性と安全性を確保するために、厳格な品質管理基準の下で行われます .
科学的研究の応用
Indinavir has a wide range of scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: Indinavir is used as a model compound in studies of protease inhibitors and their interactions with enzymes.
Biology: It is used to study the mechanisms of viral replication and the role of proteases in viral life cycles.
Medicine: Indinavir is a critical component of antiretroviral therapy for HIV/AIDS, helping to manage the disease and improve patient outcomes.
作用機序
インジナビルは、HIVウイルスのプロテアーゼ酵素を阻害します。これは、ウイルスポリタンパク質前駆体を個々の機能性タンパク質にプロテオリシス分解するために不可欠です。インジナビルはプロテアーゼの活性部位に結合することにより、これらのポリタンパク質の分解を阻止し、未成熟で非感染性のウイルス粒子の形成につながります。 この阻害により、患者のウイルス量が減少し、HIV/エイズの進行が遅くなります .
類似化合物:
- リトナビル
- サキナビル
- ネルフィナビル
- ロピナビル
比較: インジナビルは、その特異的な結合親和性と阻害機構により、プロテアーゼ阻害剤の中でユニークです。リトナビルやサキナビルなどの他のプロテアーゼ阻害剤もHIVプロテアーゼ酵素を標的にしていますが、インジナビルの分子構造により、酵素の活性部位との独特の相互作用が可能になり、異なる薬物動態的および薬力学的プロファイルが得られます。 さらに、インジナビルの溶解性とバイオアベイラビリティは、その特異的な化学修飾によって強化されています .
インジナビルのユニークな特性は、副作用や一部の症例における耐性の発達にもかかわらず、HIV/エイズの治療における貴重なツールとなっています。 他のプロテアーゼ阻害剤との比較は、効果的な抗レトロウイルス療法を開発する際の構造的多様性の重要性を浮き彫りにしています .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Indinavir interacts with HIV-1 protease, an enzyme required for the proteolytic cleavage of the viral polyprotein precursors into the individual functional proteins found in infectious HIV-1 . The interaction between Indinavir and HIV-1 protease inhibits the activity of the enzyme .
Cellular Effects
Indinavir influences cell function by preventing the cleavage of the viral polyproteins, resulting in the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles . This impacts cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism.
Molecular Mechanism
Indinavir exerts its effects at the molecular level by binding to the protease active site, inhibiting the enzyme’s activity . This inhibition prevents the cleavage of the viral polyproteins, leading to the formation of immature non-infectious viral particles .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that Indinavir is a potent and specific HIV protease inhibitor .
Metabolic Pathways
Indinavir is metabolized in the body, with seven metabolites identified, one glucuronide conjugate and six oxidative metabolites . Cytochrome P-450 3A4 (CYP3A4) is the major enzyme responsible for the formation of these oxidative metabolites .
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Indinavir is synthesized through a multi-step process involving the formation of several intermediatesThe reaction conditions typically involve the use of organic solvents, catalysts, and controlled temperatures to ensure the desired chemical transformations occur efficiently .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of indinavir involves large-scale synthesis using optimized reaction conditions to maximize yield and purity. The process includes rigorous purification steps such as crystallization and chromatography to obtain the final product in its pure form. The production is carried out under strict quality control measures to ensure consistency and safety .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: インジナビルは、以下を含むさまざまな化学反応を起こします。
酸化: インジナビルは特定の条件下で酸化され、酸化誘導体の形成につながります。
還元: 還元反応は、インジナビル内の官能基を修飾し、その活性を変化させる可能性があります。
一般的な試薬と条件:
酸化: 一般的な酸化剤には、過酸化水素と過マンガン酸カリウムが含まれます。
還元: 水素化ホウ素ナトリウムと水素化リチウムアルミニウムなどの還元剤が使用されます。
生成される主な生成物: これらの反応から生成される主な生成物は、使用される特定の試薬と条件によって異なります。 たとえば、酸化はヒドロキシル化またはケトン誘導体の形成につながる可能性があり、一方、還元はアルコールまたはアミンの生成につながる可能性があります .
4. 科学研究への応用
インジナビルは、以下を含む幅広い科学研究の応用を持っています。
化学: インジナビルは、プロテアーゼ阻害剤とその酵素との相互作用の研究におけるモデル化合物として使用されます。
生物学: ウイルス複製メカニズムと、ウイルス生活環におけるプロテアーゼの役割を研究するために使用されます。
医学: インジナビルは、HIV/エイズの抗レトロウイルス療法の重要な成分であり、病気の管理と患者の転帰の改善に役立っています。
類似化合物との比較
- Ritonavir
- Saquinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Lopinavir
Comparison: Indinavir is unique among protease inhibitors due to its specific binding affinity and inhibition mechanism. While other protease inhibitors like ritonavir and saquinavir also target the HIV protease enzyme, indinavir’s molecular structure allows for distinct interactions with the enzyme’s active site, leading to different pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles. Additionally, indinavir’s solubility and bioavailability are enhanced by its specific chemical modifications .
Indinavir’s unique properties make it a valuable tool in the treatment of HIV/AIDS, despite its side effects and the development of resistance in some cases. Its comparison with other protease inhibitors highlights the importance of structural diversity in developing effective antiretroviral therapies .
特性
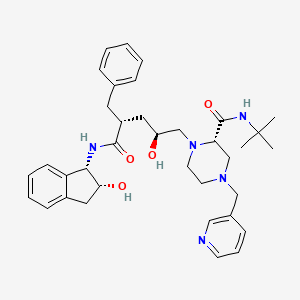
IUPAC Name |
(2S)-1-[(2S,4R)-4-benzyl-2-hydroxy-5-[[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-2,3-dihydro-1H-inden-1-yl]amino]-5-oxopentyl]-N-tert-butyl-4-(pyridin-3-ylmethyl)piperazine-2-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C36H47N5O4/c1-36(2,3)39-35(45)31-24-40(22-26-12-9-15-37-21-26)16-17-41(31)23-29(42)19-28(18-25-10-5-4-6-11-25)34(44)38-33-30-14-8-7-13-27(30)20-32(33)43/h4-15,21,28-29,31-33,42-43H,16-20,22-24H2,1-3H3,(H,38,44)(H,39,45)/t28-,29+,31+,32-,33+/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CBVCZFGXHXORBI-PXQQMZJSSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)C1CN(CCN1CC(CC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)NC3C(CC4=CC=CC=C34)O)O)CC5=CN=CC=C5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)[C@@H]1CN(CCN1C[C@H](C[C@@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)N[C@@H]3[C@@H](CC4=CC=CC=C34)O)O)CC5=CN=CC=C5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C36H47N5O4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
157810-81-6 (sulfate (1:1) (salt)) | |
| Record name | Indinavir [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0150378179 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4043802 | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4043802 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
613.8 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
4.82e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Indinavir inhibits the HIV viral protease enzyme which prevents cleavage of the gag-pol polyprotein, resulting in noninfectious, immature viral particles. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
150378-17-9 | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=150378-17-9 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Indinavir [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0150378179 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4043802 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | INDINAVIR ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/9MG78X43ZT | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
167.5-168 °C, 167.5 - 168 °C | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00224 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Indinavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014369 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。


![manganese(2+);(4R,9R,14R,19R)-3,10,13,20,26-pentazatetracyclo[20.3.1.04,9.014,19]hexacosa-1(26),22,24-triene;dichloride](/img/structure/B1671796.png)