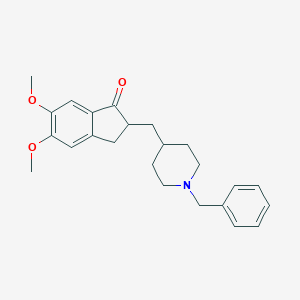
Donepezil
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Donepezil is a medication primarily used to treat dementia associated with Alzheimer’s disease. It is a centrally acting reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, which means it works by inhibiting the enzyme acetylcholinesterase, thereby increasing the concentration of acetylcholine in the brain. This increase in acetylcholine helps improve cognitive function and memory in patients with Alzheimer’s disease .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: The synthesis of donepezil typically involves the aldol condensation of benzylpiperidine-carboxyaldehyde with dimethoxyindanone, utilizing the Wittig reaction. This is followed by a subsequent dehydration step and catalytic reduction of the exocyclic double bond, yielding the desired product .
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of this compound involves similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process is optimized for efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability. Eco-friendly strategies are also being explored to reduce the environmental impact of the production process .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Donepezil durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: this compound kann mit milden Oxidationsmitteln wie Chloramin-T in saurem Medium oxidiert werden.
Hauptprodukte: Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, umfassen verschiedene this compound-Analoga und -Derivate, die auf ihre potenziellen therapeutischen Vorteile untersucht werden .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Donepezil hat eine breite Palette von Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Medizin: this compound wird umfassend zur Behandlung der Alzheimer-Krankheit und anderer Formen von Demenz eingesetzt.
Industrie: Die pharmazeutische Industrie nutzt this compound bei der Entwicklung neuer Medikamente und Therapeutika.
5. Wirkmechanismus
This compound hemmt selektiv und reversibel das Enzym Acetylcholinesterase, das normalerweise Acetylcholin abbaut. Durch die Hemmung dieses Enzyms erhöht this compound die Konzentration von Acetylcholin im Gehirn und verstärkt die cholinerge Transmission. Dies trägt dazu bei, die Symptome der Alzheimer-Demenz zu lindern, indem die kognitive Funktion und das Gedächtnis verbessert werden .
Ähnliche Verbindungen:
Rivastigmin: Ein weiterer Acetylcholinesterase-Hemmer zur Behandlung von Demenz. Im Gegensatz zu this compound hemmt es auch Butyrylcholinesterase.
Galantamin: Ein Acetylcholinesterase-Hemmer, der auch nikotinerge Rezeptoren moduliert.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound: this compound ist einzigartig in seiner selektiven und reversiblen Hemmung der Acetylcholinesterase, was es hochwirksam macht, um die Acetylcholinspiegel im Gehirn zu erhöhen. Seine lange Halbwertszeit und seine Fähigkeit, die Blut-Hirn-Schranke zu passieren, tragen zu seiner Wirksamkeit bei der Bewältigung der Symptome der Alzheimer-Krankheit bei .
Wirkmechanismus
Donepezil selectively and reversibly inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which normally breaks down acetylcholine. By inhibiting this enzyme, this compound increases the concentration of acetylcholine in the brain, enhancing cholinergic transmission. This helps alleviate the symptoms of Alzheimer’s dementia by improving cognitive function and memory .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Rivastigmine: Another acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used to treat dementia. Unlike donepezil, it also inhibits butyrylcholinesterase.
Galantamine: An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that also modulates nicotinic receptors.
Uniqueness of this compound: this compound is unique in its selective and reversible inhibition of acetylcholinesterase, which makes it highly effective in increasing acetylcholine levels in the brain. Its long half-life and ability to cross the blood-brain barrier contribute to its effectiveness in managing Alzheimer’s disease symptoms .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
2-[(1-benzylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl]-5,6-dimethoxy-2,3-dihydroinden-1-one | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C24H29NO3/c1-27-22-14-19-13-20(24(26)21(19)15-23(22)28-2)12-17-8-10-25(11-9-17)16-18-6-4-3-5-7-18/h3-7,14-15,17,20H,8-13,16H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ADEBPBSSDYVVLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
COC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)CC(C2=O)CC3CCN(CC3)CC4=CC=CC=C4)OC | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C24H29NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
120011-70-3 | |
| Record name | Donepezil [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0120014064 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID8048317 | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8048317 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
379.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0005041 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
31mg/mL | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00843 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
The commonly accepted cholinergic hypothesis proposes that a portion of the cognitive and behavioral decline associated with Alzheimer's are the result of decreased cholinergic transmission in the central nervous system. Donepezil selectively and reversibly inhibits the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which normally breaks down acetylcholine. The main pharmacological actions of this drug are believed to occur as the result of this enzyme inhibition, enhancing cholinergic transmission, which relieves the symptoms of Alzheimer's dementia. In addition to the above, other mechanisms of action of donepezil are possible, including the opposition of glutamate-induced excitatory transmission via downregulation of NMDA receptors and the regulation of amyloid proteins, which have demonstrated significant effects on the disease process of Alzheimer's. Other possible targets for donepezil may also include the inhibition various inflammatory signaling pathways, exerting neuroprotective effects., Donepezil hydrochloride, a piperidine derivative, is a centrally active, reversible inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase. The drug is structurally unrelated to other anticholinesterase agents (eg, tacrine, physostigmine)., The precise mechanism(s) of action of donepezil in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer's type (Alzheimer's disease) has not been fully elucidated. The drug is an anticholinesterase agent that binds reversibly with and inactivates cholinesterases (eg, acetylcholinesterase), thus inhibiting hydrolysis of acetylcholine. As a result, the concentration of acetylcholine increases at cholinergic synapses. In vitro data and data in animals indicate that the anticholinesterase activity of donepezil is relatively specific for acetylcholinesterase in the brain compared with butyrylcholinesterase inhibition in peripheral tissues., A deficiency of acetylcholine caused by selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the cerebral cortex, nucleus basalis, and hippocampus is recognized as one of the early pathophysiologic features of Alzheimer's disease associated with memory loss and cognitive deficits. Because the resultant cortical deficiency of this neurotransmitter is believed to account for some of the clinical manifestations of mild to moderate dementia, enhancement of cholinergic function with an anticholinesterase agent, such as tacrine or donepezil, is one of the pharmacologic approaches to treatment. Because widespread degeneration of multiple central neuronal systems eventually occurs in patients with Alzheimer's disease, potentially beneficial effects of anticholinesterase agents theoretically would diminish as the disease process advances and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functioning., Current theories on the pathogenesis of the cognitive signs and symptoms of Alzheimer's Disease attribute some of them to a deficiency of cholinergic neurotransmission. Donepezil hydrochloride is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by acetylcholinesterase. There is no evidence that donepezil alters the course of the underlying dementing process., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for Donepezil (6 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00843 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7743 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
120014-06-4 | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=120014-06-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Donepezil [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0120014064 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00843 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID8048317 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | DONEPEZIL | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/8SSC91326P | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7743 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0005041 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
223-227 | |
| Record name | Donepezil | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00843 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details




Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods V
Procedure details









Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![[4-(1H-pyrazol-1-yl)phenyl]acetonitrile](/img/structure/B133141.png)
![2-[(1S)-2-[(2-methylpropan-2-yl)oxy]-2-oxo-1-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)ethyl]pent-4-enoic acid](/img/structure/B133171.png)