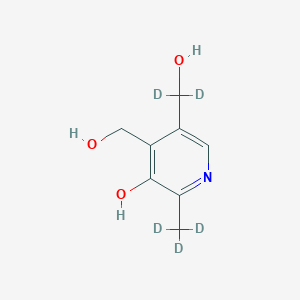
Pyridoxin-d5
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Pyridoxine-d5, also known as Pyridoxol-d5, is a deuterated form of Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6). It is a pyridine derivative and is chemically similar to natural Pyridoxine. The compound is labeled with deuterium, which is a stable isotope of hydrogen. Pyridoxine-d5 is primarily used in scientific research as a tracer in metabolic studies and for the investigation of biochemical pathways involving Vitamin B6.
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Pyridoxine-d5 is widely used in scientific research due to its stable isotopic labeling. Some of its applications include:
Chemistry: Used as a tracer in metabolic studies to investigate the biochemical pathways of Vitamin B6.
Biology: Helps in studying the role of Vitamin B6 in cellular processes and enzyme functions.
Medicine: Used in pharmacokinetic studies to understand the metabolism and distribution of Vitamin B6 in the body.
Industry: Employed in the development of new drugs and therapeutic agents involving Vitamin B6.
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Pyridoxine-d5, also known as Pyridoxol-d5, is a deuterium-labeled form of Pyridoxine . Pyridoxine, also known as Vitamin B6, is an essential nutrient required for normal functioning of many biological systems within the body . It is converted to pyridoxal 5-phosphate in the body, which is an important coenzyme for the synthesis of amino acids, neurotransmitters (serotonin, norepinephrine), sphingolipids, and aminolevulinic acid . Therefore, the primary targets of Pyridoxine-d5 are these biological systems that require Vitamin B6 for their normal functioning.
Mode of Action
Pyridoxine-d5 interacts with its targets by being converted into pyridoxal 5’-phosphate, which then acts as a coenzyme in various biochemical reactions . For instance, it plays a crucial role in the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats . It also aids in the release of liver and muscle-stored glycogen and in the synthesis of GABA (within the central nervous system) and heme .
Biochemical Pathways
Pyridoxine-d5 affects several biochemical pathways. It is involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions, including the metabolism of amino acids and glycogen, the synthesis of nucleic acids, hemoglobin, sphingomyelin and other sphingolipids, and the synthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) .
Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of Pyridoxine-d5 involves its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME). Pyridoxine’s peak absorption is observed after 1.3 hours, and its half-life is very short (0.75 hours), which may be responsible for a large intra-subject variability . Pyridoxine is considered a highly soluble and highly permeable drug substance .
Result of Action
The result of Pyridoxine-d5’s action is the facilitation of numerous biochemical reactions in the body. By acting as a coenzyme, it aids in the synthesis of essential biomolecules and helps maintain normal physiological functions . For instance, it plays a role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, which are crucial for normal brain function .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Pyridoxine-d5, like its non-deuterated form, is involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions. It interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. The active endogenous metabolites of these molecules, pyridoxal phosphate and pyridoxamine phosphate, are the most important coenzymes involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions necessary for cell activity .
Cellular Effects
Pyridoxine-d5 has been shown to exert antioxidant effects in a cell model of Alzheimer’s disease via the Nrf-2/HO-1 pathway . In pancreatic acinar cells, pyridoxine availability can affect the gene expression profile .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Pyridoxine-d5 involves its conversion to the active form, Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP), which is involved in many biochemical reactions, including the metabolism of amino acids and glycogen, the synthesis of nucleic acids, hemoglobin, sphingomyelin and other sphingolipids, and the synthesis of the neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
It is known that pyridoxine, the non-deuterated form, has a significant impact on post-prandial glucose levels when administered over a period of time .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, Pyridoxine-d5 has been shown to have a significant reduction to the postprandial glucose levels, when compared to the control. The maximum blood glucose levels of Pyridoxine-d5 administration group were decreased by about 18% and 19% in sucrose and starch loading tests, respectively .
Metabolic Pathways
Pyridoxine-d5 is involved in the Vitamin B6 metabolic pathway. This pathway involves the conversion of Pyridoxine-d5 to its active form, Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP), which is involved in a wide range of biochemical reactions .
Transport and Distribution
Pancreatic acinar cells obtain Pyridoxine-d5 from circulation, but little is known about the mechanism involved in the uptake process . After absorption, Pyridoxine-d5 is transported to the blood and other organs .
Subcellular Localization
It is known that the active form of Pyridoxine-d5, Pyridoxal 5’-phosphate (PLP), is involved in many biochemical reactions in various compartments of the cell .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of Pyridoxine-d5 involves the incorporation of deuterium into the Pyridoxine molecule. One common method is the catalytic hydrogenation of Pyridoxine in the presence of deuterium gas. This process replaces the hydrogen atoms in the molecule with deuterium atoms. The reaction typically occurs under mild conditions, using a palladium or platinum catalyst.
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of Pyridoxine-d5 follows similar synthetic routes but on a larger scale. The process involves the use of high-pressure reactors and specialized equipment to handle deuterium gas. The final product is purified through crystallization or chromatography to achieve the desired purity and isotopic labeling.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Types of Reactions
Pyridoxine-d5 undergoes various chemical reactions similar to those of natural Pyridoxine. These include:
Oxidation: Pyridoxine-d5 can be oxidized to Pyridoxal-d5, a form of Vitamin B6.
Reduction: Pyridoxal-d5 can be reduced back to Pyridoxine-d5.
Substitution: The hydroxyl group in Pyridoxine-d5 can be substituted with other functional groups.
Common Reagents and Conditions
Oxidation: Common oxidizing agents include potassium permanganate and hydrogen peroxide.
Reduction: Reducing agents such as sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride are used.
Substitution: Various reagents like alkyl halides or acyl chlorides can be used for substitution reactions.
Major Products Formed
Oxidation: Pyridoxal-d5
Reduction: Pyridoxine-d5
Substitution: Various substituted Pyridoxine-d5 derivatives
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Pyridoxine-d5 is compared with other deuterated and non-deuterated forms of Vitamin B6, such as:
Pyridoxine: The natural form of Vitamin B6.
Pyridoxal: An oxidized form of Vitamin B6.
Pyridoxamine: Another form of Vitamin B6 involved in amino acid metabolism.
Uniqueness
The uniqueness of Pyridoxine-d5 lies in its deuterium labeling, which makes it an ideal tracer for metabolic studies. The presence of deuterium allows for precise tracking and analysis of biochemical pathways without altering the compound’s biological activity.
Conclusion
Pyridoxine-d5 is a valuable compound in scientific research, offering insights into the metabolic pathways and biochemical roles of Vitamin B6. Its stable isotopic labeling and similarity to natural Pyridoxine make it an essential tool in various fields, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry.
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
5-[dideuterio(hydroxy)methyl]-4-(hydroxymethyl)-2-(trideuteriomethyl)pyridin-3-ol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C8H11NO3/c1-5-8(12)7(4-11)6(3-10)2-9-5/h2,10-12H,3-4H2,1H3/i1D3,3D2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
LXNHXLLTXMVWPM-WNWXXORZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1=NC=C(C(=C1O)CO)CO | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
[2H]C([2H])([2H])C1=NC=C(C(=C1O)CO)C([2H])([2H])O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C8H11NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID10574085 | |
| Record name | 4-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-[hydroxy(~2~H_2_)methyl]-2-(~2~H_3_)methylpyridin-3-ol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID10574085 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
174.21 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
688302-31-0 | |
| Record name | 4-(Hydroxymethyl)-5-[hydroxy(~2~H_2_)methyl]-2-(~2~H_3_)methylpyridin-3-ol | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID10574085 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details











Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.

![Pentanoic acid, 5-[(6-amino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1,3-dimethyl-2,4-dioxo-5-pyrimidinyl)amino]-5-oxo-](/img/structure/B25794.png)