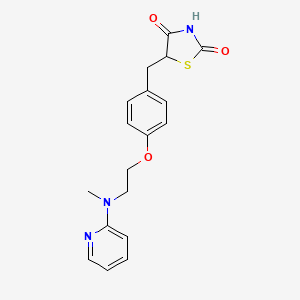
Rosiglitazon
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Rosiglitazon ist eine synthetische Verbindung, die zur Klasse der Thiazolidindione-Medikamente gehört. Es wird hauptsächlich als Antidiabetikum eingesetzt, um die Blutzuckerkontrolle bei Patienten mit Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus zu verbessern. This compound wirkt als Insulin-Sensibilisator, indem es an Peroxisom-Proliferator-aktivierte Rezeptoren in Fettzellen bindet und die Empfindlichkeit der Zellen gegenüber Insulin erhöht .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Rosiglitazone primarily targets the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) , specifically PPARγ . PPARs are a group of nuclear receptor proteins that function as transcription factors regulating the expression of genes. PPARγ is involved in the regulation of fatty acid storage and glucose metabolism .
Mode of Action
Rosiglitazone acts as a selective ligand of PPARγ, meaning it binds to this receptor and activates it . This activation regulates the transcription of certain genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and anti-inflammatory response .
Biochemical Pathways
Rosiglitazone’s activation of PPARγ impacts several biochemical pathways. It’s involved in metabolic pathways, carbon metabolism, and the citrate cycle . By influencing these pathways, Rosiglitazone can help regulate glucose levels and lipid metabolism, which are crucial for managing conditions like type 2 diabetes .
Result of Action
Rosiglitazone’s action leads to several molecular and cellular effects. It improves insulin sensitivity, which helps lower blood glucose levels . It also appears to have an anti-inflammatory effect, as evidenced by the decrease in nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) levels and increase in inhibitor (IκB) levels in patients on Rosiglitazone . Furthermore, it has been found to promote adipocyte browning, which could have implications for obesity treatment .
Action Environment
The efficacy and stability of Rosiglitazone can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, the drug is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to maintain glycemic control in type 2 diabetes, suggesting that lifestyle factors can impact its effectiveness . .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Rosiglitazone has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound in studies of thiazolidinedione synthesis and reaction mechanisms.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Medicine: Primarily used to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus by improving insulin sensitivity.
Industry: Utilized in the pharmaceutical industry for the production of antidiabetic medications.
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Rosiglitazone works by activating the intracellular receptor class of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPARγ . It is a selective ligand of PPARγ, and has no PPARα-binding action . Apart from its effect on insulin resistance, it appears to have an anti-inflammatory effect .
Cellular Effects
Rosiglitazone has been shown to suppress the growth of human glioma cell lines U87 and U251 . It also induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis . In addition, rosiglitazone has been found to exhibit anti-inflammatory properties and can target cardiomyocytes secreting CXCL10, under interferon (IFN)γ and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)α challenge .
Molecular Mechanism
The mechanism of action of rosiglitazone is by activation of the intracellular receptor class of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPARγ . Rosiglitazone is a selective ligand of PPARγ, and has no PPARα-binding action . Apart from its effect on insulin resistance, it appears to have an anti-inflammatory effect: nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) levels fall and inhibitor (IκB) levels increase in patients on rosiglitazone .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Rosiglitazone has been shown to have a significant effect on the reduction of glucose and HbA1c treatment effects in rats . This effect was observed over a period of 6 weeks of treatment with rosiglitazone .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, rosiglitazone has been shown to be the most effective treatment in thiazolidinediones (TZDs) not only for its hypoglycemic effect but also for its additional effects such as anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer capabilities, retinopathy, and ischemia–reperfusion injury protection effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Rosiglitazone is extensively metabolized in the liver to inactive metabolites via N-demethylation, hydroxylation, and conjugation with sulfate and glucuronic acid . In vitro data have shown that Cytochrome (CYP) P450 isoenzyme 2C8 (CYP2C8) and to a minor extent CYP2C9 are involved in the hepatic metabolism of rosiglitazone .
Transport and Distribution
Rosiglitazone is primarily distributed in the liver, where it is extensively metabolized . It is also distributed in fat cells, where it works as an insulin sensitizer, by binding to the PPAR in fat cells and making the cells more responsive to insulin .
Subcellular Localization
Rosiglitazone acts at the level of the nucleus, where it binds to the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), specifically PPARγ . This binding activates the PPARγ, leading to the transcription of insulin-responsive genes involved in the control of glucose production, transport, and utilization .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von Rosiglitazon umfasst mehrere wichtige Schritte:
Reaktion von 2-Chlorpyridin mit 2-Methylaminoethanol: Diese Reaktion wird durch Trityl-Natrium katalysiert, um 2-[N-Methyl-N-(2-Pyridin)amino]ethanol zu erzeugen.
Williamson-Synthesereaktion: Das N-substituierte Benzaldehyd und 4-Fluorbenzaldehyd unterliegen einer Williamson-Synthesereaktion, die durch Bis(trimethylsilyl)amino-Kalium katalysiert wird, um 4-[2-[N-Methyl-N-(2-Pyridin)amino]ethoxy]benzaldehyd zu bilden.
Kondensationsreaktion: Die resultierende Verbindung wird dann mit Thiazolin-2,4-diketon kondensiert, um 5-{4-[2-[N-Methyl-N-(2-Pyridin)amino]ethoxy]benzyliden}thiazolin-2,4-diketon zu ergeben.
Reduktionsreaktion: Schließlich wird die Verbindung einer Reduktionsreaktion unterzogen, die durch ein organisches Mangan-Reagenz katalysiert wird, um this compound zu erzeugen.
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Für die industrielle Produktion wird die Synthese von this compound auf Skalierbarkeit und Effizienz optimiert. Der Prozess umfasst einen fünfschrittigen Syntheseweg mit kommerziell erhältlichen Ausgangsmaterialien, darunter 2-Chlorpyridin, N-Methylethanolamin, 4-Fluorbenzaldehyd und 1,3-Thiazolidin-2,4-dion. Die Schritte umfassen Cyclisierung, Alkylierung, Etherifizierung, Kondensation und Reduktion, mit einer Gesamtausbeute von etwa 40% .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Rosiglitazon durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter:
Kondensation: Die Kondensationsreaktion mit Thiazolin-2,4-diketon ist ein entscheidender Schritt in seiner Synthese.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Natriumborhydrid: Wird im Reduktionsschritt verwendet.
Kobaltchlorid-Hexahydrat und Dimethylglyoxim: Katalysatoren für die Reduktionsreaktion.
Trityl-Natrium: Katalysator für die Reaktion von 2-Chlorpyridin mit 2-Methylaminoethanol.
Bis(trimethylsilyl)amino-Kalium: Katalysator für die Williamson-Synthesereaktion.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Das Hauptprodukt, das aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet wird, ist this compound selbst, mit Zwischenprodukten wie 2-[N-Methyl-N-(2-Pyridin)amino]ethanol und 4-[2-[N-Methyl-N-(2-Pyridin)amino]ethoxy]benzaldehyd .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound hat eine breite Palette von wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen:
Chemie: Wird als Modellverbindung in Studien zur Synthese von Thiazolidindionen und Reaktionsmechanismen verwendet.
Biologie: Untersucht auf seine Auswirkungen auf die Insulinsensitivität und den Glukosestoffwechsel.
Medizin: Wird hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt, indem die Insulinsensitivität verbessert wird.
Industrie: Wird in der pharmazeutischen Industrie zur Herstellung von Antidiabetika eingesetzt.
Wirkmechanismus
This compound übt seine Wirkungen aus, indem es die Klasse der intrazellulären Rezeptoren von Peroxisom-Proliferator-aktivierten Rezeptoren aktiviert, insbesondere PPAR-gamma. Diese Aktivierung beeinflusst die Produktion von Genprodukten, die am Glukose- und Lipidstoffwechsel beteiligt sind. This compound ist ein selektiver Ligand von PPAR-gamma und bindet nicht an PPAR-alpha. Neben seiner Wirkung auf die Insulinresistenz scheint es auch entzündungshemmende Wirkungen zu haben, indem es die Nuclear Factor Kappa-B-Spiegel moduliert .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Pioglitazon: Ein weiteres Thiazolidindion zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus.
Troglitazon: Ein Thiazolidindion, das aufgrund von Hepatotoxizitätsbedenken vom Markt genommen wurde.
Einzigartigkeit von Rosiglitazon
This compound ist einzigartig in seiner spezifischen Bindung an PPAR-gamma, ohne PPAR-alpha zu beeinflussen. Im Vergleich zu Pioglitazon wurde this compound mit einem höheren Risiko für Myokardinfarkt und kongestive Herzinsuffizienz in Verbindung gebracht, was zu Sicherheitsbedenken führte . Es bleibt ein effektiver Insulin-Sensibilisator und wurde für zusätzliche therapeutische Anwendungen über die Diabetesbehandlung hinaus untersucht .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
5-[[4-[2-[methyl(pyridin-2-yl)amino]ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-1,3-thiazolidine-2,4-dione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C18H19N3O3S/c1-21(16-4-2-3-9-19-16)10-11-24-14-7-5-13(6-8-14)12-15-17(22)20-18(23)25-15/h2-9,15H,10-12H2,1H3,(H,20,22,23) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
YASAKCUCGLMORW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(CCOC1=CC=C(C=C1)CC2C(=O)NC(=O)S2)C3=CC=CC=N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C18H19N3O3S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7037131 | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7037131 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
357.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0005031 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Rosiglitazone acts as a highly selective and potent agonist at peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPAR) in target tissues for insulin action such as adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and liver. Activation of PPAR-gamma receptors regulates the transcription of insulin-responsive genes involved in the control of glucose production, transport, and utilization. In this way, rosiglitazone enhances tissue sensitivity to insulin., Because osteoblasts and marrow adipocytes are derived from a common mesenchymal progenitor, increased adipogenesis may occur at the expense of osteoblasts, leading to bone loss. Our previous in vitro studies indicated that activation of the proadipogenic transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor isoform gamma 2 with rosiglitazone suppressed osteoblast differentiation. Here, we show that 5-month-old Swiss-Webster mice receiving rosiglitazone for 28 day exhibited bone loss associated with an increase in marrow adipocytes, a decrease in the ratio of osteoblasts to osteoclasts, a reduction in bone formation rate, and a reduction in wall width--an index of the amount of bone formed by each team of osteoblasts. Rosiglitazone had no effect on the number of early osteoblast or osteoclast progenitors, or on osteoblast life span, but decreased the expression of the key osteoblastogenic transcription factors Runx2 and Osterix in cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitors. These effects were associated with diversion of bipotential progenitors from the osteoblast to the adipocyte lineage, and suppression of the differentiation of monopotential osteoblast progenitors. However, rosiglitazone had no effect on osteoblastic cells at later stages of differentiation. Hence, rosiglitazone attenuates osteoblast differentiation and thereby reduces bone formation rate in vivo, leading to bone loss. These findings provide a mechanistic explanation for the recent evidence that peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor isoform gamma activation is a negative regulator of bone mass and suggest that the increased production of oxidized fatty acids with age may indeed be an important mechanism for age-related osteoporosis in humans., Brain peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma), a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily of ligand-dependent transcription factors, is involved in neuroprotection. It is activated by the drug rosiglitazone, which then can increase the pro-survival protein B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2), to mediate neuroprotection. However, the mechanism underlying this molecular cascade remains unknown. Here, we show that the neuroprotective protein neurotrophic factor-a1 (NF-a1), which also induces the expression of BCL-2, has a promoter that contains PPARgamma-binding sites that are activated by rosiglitazone. Treatment of Neuro2a cells and primary hippocampal neurons with rosiglitazone increased endogenous NF-a1 expression and prevented H2 O2 -induced cytotoxicity. Concomitant with the increase in NF-a1, BCL-2 was also increased in these cells. When siRNA against NF-a1 was used, the induction of BCL-2 by rosiglitazone was prevented, and the neuroprotective effect of rosiglitazone was reduced. These results demonstrate that rosiglitazone-activated PPARgamma directly induces the transcription of NF-a1, contributing to neuroprotection in neurons. We proposed the following cascade for neuroprotection against oxidative stress by rosiglitazone: Rosiglitazone enters the neuron and binds to peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) in the nucleus. The PPARgamma-rosiglitazone complex binds to the neurotrophic factor-a1 (NF-a1) promoter and activates the transcription of NF-a1 mRNA which is then translated to the protein. NF-a1 is the secreted, binds to a cognate receptor and activates the extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK) pathway. This in turn enhances the expression of the pro-survival protein, B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) and inhibition of caspase 3 (Csp-3) to mediate neuroprotection under oxidative stress. Akt, protein kinase B (PKB)., Rosiglitazone, a member of the thiazolidinedione class of antidiabetic agents, improves glycemic control by improving insulin sensitivity. Rosiglitazone is a highly selective and potent agonist for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). In humans, PPAR receptors are found in key target tissues for insulin action such as adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and liver. Activation of PPARgamma nuclear receptors regulates the transcription of insulin-responsive genes involved in the control of glucose production, transport, and utilization. In addition, PPARgamma- responsive genes also participate in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism, Rosiglitazone acts principally by increasing insulin sensitivity in target tissues, as well as decreasing hepatic gluconeogenesis. Rosiglitazone is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma (PPARgamma) agonist that increases transcription of insulin-responsive genes and increases insulin sensitivity. Rosiglitazone, like other thiazolidinediones, ameliorates insulin resistance associated with type diabetes mellitus without stimulating insulin release from pancreatic beta cells, thus avoiding the risk of hypoglycemia. Because rosiglitazone does not lower glucose concentrations below euglycemia, the drug is appropriately referred to as an antidiabetic agent rather than a hypoglycemic agent. Some evidence suggests that the glucoregulatory effects of thiazolidinediones are mediated in part via reduced systemic and tissue lipid availability. Circulating concentrations of insulin and C-peptide are reduced during rosiglitazone therapy. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00412 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7555 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Colorless crystals from methanol | |
CAS No. |
122320-73-4 | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=122320-73-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0122320734 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00412 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | rosiglitazone | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=758698 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7037131 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 5-(4-(2-(N-METHYL-N-(2-PYRIDYL)AMINO)ETHOXY)BENZYL)THIAZOLIDINE-2,4 -DIONE | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | ROSIGLITAZONE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/05V02F2KDG | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7555 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0005031 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
122-123 °C, 153-155 °C | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00412 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Rosiglitazone | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7555 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![(2E,4E)-5-(3-methoxyphenyl)-N-[(2R)-5-pyridin-3-ylpentan-2-yl]nona-2,4-dienamide](/img/structure/B1679469.png)
![[[1-[N-Hydroxy-acetamidyl]-3-methyl-butyl]-carbonyl-leucinyl]-alanine ethyl ester](/img/structure/B1679480.png)
