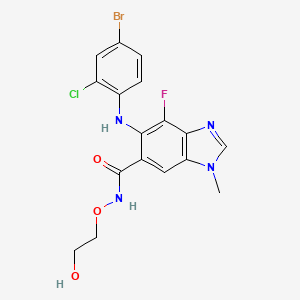
Selumetinib
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Selumetinib, unter dem Markennamen Koselugo vertrieben, ist ein Medikament, das hauptsächlich zur Behandlung der Neurofibromatose Typ 1 (NF-1) bei Kindern ab zwei Jahren eingesetzt wird. NF-1 ist eine genetische Erkrankung des Nervensystems, die das Wachstum von Tumoren an Nerven verursacht . This compound ist ein selektiver Inhibitor der Mitogen-aktivierten Proteinkinase 1 und 2 (MEK1/2), die Schlüsselkomponenten des Raf-MEK-ERK-Signalwegs sind .
Herstellungsmethoden
This compound wird durch einen mehrstufigen chemischen Prozess synthetisiertDer letzte Schritt beinhaltet die Bildung der Carboxamidgruppe . Industrielle Produktionsmethoden beinhalten in der Regel die Optimierung der Reaktionsbedingungen, um die Ausbeute und Reinheit zu maximieren und gleichzeitig die Bildung von Verunreinigungen zu minimieren.
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Selumetinib hat eine Vielzahl von Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, darunter:
Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine Wirkung, indem es selektiv MEK1 und MEK2 inhibiert, die Schlüsselkomponenten des Raf-MEK-ERK-Signalwegs sind . Durch die Hemmung dieser Proteine blockiert this compound die nachgeschaltete Signalübertragung, die die Zellproliferation und das Überleben fördert. Diese Hemmung führt zur Arretierung des Zellzyklus in der G1-S-Phase und induziert Apoptose in Krebszellen .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Selumetinib, also known as AZD6244 or ARRY-142886, is a highly specific inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase 1/2 (MEK1/2) . MEK1/2 are key components of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in the survival, propagation, and drug resistance of human cancers .
Mode of Action
This compound works by selectively binding to MEK1/2 proteins, thereby inhibiting their activity . This inhibition prevents the phosphorylation and activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERK1/2), which are the sole targets of MEK . By blocking this critical step, this compound effectively arrests the MAPK-ERK signaling pathway .
Biochemical Pathways
The MAPK-ERK pathway is often overactive in various types of cancers, leading to uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation . By inhibiting MEK1/2, this compound disrupts this pathway, leading to a decrease in cellular growth, cell cycle arrest in the G1-S phase, and induction of apoptosis .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound and its active metabolite, N-desmethyl this compound, have been well characterized in both adults and children . Both compounds exhibit rapid absorption and mean terminal elimination half-lives of about 7.5 hours, with minimal accumulation at steady state . Factors such as food intake, weight metrics, age, co-administration of cytochrome modulators, and Asian ethnicity can significantly influence this compound’s apparent oral clearance .
Result of Action
The primary result of this compound’s action is the shrinkage of associated tumors, as seen in patients with Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) who have symptomatic, inoperable plexiform neurofibromas (PN) . This leads to positive clinical outcomes, including a decrease in symptoms and improved quality of life .
Action Environment
For instance, food intake has been identified as a significant covariate on this compound absorption . Therefore, understanding these factors and tailoring treatment plans accordingly can help optimize the therapeutic benefits of this compound.
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Selumetinib is synthesized through a multi-step chemical processThe final step involves the formation of the carboxamide group . Industrial production methods typically involve optimizing reaction conditions to maximize yield and purity while minimizing the formation of impurities.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Selumetinib durchläuft verschiedene Arten von chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: This compound ist empfindlich gegenüber Oxidation, was zur Bildung eines Amidderivats führt.
Photooxidation: Lichteinwirkung kann Photooxidation verursachen, was zur Bildung eines Esterderivats führt.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen, die bei diesen Reaktionen verwendet werden, sind Oxidationsmittel, Lichteinwirkung und saure oder basische Lösungen. Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, sind Amid- und Esterderivate.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Selumetinib wird mit anderen MEK-Inhibitoren wie Trametinib und Cobimetinib verglichen. Obwohl alle drei Verbindungen die MEK1/2-Proteine als Ziel haben, ist this compound in seiner chemischen Struktur und seinen pharmakokinetischen Eigenschaften einzigartig . Zum Beispiel haben Trametinib und Cobimetinib unterschiedliche Molekülstrukturen und können in klinischen Umgebungen unterschiedliche Wirksamkeits- und Sicherheitsprofile aufweisen .
Ähnliche Verbindungen
- Trametinib
- Cobimetinib
- Binimetinib
Die Einzigartigkeit von this compound liegt in seiner spezifischen Bindungsaffinität und Selektivität für MEK1/2, was zu seiner Wirksamkeit bei der Behandlung der Neurofibromatose Typ 1 und anderer Tumoren beiträgt .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
6-(4-bromo-2-chloroanilino)-7-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-3-methylbenzimidazole-5-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C17H15BrClFN4O3/c1-24-8-21-16-13(24)7-10(17(26)23-27-5-4-25)15(14(16)20)22-12-3-2-9(18)6-11(12)19/h2-3,6-8,22,25H,4-5H2,1H3,(H,23,26) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CYOHGALHFOKKQC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN1C=NC2=C1C=C(C(=C2F)NC3=C(C=C(C=C3)Br)Cl)C(=O)NOCCO | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C17H15BrClFN4O3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID3048944 | |
| Record name | Selumetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3048944 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
457.7 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
The Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK signaling cascade is known to be activated in several types of cancer, and regulates the transcription of proteins involved in apoptosis. In addition, studies have shown that mutations of the Raf component of the pathway can contribute to chemotherapy drug resistance. Ras as well as several kinases and phosphatases are responsible for regulating the Raf-MEK-ERK pathway. Often in cancers, Ras (a G-protein coupled receptor) is deregulated, allowing downstream signalling to proceed unchecked. Through several complex steps, Raf phosphorylates and activates MEK, which then phosphorylates and activates ERK. ERK is then able to exert its effects on several downstream targets. As such, therapies inhibiting upstream components of this pathway have become attractive targets for cancer treatment. Selumetinib exerts its effects by selectively inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2 which can effectively blunt the pleiotropic effects of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK cascade. By inhibiting this oncogenic pathway, selumetinib reduces cell proliferation, and promotes pro-apoptotic signal transduction. | |
| Record name | Selumetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11689 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
606143-52-6 | |
| Record name | Selumetinib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=606143-52-6 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Selumetinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0606143526 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Selumetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11689 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Selumetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID3048944 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 5-[(4-bromo-2-chlorophenyl)amino]-4-fluoro-N-(2-hydroxyethoxy)-1-methyl-1H-1,3-benzodiazole-6-carboxamide | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | SELUMETINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/6UH91I579U | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![1-Ethyl-4-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-(1-ethylpyridin-1-ium-4-yl)-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl]pyridin-1-ium;dibromide](/img/structure/B1684252.png)
![But-2-enedioic acid;8-(2,3-dihydro-1,4-benzodioxin-3-ylmethyl)-1-thia-4,8-diazaspiro[4.5]decan-3-one](/img/structure/B1684254.png)
![2-[3-Cyano-5-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-4,5-dimethylfuran-2-ylidene]propanedinitrile](/img/structure/B1684258.png)
![2-Hydroxynaphthalene-1-carbaldehyde [(2-hydroxy-1-naphthyl)methylene]hydrazone](/img/structure/B1684262.png)