Semaglutide
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Semaglutid ist ein Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Rezeptoragonist, der zur Verbesserung der Blutzuckerkontrolle bei Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus, zur Behandlung von Fettleibigkeit und zur Reduzierung des Risikos für schwerwiegende kardiovaskuläre Ereignisse bei ausgewählten Erwachsenen eingesetzt wird . Es ist ein synthetisches Analogon des menschlichen Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Hormons, das eine entscheidende Rolle im Glukosestoffwechsel spielt .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Semaglutid wird durch eine konvergente Synthesestrategie synthetisiert. Der Prozess beinhaltet die schrittweise Kupplung von Aminosäuren an ein Festphasenharz, gefolgt von Spaltung und Reinigung, um das Endprodukt zu erhalten . Industrielle Produktionsverfahren umfassen die Verwendung von Flüssigphasen- und Festphasen-Synthesetechniken, um eine hohe Reinheit und Ausbeute zu gewährleisten . Die Herstellung von Semaglutid in Form von langwirksamen injizierbaren Mikrokapseln beinhaltet ein Doppel-Emulsionsverfahren, um eine verlängerte Freisetzung und verbesserte Stabilität zu erreichen .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
Semaglutid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution . Häufig verwendete Reagenzien in diesen Reaktionen sind Trifluoressigsäure, Ameisensäure und Acetonitril . Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen entstehen, sind das Peptid selbst und seine modifizierten Formen, die mit Hilfe der Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie und Massenspektrometrie analysiert werden .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Semaglutid hat eine breite Palette an wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen. In der Medizin wird es zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes und Fettleibigkeit eingesetzt . Es hat Potenzial bei der Behandlung von nicht-alkoholischer Fettleberhepatitis und neurodegenerativen Erkrankungen wie Parkinson und Alzheimer gezeigt . In der Biologie wird Semaglutid verwendet, um die Auswirkungen von Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Rezeptoragonisten auf den Glukosestoffwechsel und die Insulinsekretion zu untersuchen . In der Industrie wird es bei der Entwicklung von langwirksamen injizierbaren Formulierungen für eine verlängerte Wirkstofffreigabe eingesetzt .
Wirkmechanismus
Semaglutid wirkt durch Bindung an und Aktivierung des Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Rezeptors, wodurch die Insulinsekretion stimuliert und der Blutzuckerspiegel gesenkt wird . Es reduziert auch die ungeeignete Glucagonsekretion und verlangsamt die Magenentleerung . Die beteiligten molekularen Zielstrukturen umfassen den Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Rezeptor und verschiedene Signalwege, die den Glukosestoffwechsel regulieren .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Semaglutide undergoes various chemical reactions, including oxidation, reduction, and substitution . Common reagents used in these reactions include trifluoroacetic acid, formic acid, and acetonitrile . Major products formed from these reactions include the peptide itself and its modified forms, which are analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Semaglutide has a wide range of scientific research applications. In medicine, it is used to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity . It has shown potential in treating non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s . In biology, this compound is used to study the effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists on glucose metabolism and insulin secretion . In industry, it is used in the development of long-acting injectable formulations for sustained drug release .
Wirkmechanismus
Semaglutide works by binding to and activating the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor, thereby stimulating insulin secretion and reducing blood glucose . It also decreases inappropriate glucagon secretion and slows gastric emptying . The molecular targets involved include the glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor and various signaling pathways that regulate glucose metabolism .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Semaglutid ähnelt anderen Glucagon-like-Peptid-1-Rezeptoragonisten wie Exenatid und Liraglutid . Es bietet einen Wettbewerbsvorteil aufgrund seiner längeren Halbwertszeit und der einmal wöchentlichen Dosierung . Im Gegensatz zu Exenatid und Liraglutid ist Semaglutid sowohl in subkutanen als auch in oralen Formulierungen erhältlich . Andere ähnliche Verbindungen umfassen Tirzepatid, das sowohl Glucagon-like-Peptid-1 als auch Glucose-abhängiges insulinotropes Polypeptid nachahmt .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
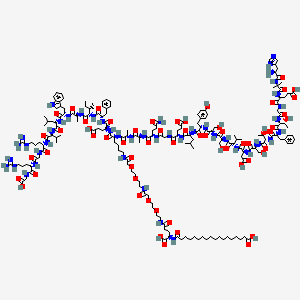
18-[[(1R)-4-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-2-methylpropanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2-oxoethoxy]ethoxy]ethylamino]-2-oxoethoxy]ethoxy]ethylamino]-1-carboxy-4-oxobutyl]amino]-18-oxooctadecanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C187H291N45O59/c1-18-105(10)154(180(282)208-108(13)159(261)216-133(86-114-89-200-119-50-40-39-49-117(114)119)170(272)218-129(82-102(4)5)171(273)228-152(103(6)7)178(280)215-121(53-44-72-199-186(192)193)162(264)201-91-141(242)209-120(52-43-71-198-185(190)191)161(263)204-94-151(257)258)230-172(274)131(83-111-45-33-31-34-46-111)219-167(269)126(64-69-149(253)254)214-166(268)122(51-41-42-70-195-144(245)98-290-79-78-289-76-74-197-145(246)99-291-80-77-288-75-73-196-139(240)66-61-127(183(285)286)211-140(241)54-37-29-27-25-23-21-19-20-22-24-26-28-30-38-55-146(247)248)212-158(260)107(12)206-157(259)106(11)207-165(267)125(60-65-138(189)239)210-142(243)92-202-163(265)123(62-67-147(249)250)213-168(270)128(81-101(2)3)217-169(271)130(85-113-56-58-116(238)59-57-113)220-175(277)135(95-233)223-177(279)137(97-235)224-179(281)153(104(8)9)229-174(276)134(88-150(255)256)221-176(278)136(96-234)225-182(284)156(110(15)237)231-173(275)132(84-112-47-35-32-36-48-112)222-181(283)155(109(14)236)227-143(244)93-203-164(266)124(63-68-148(251)252)226-184(287)187(16,17)232-160(262)118(188)87-115-90-194-100-205-115/h31-36,39-40,45-50,56-59,89-90,100-110,118,120-137,152-156,200,233-238H,18-30,37-38,41-44,51-55,60-88,91-99,188H2,1-17H3,(H2,189,239)(H,194,205)(H,195,245)(H,196,240)(H,197,246)(H,201,264)(H,202,265)(H,203,266)(H,204,263)(H,206,259)(H,207,267)(H,208,282)(H,209,242)(H,210,243)(H,211,241)(H,212,260)(H,213,270)(H,214,268)(H,215,280)(H,216,261)(H,217,271)(H,218,272)(H,219,269)(H,220,277)(H,221,278)(H,222,283)(H,223,279)(H,224,281)(H,225,284)(H,226,287)(H,227,244)(H,228,273)(H,229,276)(H,230,274)(H,231,275)(H,232,262)(H,247,248)(H,249,250)(H,251,252)(H,253,254)(H,255,256)(H,257,258)(H,285,286)(H4,190,191,198)(H4,192,193,199)/t105-,106-,107-,108-,109+,110+,118-,120-,121-,122-,123-,124-,125-,126-,127+,128-,129-,130-,131-,132-,133-,134-,135-,136-,137-,152-,153-,154-,155-,156-/m0/s1 | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
DLSWIYLPEUIQAV-CCUURXOWSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCC(C)C(C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CCCCNC(=O)COCCOCCNC(=O)COCCOCCNC(=O)CCC(C(=O)O)NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)(C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CN=CN6)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC[C@H](C)[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CNC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CCCCNC(=O)COCCOCCNC(=O)COCCOCCNC(=O)CC[C@H](C(=O)O)NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)(C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC6=CN=CN6)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C187H291N45O59 | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
4114 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
910463-68-2 | |
| Record name | Semaglutide [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0910463682 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Semaglutide18-[[(1R)-4-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[2-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1Himidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]-2-methylpropanoyl]amino]-4 carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4 carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5 oxopentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2-oxoethoxy]ethoxy]ethylamino]-2-oxoethoxy]ethoxy]ethylamino]-1-carboxy-4-oxobutyl]amino]-18-oxooctadecanoic acid | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.