Nateglinid
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Nateglinid ist ein orales Antidiabetikum, das zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt wird. Es gehört zur Klasse der Meglitinide, die den Blutzuckerspiegel senken. This compound wurde von Ajinomoto, einem japanischen Unternehmen, entwickelt und wird von Novartis unter dem Handelsnamen Starlix vermarktet .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Nateglinide primarily targets the β cells of the pancreas . These cells play a crucial role in the regulation of blood glucose levels by secreting insulin, a hormone that promotes the uptake of glucose into cells .
Mode of Action
Nateglinide interacts with its targets by binding to ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the membrane of the β cells . This binding action leads to the closure of these channels, causing the β cells to depolarize . The depolarization then opens voltage-gated calcium channels, leading to an influx of calcium ions . This calcium influx triggers the fusion of insulin-containing vesicles with the cell membrane, resulting in the secretion of insulin .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by nateglinide is the insulin secretion pathway . By stimulating the release of insulin, nateglinide helps lower blood glucose levels. It achieves this by modulating the activity of ATP-sensitive potassium channels and voltage-gated calcium channels in pancreatic β cells .
Pharmacokinetics
Nateglinide exhibits rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes extensive biotransformation in the liver to at least nine metabolites . The major metabolites are less active than the parent compound, with one minor metabolite, the isoprene, having the same potency . Nateglinide is predominantly excreted in urine (83%) as metabolites, with only 16% of the dose excreted unchanged . Its elimination half-life is approximately 1.4 hours .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of nateglinide’s action primarily involve the stimulation of insulin secretion from the pancreas . This results in a decrease in postprandial (after meal) blood glucose levels . Nateglinide induces an early insulin response to meals, which is crucial for maintaining glucose homeostasis .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of nateglinide can be influenced by various environmental factors. Additionally, genetic polymorphisms in hepatic-uptake transporter SLCO1B1 (OATP1B1) and cytochrome P450 enzymes like CYP2C9 and CYP3A4, which are involved in nateglinide metabolism, can also influence its pharmacokinetics .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Nateglinid hat mehrere Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Medizin: this compound wird hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus eingesetzt. .
Pharmazeutische Forschung: This compound wird bei der Entwicklung von Retardformulierungen eingesetzt, um seine Bioverfügbarkeit und therapeutische Wirksamkeit zu verbessern.
Biologische Studien: This compound wird in Studien eingesetzt, die die Mechanismen der Insulinsekretion und des Glukosestoffwechsels untersuchen.
Industrielle Anwendungen: This compound wird bei der Formulierung von schnell zerfallenden Tabletten eingesetzt, um die Patientencompliance zu verbessern.
Wirkmechanismus
This compound senkt den Blutzuckerspiegel, indem es die Freisetzung von Insulin aus der Bauchspeicheldrüse stimuliert. Dies erreicht es, indem es ATP-abhängige Kaliumkanäle in der Membran der Betazellen verschließt. Dies depolarisiert die Betazellen und führt dazu, dass spannungsgesteuerte Kalziumkanäle geöffnet werden. Der resultierende Kalziumeinstrom induziert die Fusion von Insulin-haltigen Vesikeln mit der Zellmembran, was zur Insulinsekretion führt .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Nateglinide plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by interacting with specific enzymes and proteins. It primarily targets the ATP-sensitive potassium channels (K_ATP channels) on the pancreatic beta cells. By binding to these channels, Nateglinide inhibits their activity, leading to cell membrane depolarization. This depolarization opens voltage-gated calcium channels, resulting in an influx of calcium ions. The increased intracellular calcium concentration triggers the exocytosis of insulin-containing vesicles, thereby increasing insulin secretion .
Cellular Effects
Nateglinide influences various cellular processes, particularly in pancreatic beta cells. It enhances insulin secretion, which is crucial for glucose homeostasis. Additionally, Nateglinide affects cell signaling pathways by modulating the activity of K_ATP channels and calcium channels. This modulation impacts gene expression related to insulin synthesis and secretion. In other cell types, Nateglinide’s effects are less pronounced but may include alterations in cellular metabolism and signaling pathways .
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, Nateglinide exerts its effects by binding to the sulfonylurea receptor 1 (SUR1) subunit of the K_ATP channels on pancreatic beta cells. This binding inhibits the channel’s activity, leading to membrane depolarization and subsequent opening of voltage-gated calcium channels. The resulting calcium influx promotes insulin vesicle fusion with the cell membrane and insulin release. Nateglinide’s rapid binding and dissociation from the SUR1 subunit contribute to its short duration of action .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Nateglinide have been observed to change over time. The compound is relatively stable under standard conditions but can degrade under extreme pH or temperature conditions. Long-term studies have shown that Nateglinide maintains its efficacy in stimulating insulin secretion over extended periods, although its rapid onset and short duration of action mean that its effects are most pronounced shortly after administration .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of Nateglinide vary with dosage. At therapeutic doses, Nateglinide effectively lowers postprandial blood glucose levels without causing significant hypoglycemia. At higher doses, adverse effects such as hypoglycemia and potential toxicity have been observed. These effects highlight the importance of careful dosage management to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing risks .
Metabolic Pathways
Nateglinide is metabolized primarily in the liver through the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, particularly CYP2C9 and CYP3A4. The major metabolites are less active than the parent compound and are excreted in urine and feces. Nateglinide’s metabolism involves hydroxylation and subsequent conjugation reactions, which facilitate its elimination from the body .
Transport and Distribution
Within cells, Nateglinide is transported and distributed through passive diffusion and active transport mechanisms. It binds to plasma proteins, which influences its distribution and bioavailability. Nateglinide’s rapid absorption and distribution are critical for its quick onset of action, allowing it to effectively manage postprandial glucose levels .
Subcellular Localization
Nateglinide’s subcellular localization is primarily within the cytoplasm of pancreatic beta cells, where it interacts with K_ATP channels on the cell membrane. This localization is essential for its role in modulating insulin secretion. Nateglinide does not require specific targeting signals or post-translational modifications for its activity, as its effects are mediated through direct binding to its target channels .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Nateglinid kann mit verschiedenen Methoden synthetisiert werden. Eine gängige Methode beinhaltet die Reaktion von D-Phenylalanin mit trans-4-Isopropylcyclohexancarbonsäure. Die Reaktion wird typischerweise in Gegenwart eines Kupplungsgases wie Dicyclohexylcarbodiimid (DCC) und eines Katalysators wie 4-Dimethylaminopyridin (DMAP) in einem organischen Lösungsmittel durchgeführt . Eine andere Methode beinhaltet die Herstellung von this compound-beladenen Retard-Ethylcellulose-Mikrokugeln unter Verwendung einer Öl-in-Wasser- (O/W)-Solvent-Emulsionstechnik .
Chemische Reaktionsanalyse
This compound durchläuft verschiedene chemische Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann zu Hydroxy- und Glucuronid-Metaboliten oxidiert werden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen von this compound sind seltener, können aber unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten.
Substitution: this compound kann Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, insbesondere in Gegenwart starker Nukleophile.
Hydrolyse: this compound kann unter sauren oder basischen Bedingungen zu seinen konstitutiven Aminosäuren hydrolysiert werden.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Nateglinide undergoes various chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Nateglinide can be oxidized to form hydroxy and glucuronide metabolites.
Reduction: Reduction reactions of nateglinide are less common but can occur under specific conditions.
Substitution: Nateglinide can undergo substitution reactions, particularly in the presence of strong nucleophiles.
Hydrolysis: Nateglinide can be hydrolyzed to its constituent amino acids under acidic or basic conditions.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Nateglinid wird oft mit anderen Antidiabetika wie Repaglinid und Metformin verglichen:
Repaglinid: Sowohl this compound als auch Repaglinid gehören zur Klasse der Meglitinide und stimulieren die Insulinsekretion.
Metformin: Im Gegensatz zu this compound verbessert Metformin die Insulinsensitivität und reduziert die hepatische Glukoseproduktion.
Semaglutid: Semaglutid ist ein Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1)-Rezeptoragonist, der den Blutzuckerspiegel senkt, indem er die Insulinsekretion stimuliert und die Glukagonsekretion reduziert.
Ähnliche Verbindungen
- Repaglinid
- Metformin
- Semaglutid
Der schnelle Wirkungseintritt und die kurze Wirkdauer von this compound machen es einzigartig unter den Antidiabetika und bieten einen gezielten Ansatz zur Behandlung der postprandialen Hyperglykämie .
Eigenschaften
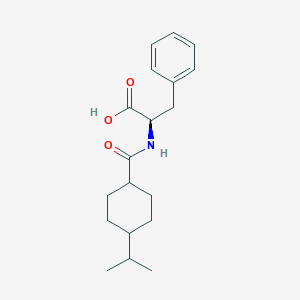
IUPAC Name |
(2R)-3-phenyl-2-[(4-propan-2-ylcyclohexanecarbonyl)amino]propanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H27NO3/c1-13(2)15-8-10-16(11-9-15)18(21)20-17(19(22)23)12-14-6-4-3-5-7-14/h3-7,13,15-17H,8-12H2,1-2H3,(H,20,21)(H,22,23)/t15?,16?,17-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
OELFLUMRDSZNSF-OFLPRAFFSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)C1CCC(CC1)C(=O)N[C@H](CC2=CC=CC=C2)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C19H27NO3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID9040687 | |
| Record name | Nateglinide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9040687 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
317.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Practically insoluble | |
| Record name | Nateglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00731 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Mechanism of Action |
Nateglinide activity is dependent on the presence functioning β cells and glucose. In contrast to sulfonylurea insulin secretatogogues, nateglinide has no effect on insulin release in the absence of glucose. Rather, it potentiates the effect of extracellular glucose on ATP-sensitive potassium channel and has little effect on insulin levels between meals and overnight. As such, nateglinide is more effective at reducing postprandial blood glucose levels than fasting blood glucose levels and requires a longer duration of therapy (approximately one month) before decreases in fasting blood glucose are observed. The insulinotropic effects of nateglinide are highest at intermediate glucose levels (3 to 10 mmol/L) and it does not increase insulin release already stimulated by high glucose concentrations (greater than 15 mmol/L). Nateglinide appears to be selective for pancreatic β cells and does not appear to affect skeletal or cardiac muscle or thyroid tissue. | |
| Record name | Nateglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00731 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
105816-04-4, 105816-06-6 | |
| Record name | Nateglinide [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0105816044 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | N-((cis-4-(1-Methylethyl)cyclohexyl)carbonyl)-D-phenylalanine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0105816066 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Nateglinide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00731 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Nateglinide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID9040687 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | NATEGLINIDE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/41X3PWK4O2 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | N-((CIS-4-(1-METHYLETHYL)CYCLOHEXYL)CARBONYL)-D-PHENYLALANINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/XTM4DQP5S5 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.