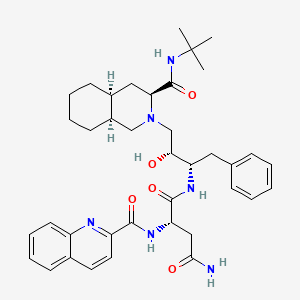
Saquinavir
Descripción general
Descripción
Saquinavir es un medicamento antirretroviral que se utiliza en combinación con otros medicamentos para tratar o prevenir el VIH/SIDA. Pertenece a la clase de inhibidores de la proteasa y funciona bloqueando la enzima proteasa del VIH, que es esencial para que el virus madure y se replique . This compound fue el primer inhibidor de la proteasa aprobado por la FDA en 1995 y se comercializa con nombres de marca como Invirase y Fortovase .
Mecanismo De Acción
Saquinavir ejerce su actividad antiviral inhibiendo la enzima proteasa del VIH-1. Esta enzima es crucial para la escisión de poliproteínas en proteínas virales funcionales. Al bloquear esta enzima, this compound previene la maduración del virus, lo que lleva a la formación de partículas virales no infecciosas . El objetivo molecular principal es la proteasa del VIH-1, y la vía involucra la interrupción de la replicación y ensamblaje viral .
Compuestos Similares:
Ritonavir: Otro inhibidor de la proteasa utilizado en combinación con otros antirretrovirales. Es conocido por su capacidad de aumentar la efectividad de otros inhibidores de la proteasa inhibiendo su metabolismo.
Indinavir: Un inhibidor de la proteasa que también se dirige a la proteasa del VIH-1, pero tiene diferentes propiedades farmacocinéticas.
Lopinavir: A menudo utilizado en combinación con Ritonavir, tiene un mecanismo de acción similar, pero diferentes perfiles de resistencia.
Singularidad de this compound: this compound fue el primer inhibidor de la proteasa en ser aprobado y tiene un perfil de efectos adversos relativamente benigno en comparación con otras terapias antirretrovirales . Su estructura única y afinidad de unión a la proteasa del VIH-1 lo convierten en un componente valioso de las terapias combinadas para el VIH/SIDA .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Saquinavir tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Química: Utilizado como un compuesto modelo para estudiar inhibidores de la proteasa y sus interacciones con las enzimas.
Biología: Investigado por sus efectos sobre la replicación viral y la síntesis de proteínas.
Medicina: Principalmente utilizado en el tratamiento del VIH/SIDA.
Industria: Employed in the development of new antiviral drugs and therapeutic agents.
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Saquinavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease enzyme . It interacts with this enzyme, preventing the proteolysis of the Gag polyprotein, which results in the production of immature, non-infectious viral particles . More than 90% of its biotransformation is mediated by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme .
Cellular Effects
This compound exerts its antiviral activity by inhibiting an enzyme critical for the HIV-1 viral lifecycle . It influences cell function by preventing HIV-1 protease activity, thus inhibiting the production of mature, infectious viral particles . This impacts cellular metabolism and gene expression related to viral replication.
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves the inhibition of the HIV-1 protease enzyme . Its design is based on the “peptidomimetic” principle, where the molecule contains a hydroxyethylene scaffold that mimics the normal peptide linkage (cleaved by HIV protease) but which itself cannot be cleaved . This prevents HIV-1 protease activity, inhibiting the proteolysis of the Gag polyprotein, and resulting in the production of immature, non-infectious viral particles .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The effects of this compound over time in laboratory settings have been observed to change. It has been found that all fatty acid levels were lower compared with pre-treatment levels after 4 weeks of treatment, suggesting a prolonged effect of the antiretroviral drug treatment lasting beyond the 4 week post-treatment observation period .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, the effects of this compound vary with different dosages. The oral LD50 of this compound in both rats and mice is >5 g/kg . No acute toxicities or sequelae were noted in a patient ingesting 8 grams of this compound as a single dose .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is extensively metabolized in the liver following oral administration . In vitro studies have shown that more than 90% of its biotransformation is mediated by the CYP3A4 isoenzyme . This compound is rapidly metabolized to a number of inactive mono- and di-hydroxylated compounds .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported by multidrug resistance-associated protein (MRP1) and canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter (MRP2) . The steady-state volume of distribution of this compound is approximately 700 L, suggesting extensive distribution into tissues .
Subcellular Localization
Given its role as a protease inhibitor and its extensive distribution into tissues , it can be inferred that this compound likely localizes to the sites of viral protein synthesis and assembly within the cell
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas Sintéticas y Condiciones de Reacción: La síntesis de Saquinavir involucra múltiples pasos, comenzando con la preparación de intermediarios clave. Un método involucra la sulfonilación de metilo de (1S, 2S)-(1-bencil-3-cloro-2-hidroxilpropil) carbamato de tert-butilo usando cloruro de metilsulfonilo en presencia de trietilamina y metilbenceno bajo una atmósfera de nitrógeno. Este intermedio luego se hace reaccionar con acetato metálico en presencia de éter 18-corona-6 y metilbenceno para obtener (1S, 2R)-(1-bencil-3-cloro-2-ácido acético propil) carbamato de tert-butilo. Reacciones adicionales con KOH, THF y etanol producen (2R, 3S)-1,2-epoxi-3-tert-butiloxicarbonil amino-4-fenil butano .
Métodos de Producción Industrial: La producción industrial de this compound generalmente involucra la síntesis a gran escala utilizando condiciones de reacción optimizadas para asegurar un alto rendimiento y pureza. El proceso incluye el uso de técnicas avanzadas como calorimetría de barrido diferencial (DSC), difracción de rayos X de polvo (PXRD) y espectroscopia infrarroja de transformada de Fourier (FT-IR) para la caracterización y el control de calidad .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de Reacciones: Saquinavir experimenta varias reacciones químicas, incluyendo oxidación, reducción y sustitución. Estas reacciones son cruciales para su metabolismo y eliminación del cuerpo.
Reactivos y Condiciones Comunes:
Oxidación: this compound puede oxidarse utilizando reactivos como peróxido de hidrógeno o permanganato de potasio.
Reducción: Las reacciones de reducción pueden involucrar agentes como borohidruro de sodio o hidruro de aluminio y litio.
Sustitución: Las reacciones de sustitución a menudo usan agentes halogenantes como cloruro de tionilo o tribromuro de fósforo.
Productos Principales: Los productos principales formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen varios metabolitos que se excretan principalmente a través de las heces y la orina .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
Ritonavir: Another protease inhibitor used in combination with other antiretrovirals. It is known for its ability to boost the effectiveness of other protease inhibitors by inhibiting their metabolism.
Indinavir: A protease inhibitor that also targets the HIV-1 protease but has different pharmacokinetic properties.
Lopinavir: Often used in combination with Ritonavir, it has a similar mechanism of action but different resistance profiles.
Uniqueness of Saquinavir: this compound was the first protease inhibitor to be approved and has a relatively benign adverse effect profile compared to other antiretroviral therapies . Its unique structure and binding affinity to the HIV-1 protease make it a valuable component of combination therapies for HIV/AIDS .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
(2S)-N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(3S,4aS,8aS)-3-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-3,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1H-isoquinolin-2-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]-2-(quinoline-2-carbonylamino)butanediamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C38H50N6O5/c1-38(2,3)43-37(49)32-20-26-14-7-8-15-27(26)22-44(32)23-33(45)30(19-24-11-5-4-6-12-24)41-36(48)31(21-34(39)46)42-35(47)29-18-17-25-13-9-10-16-28(25)40-29/h4-6,9-13,16-18,26-27,30-33,45H,7-8,14-15,19-23H2,1-3H3,(H2,39,46)(H,41,48)(H,42,47)(H,43,49)/t26-,27+,30-,31-,32-,33+/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
QWAXKHKRTORLEM-UGJKXSETSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)C1CC2CCCCC2CN1CC(C(CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)(C)NC(=O)[C@@H]1C[C@@H]2CCCC[C@@H]2CN1C[C@H]([C@H](CC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)N)NC(=O)C4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C=C4)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C38H50N6O5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
149845-06-7 (monomethanesulfonate (salt)) | |
| Record name | Saquinavir [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0127779208 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID6044012 | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6044012 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
670.8 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
Insoluble, In water, 0.22 g/100 mL @ 25 °C | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01232 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SAQUINAVIR | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7161 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Vapor Pressure |
2X10-31 mm Hg @ 25 °C /Estimated/ | |
| Record name | SAQUINAVIR | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7161 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The HIV lifecycle is comprised of 3 distinct stages: assembly, involving creation and packaging of essential viral components; budding, wherein the viral particle crosses the host cell plasma membrane and forms a lipid envelope; and maturation, wherein the viral particle alters its structure and becomes infectious. At the center of this lifecycle is the Gag polyprotein which, along with the products of its proteolysis, coordinate these stages and function as the major structural proteins of the virus. The HIV-1 protease enzyme, a dimeric aspartic protease, is the enzyme responsible for cleaving the Gag polyprotein and thus plays a critical role in many aspects of the HIV viral lifecycle. Saquinavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease enzyme. Its design is based on the "peptidomimetic" principle, wherein the molecule contains a hydroxyethylene scaffold that mimics the normal peptide linkage (cleaved by HIV protease) but which itself cannot be cleaved. By preventing HIV-1 protease activity, and thus the proteolysis of the Gag polyprotein, saquinavir results in the production of immature, non-infectious viral particles., While the complete mechanisms of antiviral activity of saquinavir have not been fully elucidated, saquinavir apparently inhibits replication of retroviruses, including human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) and type 2 (HIV-2), by interfering with HIV protease. The drug, therefore, exerts a virustatic effect against retroviruses by acting as an HIV protease inhibitor., Saquinavir is a selective, competitive, reversible inhibitor of HIV protease. HIV protease, an aspartic endopeptidase that functions as a homodimer, plays an essential role in the replication cycle of HIV and the formation of infectious virus. During HIV replication, HIV protease cleaves viral polypeptide products of the gag and gag-pol genes (i.e., p55 and p160) to form structural proteins of the virion core (i.e., p17, p24, p9, and p7) and essential viral enzymes (i.e., reverse transcriptase, integrase, and protease). Because saquinavir is a structural analog of the HIV Phe-Pro protease cleavage site, the drug inhibits the function of the enzyme. By interfering with the formation of these essential proteins and enzymes, saquinavir blocks maturation of the virus and causes the formation of nonfunctional, immature, noninfectious virions. Saquinavir is active in both acutely and chronically infected cells since it targets the HIV replication cycle after translation and before assembly. Thus, the drug is active in chronically infected cells (e.g., monocytes and macrophages) that generally are not affected by nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (e.g., didanosine, lamivudine, stavudine, zalcitabine, zidovudine). Saquinavir does not affect early stages of the HIV replication cycle; however, the drug interferes with the production of infectious HIV and limits further infectious spread of the virus., Unlike nucleoside antiretroviral agents, the antiviral activity of saquinavir does not depend on intracellular conversion to an active metabolite. Saquinavir and other HIV protease inhibitors (e.g., amprenavir, indinavir, lopinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir) act at a different stage of the HIV replication cycle than nucleoside and nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors, and results of in vitro studies indicate that the antiretroviral effects of some nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors and HIV protease inhibitors may be additive or synergistic. | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01232 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | SAQUINAVIR | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7161 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
White crystalline solid, Off-white to white very fine powder | |
CAS No. |
127779-20-8 | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=127779-20-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Saquinavir [USAN:USP:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0127779208 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01232 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Saquinavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID6044012 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | SAQUINAVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/L3JE09KZ2F | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | SAQUINAVIR | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7161 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.


![2-(5-Bromo-2-thienyl)-2,3-dihydro-1H-naphtho[1,8-de][1,3,2]diazaborine](/img/structure/B1662095.png)