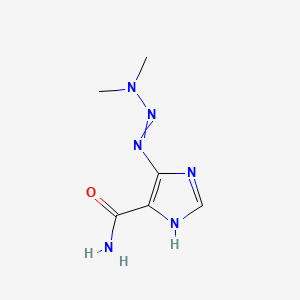
Dacarbazina
Descripción general
Descripción
Mecanismo De Acción
Target of Action
Dacarbazine is an antineoplastic agent used to treat malignant melanoma and Hodgkin’s disease . The primary targets of dacarbazine are cancer cells, specifically melanoma cells and the cells involved in Hodgkin’s disease .
Mode of Action
It appears to exert cytotoxic effects via its action as an alkylating agent . Other theories include DNA synthesis inhibition by its action as a purine analog, and interaction with SH groups .
Biochemical Pathways
Dacarbazine is a synthetic analog of naturally occurring purine precursor 5-amino-1H-imidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC) . It works by sticking to the cancer cell’s DNA and damaging it . DNA makes up genes, which control everything cells do. If the DNA is damaged, the cancer cell cannot divide and make more cancer cells .
Pharmacokinetics
After intravenous administration of dacarbazine, the volume of distribution exceeds total body water content suggesting localization in some body tissue, probably the liver . The bioavailability of dacarbazine is 100% . It undergoes extensive metabolism and has an elimination half-life of 5 hours . Approximately 40% of dacarbazine is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug .
Result of Action
The result of dacarbazine’s action is the slowing or stopping of the growth of cancer cells in the body . By damaging the DNA of cancer cells, dacarbazine prevents these cells from dividing and proliferating, thereby inhibiting the progression of the disease .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of dacarbazine can be influenced by various environmental factors during its formulation. For instance, the process parameters such as homogenization speed, duration, and temperature during the preparation of dacarbazine-loaded cubosomes can significantly impact the particle size and encapsulation efficiency . These factors can, in turn, affect the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of dacarbazine.
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Dacarbazine has extensive applications in scientific research, particularly in the fields of chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry. It is widely used as an antineoplastic agent in cancer therapy, especially for treating metastatic melanoma and Hodgkin’s lymphoma . Researchers are exploring various strategies to optimize dacarbazine therapy, such as designing laser-triggered delivery systems based on β-cyclodextrin and plasmonic gold nanoparticles to improve its solubility, stability, and specificity . Additionally, studies have shown that combining dacarbazine with hyperthermia can enhance its cytotoxic effects on melanoma cells .
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Dacarbazine is a synthetic analog of the naturally occurring purine precursor 5-amino-1H-imidazole-4-carboxamide (AIC) . It interacts with various enzymes and proteins in the body. The drug undergoes activation via cytochrome P450 in the liver to form the reactive compound, methyltriazenoimidazole carboxamide (MTIC) . The cytotoxicity of MTIC is thought to be due primarily to the formation of methylcarbonium ions that attack nucleophilic groups in DNA .
Cellular Effects
Dacarbazine exerts its effects on various types of cells, particularly cancer cells. It works by sticking to the cancer cell’s DNA and damaging it . This damage to the DNA prevents the cancer cell from dividing and creating more cancer cells . Dacarbazine commonly causes low blood cell counts, including white blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets . This can lead to problems like fatigue (from low RBCs) and higher risk for bleeding (from low platelets). It can also raise the risk for serious and life-threatening infections (from low WBCs) .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Dacarbazine involves its transformation into an active form that can interact with DNA. Dacarbazine is activated by liver microsomal enzymes to monomethyl triazeno imidazole carboxamide (MTIC), which is an alkylating compound . It causes methylation, modification, and cross-linking of DNA, thus inhibiting DNA, RNA, and protein synthesis .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Dacarbazine can change over time. After intravenous administration, the volume of distribution of Dacarbazine exceeds total body water content, suggesting localization in some body tissue, probably the liver . Dacarbazine is subject to renal tubular secretion rather than glomerular filtration . In humans, Dacarbazine is extensively degraded, with 20-50% excreted unchanged in urine and 12-24% as aminoimidazole carboxamide (AIC) .
Metabolic Pathways
Dacarbazine is metabolized primarily in the liver, principally via CYP 1A2, and secondarily by CYP 2E1 . The principle liver enzyme responsible for Dacarbazine metabolism in humans is CYP 1A2, but CYP 2E1 may participate when CYP 1A2 expression is low .
Transport and Distribution
After intravenous administration of Dacarbazine, the volume of distribution exceeds total body water content, suggesting localization in some body tissue, probably the liver . This suggests that Dacarbazine is transported and distributed within cells and tissues, likely through the bloodstream.
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it can be inferred that Dacarbazine or its active metabolite MTIC interacts with DNA within the nucleus of the cell
Métodos De Preparación
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Dacarbazine is synthesized through a multi-step chemical process. The synthesis begins with the reaction of 5-amino-1H-imidazole-4-carboxamide with nitrous acid to form 5-diazoimidazole-4-carboxamide. This intermediate is then reacted with dimethylamine to yield dacarbazine .
Industrial Production Methods: In industrial settings, dacarbazine is produced in vials containing 100 and 200 milligrams of the drug along with anhydrous citric acid and mannitol. The vials are reconstituted with sterile water for injection to yield solutions containing 10 milligrams per milliliter of dacarbazine . The reconstituted solutions are stable for up to 24 hours at room temperature and up to 96 hours under refrigeration when protected from light .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Types of Reactions: Dacarbazine undergoes various chemical reactions, including photodegradation, which is influenced by environmental pH . The drug is highly photosensitive, and its photodegradation products can cause adverse reactions such as pain at the injection site, nausea, vomiting, and hepatic toxicity .
Common Reagents and Conditions: The photodegradation of dacarbazine is monitored using UV-Vis absorbance spectra recorded during irradiation by an artificial lighting source. The reaction is influenced by pH levels ranging from 2 to 12 .
Major Products Formed: The major photodegradation product of dacarbazine is 2-azahypoxanthine . Other photoproducts may form depending on the pH and experimental conditions .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
- Procarbazine
- Temozolomide
- Carmustine
Dacarbazine’s unique properties, such as its specific mechanism of action and reduced teratogenic effects, make it a valuable chemotherapeutic agent in the treatment of various cancers.
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
4-(dimethylaminodiazenyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by Lexichem TK 2.7.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C6H10N6O/c1-12(2)11-10-6-4(5(7)13)8-3-9-6/h3H,1-2H3,(H2,7,13)(H,8,9) | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
FDKXTQMXEQVLRF-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.6 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)N=NC1=C(NC=N1)C(=O)N | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.3.0 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C6H10N6O | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0020369 | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020369 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
182.18 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Dacarbazine appears as white to ivory microcrystals or off-white crystalline solid. (NTP, 1992), Solid | |
| Details | National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | National Toxicology Program, Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health (NTP). 1992. National Toxicology Program Chemical Repository Database. Research Triangle Park, North Carolina. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
less than 0.1 mg/mL at 59 °F (NTP, 1992), Water: (1 mg/ml at room temp), 1.36e+00 g/L | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 204 (1981) | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Dacarbazine functions as an alkylating agent after metabolic activation in the liver. It appears to inhibit the synthesis of RNA and protein more than it inhibits the synthesis of DNA. It kills cells slowly, and there appears to be no phase of the cell cycle in which sensitivity is increased ... ., ...FOR CHEMOTHERAPEUTIC EFFECTIVENESS, DACARBAZINE REQUIRES INITIAL ACTIVATION BY CYTOCHROME P450 SYSTEM OF LIVER THROUGH N-DEMETHYLATION REACTION. IN TARGET CELL...OCCURS SPONTANEOUS CLEAVAGE LIBERATING AIC /5-AMINOIMIDAZOLE-4-CARBOXAMIDE/ & ALKYLATING MOIETY, PRESUMABLY DIAZOMETHANE..., Although the mechanism of action of dacarbazine is not known in detail, it is demethylated by liver microsomal enzymes to form an unstable monoalkyl derivative which can decompose spontaneously into alkylating moieties. In light, dacarbazine can also rapidly undergo chemical decomposition to form 4-diazoimidazole-5-carboxamide, which is highly toxic but which has no antitumor activity in vivo ... . | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 209 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
IVORY MICROCRYSTALINE SUBSTANCE | |
CAS No. |
4342-03-4 | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=4342-03-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0020369 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.022.179 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
482 to 491 °F (explosively decomposes) (NTP, 1992), 205 °C, Melting point: 250-255 °C (explosive decomposition) | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/20085 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | DACARBAZINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3219 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Details | IARC. Monographs on the Evaluation of the Carcinogenic Risk of Chemicals to Humans. Geneva: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, 1972-PRESENT. (Multivolume work). Available at: https://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Classification/index.php, p. V26 203 (1981) | |
| Record name | Dacarbazine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014989 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.