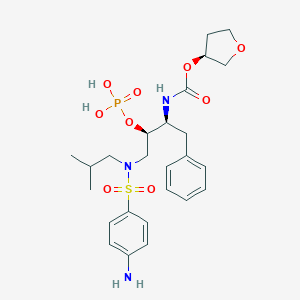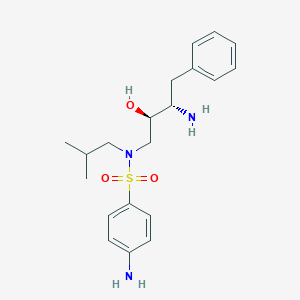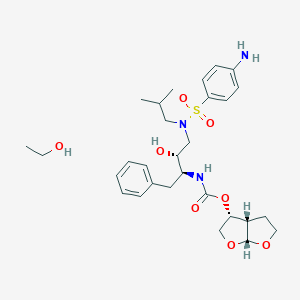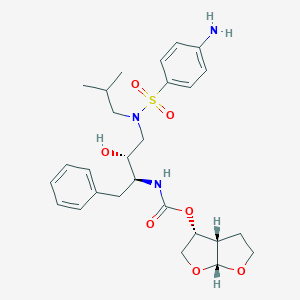
Darunavir
Descripción general
Descripción
Darunavir es un inhibidor no peptídico de la proteasa que se utiliza principalmente en el tratamiento y la prevención de la infección por el virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH). A menudo se administra en combinación con otros agentes antirretrovirales para mejorar su eficacia. This compound fue aprobado por la Administración de Alimentos y Medicamentos de los Estados Unidos en 2006 y se incluye en la Lista de Medicamentos Esenciales de la Organización Mundial de la Salud .
Mecanismo De Acción
Darunavir ejerce sus efectos inhibiendo la enzima proteasa del VIH-1, que es esencial para el procesamiento de proteínas precursoras virales y la maduración viral. Al unirse al sitio activo de la enzima, this compound previene la escisión de la poliproteína Gag-Pol del VIH, bloqueando así la formación de viriones infecciosos . Este mecanismo es crucial para su actividad antirretroviral.
Compuestos Similares:
- Amprenavir
- Indinavir
- Saquinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Ritonavir
Comparación: this compound es único entre los inhibidores de la proteasa debido a su alta barrera genética a la resistencia y su capacidad para inhibir una amplia gama de cepas de VIH-1 resistentes a los inhibidores de la proteasa . A diferencia de algunos otros inhibidores de la proteasa, this compound se utiliza a menudo en combinación con ritonavir o cobicistat para mejorar su perfil farmacocinético .
Aplicaciones Científicas De Investigación
Darunavir tiene una amplia gama de aplicaciones de investigación científica:
Análisis Bioquímico
Biochemical Properties
Darunavir plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the activity of the HIV-1 protease enzyme. This enzyme is responsible for cleaving the viral polyprotein into functional proteins necessary for viral replication . This compound binds to the active site of the HIV-1 protease through multiple hydrogen bonds, thereby preventing the enzyme from processing the viral polyprotein . This inhibition leads to the production of immature, non-infectious viral particles . This compound interacts with various biomolecules, including the HIV-1 protease enzyme and other proteins involved in the viral replication process .
Cellular Effects
This compound has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. In HIV-infected cells, this compound reduces viral load and increases CD4 cell counts, which are crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system . By inhibiting the HIV-1 protease enzyme, this compound disrupts the viral replication cycle, leading to a decrease in the production of new viral particles . This inhibition also affects cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism by preventing the virus from hijacking the host cell’s machinery .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its binding to the active site of the HIV-1 protease enzyme. This compound forms multiple hydrogen bonds with the enzyme, which stabilizes its binding and prevents the protease from cleaving the viral polyprotein . This inhibition results in the production of immature viral particles that are unable to infect new cells . Additionally, this compound’s high affinity for the protease enzyme makes it effective against HIV strains that have developed resistance to other protease inhibitors .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound have been observed to change over time. This compound is generally stable and maintains its efficacy over extended periods . Long-term studies have shown that resistance-associated mutations can emerge in patients experiencing virological failure during prolonged use of this compound . These mutations can reduce the drug’s effectiveness, necessitating adjustments in treatment regimens .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. Studies have shown that higher doses of this compound result in increased drug concentrations in the brain, liver, and plasma . At high doses, this compound can also cause toxic or adverse effects, such as gastrointestinal disturbances and lipid abnormalities . It is essential to determine the optimal dosage to maximize efficacy while minimizing adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized by the cytochrome P450 3A (CYP3A) isoenzymes in the liver . The metabolic pathways involve carbamate hydrolysis, isobutyl aliphatic hydroxylation, and aniline aromatic hydroxylation . Ritonavir, a CYP3A inhibitor, is often co-administered with this compound to enhance its bioavailability and prolong its half-life . This combination allows for lower daily doses of this compound while maintaining its therapeutic efficacy .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. It exhibits sufficient membrane permeability to achieve adequate intestinal absorption . The drug is also subject to active transport processes, such as those mediated by P-glycoprotein (P-gp) or other efflux proteins . These transporters play a role in the drug’s localization and accumulation within different tissues .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound is primarily within the cytoplasm, where it interacts with the HIV-1 protease enzyme . This compound’s activity is not significantly affected by targeting signals or post-translational modifications, as its primary function is to inhibit the protease enzyme within the cytoplasmic compartment . This localization ensures that this compound effectively disrupts the viral replication process within infected cells .
Métodos De Preparación
Rutas Sintéticas y Condiciones de Reacción: La síntesis de darunavir involucra múltiples pasos, incluida la formación de intermediarios clave y su posterior acoplamiento. Una ruta sintética común incluye la eliminación del grupo BOC utilizando ácido trifluoroacético en diclorometano, seguida de la reacción con un carbonato en presencia de trietilamina para producir this compound .
Métodos de Producción Industrial: La producción industrial de this compound etanolato implica un proceso robusto con múltiples aislamientos y pasos de secado. Este proceso garantiza un alto rendimiento químico y pureza, con impurezas críticas del proceso controladas por debajo de los límites deseados . Además, se emplean métodos como la extrusión en caliente y la pulverización para mejorar la solubilidad y la biodisponibilidad de this compound .
Análisis De Reacciones Químicas
Tipos de Reacciones: Darunavir se somete a diversas reacciones químicas, incluida la oxidación, la reducción y la sustitución. Es fuertemente oxidado y metabolizado por enzimas hepáticas del citocromo, principalmente CYP3A4 .
Reactivos y Condiciones Comunes:
Oxidación: Implica enzimas hepáticas del citocromo.
Reducción: No se ha informado comúnmente para this compound.
Sustitución: Implica reacciones con carbonatos y aminas.
Productos Principales: Los productos principales formados a partir de estas reacciones incluyen metabolitos hidroxilados y glucuronidados .
Comparación Con Compuestos Similares
- Amprenavir
- Indinavir
- Saquinavir
- Nelfinavir
- Ritonavir
Comparison: Darunavir is unique among protease inhibitors due to its high genetic barrier to resistance and its ability to inhibit a wide range of protease inhibitor-resistant HIV-1 strains . Unlike some other protease inhibitors, this compound is often used in combination with ritonavir or cobicistat to enhance its pharmacokinetic profile .
Propiedades
IUPAC Name |
[(3aS,4R,6aR)-2,3,3a,4,5,6a-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-4-yl] N-[(2S,3R)-4-[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl-(2-methylpropyl)amino]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylbutan-2-yl]carbamate | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H37N3O7S/c1-18(2)15-30(38(33,34)21-10-8-20(28)9-11-21)16-24(31)23(14-19-6-4-3-5-7-19)29-27(32)37-25-17-36-26-22(25)12-13-35-26/h3-11,18,22-26,31H,12-17,28H2,1-2H3,(H,29,32)/t22-,23-,24+,25-,26+/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
CJBJHOAVZSMMDJ-HEXNFIEUSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC(C)CN(CC(C(CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)OC2COC3C2CCO3)O)S(=O)(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC(C)CN(C[C@H]([C@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)NC(=O)O[C@H]2CO[C@@H]3[C@H]2CCO3)O)S(=O)(=O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C27H37N3O7S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0046779 | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0046779 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
547.7 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
Approximately 0.15 mg/mL at, 6.68e-02 g/L | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01264 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The HIV-1 protease enzyme is necessary for viral precursor protein processing and viral maturation in preparation for infection, and is therefore a target for antiretroviral therapy for HIV. Protease inhibitors are used as a part of highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) in patients diagnosed with HIV infection. It has been shown to effectively suppress the virus, leading to significantly decreased morbidity and mortality rates. Darunavir, a HIV protease inhibitor, prevents HIV replication through binding to the enzyme, stopping the dimerization and the catalytic activity of HIV-1 protease. In particular, it inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded Gag-Pol proteins in cells that have been infected with the virus, halting the formation of mature virus particles, which spread the infection. The close contact that darunavir makes with the primary chains of the active site amino acids (Asp-29 and Asp-30) on the protease likely contributes to its potency and efficacy against resistant variants of HIV-1. Darunavir is known to bind to different sites on the enzyme: the active site cavity and the surface of one of the flexible flaps in the protease dimer. Darunavir can adapt to changes in the shape of a protease enzyme due to its molecular flexibility., Darunavir as a protease inhibitor inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded gag-pol polyproteins in virus infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature and infectious new virions. It was selected for its potency against wild type HIV-1 and HIV strains resistant to currently approved protease inhibitors., Darunavir is an inhibitor of the HIV-1 protease. It selectively inhibits the cleavage of HIV encoded Gag-Pol polyproteins in infected cells, thereby preventing the formation of mature virus particles. | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01264 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7788 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
White, amorphous solid | |
CAS No. |
206361-99-1 | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=206361-99-1 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Darunavir [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0206361991 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01264 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0046779 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Carbamic acid, N-[(1S,2R)-3-[[(4-aminophenyl)sulfonyl](2-methylpropyl)amino]-2-hydroxy-1-(phenylmethyl)propyl]-, (3R,3aS,6aR)-hexahydrofuro[2,3-b]furan-3-yl ester | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DARUNAVIR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/YO603Y8113 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7788 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015393 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
74-76, 74 °C (decomposes) | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB01264 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Darunavir | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7788 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Descargo de responsabilidad e información sobre productos de investigación in vitro
Tenga en cuenta que todos los artículos e información de productos presentados en BenchChem están destinados únicamente con fines informativos. Los productos disponibles para la compra en BenchChem están diseñados específicamente para estudios in vitro, que se realizan fuera de organismos vivos. Los estudios in vitro, derivados del término latino "in vidrio", involucran experimentos realizados en entornos de laboratorio controlados utilizando células o tejidos. Es importante tener en cuenta que estos productos no se clasifican como medicamentos y no han recibido la aprobación de la FDA para la prevención, tratamiento o cura de ninguna condición médica, dolencia o enfermedad. Debemos enfatizar que cualquier forma de introducción corporal de estos productos en humanos o animales está estrictamente prohibida por ley. Es esencial adherirse a estas pautas para garantizar el cumplimiento de los estándares legales y éticos en la investigación y experimentación.