Mechlorethamine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Il était à l'origine dérivé de la recherche sur le gaz moutarde et est depuis devenu une pierre angulaire dans le traitement de divers cancers, notamment la maladie de Hodgkin, le lymphosarcome et certains types de leucémie . La méchlorethamine est connue pour sa capacité à interférer avec la réplication de l'ADN, conduisant à la mort cellulaire.
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions réactionnelles : La méchlorethamine est synthétisée par réaction de l'éthylèneimine avec l'acide chlorhydrique, suivie de l'addition de la méthylamine. Les conditions réactionnelles impliquent généralement :
Température : Contrôlée autour de 0-5°C pour éviter la décomposition.
Solvant : Souvent réalisée en milieu aqueux.
Purification : Le produit est purifié par distillation ou recristallisation.
Méthodes de production industrielle : Dans les milieux industriels, la méchlorethamine est produite dans des réacteurs à grande échelle avec des contrôles stricts pour garantir la pureté et la sécurité. Le processus implique :
Traitement par lots : Pour maintenir le contrôle des conditions réactionnelles.
Mesures de sécurité : En raison de sa nature toxique, les installations de production sont équipées de systèmes de ventilation et de confinement avancés.
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions : La méchlorethamine subit plusieurs types de réactions chimiques, notamment :
Alkylation : Elle forme des liaisons covalentes avec l'ADN, conduisant à des réticulations et des cassures de brins.
Hydrolyse : Dans les milieux aqueux, la méchlorethamine peut s'hydrolyser pour former des composés moins actifs.
Réactifs et conditions courantes :
Réactions d'alkylation : Typiquement réalisées en présence d'ADN ou d'autres nucléophiles.
Hydrolyse : Se produit facilement dans l'eau ou les solutions aqueuses.
Principaux produits formés :
Adduits d'ADN : Les principaux produits des réactions d'alkylation avec l'ADN.
Dérivés hydrolysés : résultant de réactions d'hydrolyse.
4. Applications de la recherche scientifique
La méchlorethamine a une large gamme d'applications dans la recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisée comme composé modèle pour étudier les réactions d'alkylation et les interactions avec l'ADN.
Biologie : Employée dans la recherche sur les mécanismes de réparation de l'ADN et la mutagenèse.
Médecine : Composant clé des schémas de chimiothérapie pour le traitement de divers cancers.
Industrie : Utilisée dans la synthèse d'autres composés pharmaceutiques
5. Mécanisme d'action
La méchlorethamine exerce ses effets par la formation d'ions carbonium, qui alkylent les bases de l'ADN. Cela conduit à la formation de liaisons croisées interbrins et intrabrins, entraînant une mauvaise traduction, des cassures de brins et, finalement, la mort cellulaire. Les principales cibles moléculaires sont les atomes d'azote N7 des bases guanine de l'ADN .
Composés similaires :
Cyclophosphamide : Un autre agent alkylant utilisé en chimiothérapie.
Chlorambucil : Un composé apparenté avec des mécanismes d'action similaires.
Melphalan : Utilisé dans le traitement du myélome multiple et du cancer de l'ovaire.
Comparaison :
Puissance : La méchlorethamine est très puissante et agit rapidement par rapport à certains autres agents alkylants.
Toxicité : Elle présente un profil de toxicité plus élevé, nécessitant une manipulation et une administration prudentes.
La méchlorethamine reste un composé essentiel dans le domaine de la chimiothérapie, avec des recherches en cours pour explorer tout son potentiel et ses applications.
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Mechlorethamine has a wide range of applications in scientific research:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound for studying alkylation reactions and DNA interactions.
Biology: Employed in research on DNA repair mechanisms and mutagenesis.
Medicine: A key component in chemotherapy regimens for treating various cancers.
Industry: Utilized in the synthesis of other pharmaceutical compounds
Mécanisme D'action
Mechlorethamine exerts its effects through the formation of carbonium ions, which alkylate DNA bases. This leads to the formation of interstrand and intrastrand cross-links, resulting in miscoding, strand breaks, and ultimately, cell death. The primary molecular targets are the N7 nitrogen atoms of guanine bases in DNA .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Cyclophosphamide: Another alkylating agent used in chemotherapy.
Chlorambucil: A related compound with similar mechanisms of action.
Melphalan: Used in the treatment of multiple myeloma and ovarian cancer.
Comparison:
Potency: Mechlorethamine is highly potent and acts rapidly compared to some other alkylating agents.
Toxicity: It has a higher toxicity profile, necessitating careful handling and administration.
Mechanism: While all these compounds alkylate DNA, this compound’s rapid action and high reactivity make it unique.
This compound remains a critical compound in the field of chemotherapy, with ongoing research exploring its full potential and applications.
Propriétés
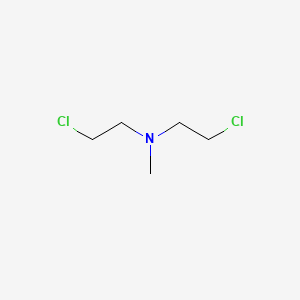
IUPAC Name |
2-chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methylethanamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C5H11Cl2N/c1-8(4-2-6)5-3-7/h2-5H2,1H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
HAWPXGHAZFHHAD-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(CCCl)CCCl | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C5H11Cl2N | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
126-85-2 (N-oxide), 302-70-5 (N-oxide, hydrochloride), 55-86-7 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000051752 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID2020975 | |
| Record name | Nitrogen mustard | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2020975 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
156.05 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Mobile liquid; faint odor of herring. Used as a drug for the treatment of cancer. Formerly used as a gas warfare agent., Colorless to pale yellow, oily liquid with a faint soapy odor or fruity odor at high concentrations; [ATSDR-MMG], Solid | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Nitrogen mustard (HN-2) | |
| Source | Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases | |
| URL | https://haz-map.com/Agents/1512 | |
| Description | Haz-Map® is an occupational health database designed for health and safety professionals and for consumers seeking information about the adverse effects of workplace exposures to chemical and biological agents. | |
| Explanation | Copyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015025 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
189 °F at 18 mmHg (EPA, 1998), 87°C at 1.80E+01 mm Hg, 87 °C @ 18 mm Hg | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00888 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Solubility |
Very soluble, Very slightly soluble in water; miscible with dimethyl formamide, carbon disulfide, carbon tetrachloride, many organic solvents and oils, 3.34e+01 g/L | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00888 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015025 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Density |
1.118 at 77 °F (EPA, 1998) - Denser than water; will sink, 1.118 @ 25 °C/4 °C | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Vapor Density |
5.9 (Air=1) | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Vapor Pressure |
0.42 [mmHg], 0.17 mm Hg @ 25 °C | |
| Record name | Nitrogen mustard (HN-2) | |
| Source | Haz-Map, Information on Hazardous Chemicals and Occupational Diseases | |
| URL | https://haz-map.com/Agents/1512 | |
| Description | Haz-Map® is an occupational health database designed for health and safety professionals and for consumers seeking information about the adverse effects of workplace exposures to chemical and biological agents. | |
| Explanation | Copyright (c) 2022 Haz-Map(R). All rights reserved. Unless otherwise indicated, all materials from Haz-Map are copyrighted by Haz-Map(R). No part of these materials, either text or image may be used for any purpose other than for personal use. Therefore, reproduction, modification, storage in a retrieval system or retransmission, in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical or otherwise, for reasons other than personal use, is strictly prohibited without prior written permission. | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Alkylating agents work by three different mechanisms: 1) attachment of alkyl groups to DNA bases, resulting in the DNA being fragmented by repair enzymes in their attempts to replace the alkylated bases, preventing DNA synthesis and RNA transcription from the affected DNA, 2) DNA damage via the formation of cross-links (bonds between atoms in the DNA) which prevents DNA from being separated for synthesis or transcription, and 3) the induction of mispairing of the nucleotides leading to mutations. Mechlorethamine is cell cycle phase-nonspecific., Mechlorethamine, as an alkylating agent, interferes with DNA replication and transcription of RNA, and ultimately results in the disruption of nucleic acid function., The alkylating agent, nitrogen mustard (HN2), is thought to cause apoptosis through production of free oxygen radicals. To explore the mechanism of HN2-induced apoptosis, we utilized ebselen, a selenoorganic compound with potent antioxidant activity. We examined whether ebselen would inhibit apoptosis in BALB/c mouse spleen lymphocytes and human MOLT-4 leukemia cells treated with HN2 (2.5 microM) in vitro. Non-toxic concentrations (<50 microM) of ebselen were found to prevent HN2-induced apoptosis of murine lymphocytes in a dose-dependent manner, as measured by cell viability, hypodiploid DNA formation, and phosphatidylserine externalization. However, ebselen was ineffective at preventing spontaneous apoptosis in these cells, pointing to the selectivity of its action. Furthermore, pretreatment with ebselen at 1-10 microM for 72 hr protected MOLT-4 cells from HN2-induced apoptosis and maintained cell viability and proliferation as monitored by the above-mentioned parameters. This was accompanied by the preservation of mitochondrial transmembrane potential and elevated glutathione levels and by a blockage of caspase-3 and -9 activation. In vivo, ebselen also had a marked protective effect against spleen weight loss associated with lymphocyte apoptosis in mice treated by HN2. Therefore, ebselen provides an efficient protection against HN2-induced cell death in normal and tumoral lymphocytes and might prove useful as an antidote against alkylating agents., Nitrogen mustard (bis(2-chloroethyl) methylamine, HN2) inhibited the binding of upstream factors Sp1 and AP2 to their consensus sequences. At concentrations where 50% of the consensus sequence DNA contained at least one lesion, HN2 inhibited formation of the Sp1 complex by 37% (40 microM HN2) and the AP2 complex by 40% (50 microM HN2). The binding of the TATA binding protein (TBP) to the TATA element was also inhibited by HN2, whereas sulphur mustard and the monofunctional sulphur mustard 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulphide (CEES) resulted in a disproportional extent of inhibition with respect to the level of alkylation. The level of alkylation of the TBP oligonucleotide varied significantly at 100 microM drug, with 80, 42 and 15% of HN2, sulphur mustard and CEES, respectively. However, this level of alkylation inhibited formation of the TBP-DNA complex by 70, 70 and 45%, respectively. This differential sensitivity of transcription factors to mustard-induced DNA damage therefore appears to reside dominantly in the stereochemical differences between the specific mustard lesions., The ability of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine to prevent apoptosis induced in lymphocytes by nitrogen mustard (HN2) was investigated. HN2 caused a concentration-dependent induction of apoptosis on C3H murine spleen cells, as identified by two criteria: morphological features revealed by microscopical observations and DNA fragmentation visualized by the characteristic "ladder" pattern observed upon agarose gel electrophoresis, as well as by hypodiploid DNA-containing cells revealed by the flow cytometric analysis of propidium iodide labelled cells. The antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) was found to markedly reduce the occurrence of HN2-induced apoptosis in these cells. This protective effect will still obtained when NAC was added 30 min after HN2. In contrast, the pretreatment of spleen cells with this antioxidant did not provide any significant protection. We also showed that lymphocytes protected by NAC are still able to respond to a mitogenic stimulation. To gain some insight into the mechanisms underlying the cytoprotective action of NAC against HN2, we tested whether or not poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP, EC 2.4.2.30), a nuclear enzyme that participates in the triggering of apoptosis induced by alkylating agents, is involved. We report that 6(5H)-phenanthridinone, a potent PARP inhibitor, did not affect the ability of NAC to prevent HN2-induced apoptosis under our experimental conditions. Thus, the exact mechanism by which NAC protects lymphocytes from HN2 cytotoxicity has yet to be determined. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00888 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Mobile liquid, Dark liquid, Liquid, colorless/pale yellow when fresh | |
CAS No. |
51-75-2 | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=51-75-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000051752 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00888 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=757087 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Nitrogen Mustard-2 | |
| Source | EPA Acute Exposure Guideline Levels (AEGLs) | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/aegl/nitrogen-mustard-2-results-aegl-program | |
| Description | Acute Exposure Guideline Levels (AEGLs) are used by emergency planners and responders worldwide as guidance in dealing with rare, usually accidental, releases of chemicals into the air. https://www.epa.gov/aegl | |
| Record name | Ethanamine, 2-chloro-N-(2-chloroethyl)-N-methyl- | |
| Source | EPA Chemicals under the TSCA | |
| URL | https://www.epa.gov/chemicals-under-tsca | |
| Description | EPA Chemicals under the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) collection contains information on chemicals and their regulations under TSCA, including non-confidential content from the TSCA Chemical Substance Inventory and Chemical Data Reporting. | |
| Record name | Nitrogen mustard | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID2020975 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Chlormethine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.110 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/50D9XSG0VR | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015025 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
-76 °F (EPA, 1998), -60 °C, 108 - 111 °C | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | CAMEO Chemicals | |
| URL | https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5046 | |
| Description | CAMEO Chemicals is a chemical database designed for people who are involved in hazardous material incident response and planning. CAMEO Chemicals contains a library with thousands of datasheets containing response-related information and recommendations for hazardous materials that are commonly transported, used, or stored in the United States. CAMEO Chemicals was developed by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's Office of Response and Restoration in partnership with the Environmental Protection Agency's Office of Emergency Management. | |
| Explanation | CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00888 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | MECHLORETHAMINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/5083 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Mechlorethamine | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0015025 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![3-Oxo-3-[(1-phenyl-3-sulfanylpropan-2-yl)amino]propanoic acid](/img/structure/B1211290.png)
![2-[4-(Pyridin-4-ylmethylsulfamoyl)phenoxy]acetic acid methyl ester](/img/structure/B1211304.png)