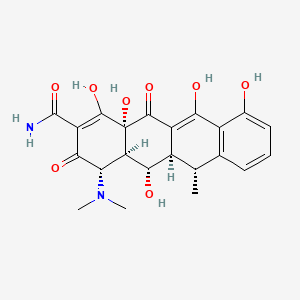
Doxycycline
Vue d'ensemble
Description
La doxycycline est un antibiotique à large spectre appartenant à la classe des tétracyclines. Elle est utilisée pour traiter une variété d’infections bactériennes, notamment la pneumonie bactérienne, l’acné, les infections à chlamydia, la maladie de Lyme, le choléra, le typhus et la syphilis. Elle est également utilisée pour prévenir le paludisme . La this compound a été brevetée pour la première fois en 1957 et commercialisée en 1967 . Elle est disponible en tant que médicament générique et figure sur la Liste des médicaments essentiels de l’Organisation mondiale de la santé .
Mécanisme D'action
La doxycycline exerce ses effets en inhibant la synthèse des protéines bactériennes. Elle se lie de manière réversible à la sous-unité ribosomale 30S, empêchant l’association de l’aminoacyl-ARNt avec le ribosome bactérien . Cette inhibition de la synthèse des protéines est bactériostatique, ce qui signifie qu’elle empêche la croissance et la reproduction des bactéries. La this compound cible également l’apicoplaste dans les parasites responsables du paludisme, perturbant leur fonctionnement .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Doxycycline has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Medicine: It is used to treat various bacterial infections and as a prophylactic agent for malaria.
Industry: This compound is used in veterinary medicine and as an animal feed supplement to prevent diseases.
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Doxycycline interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It is a highly lipophilic drug, which allows it to cross multiple membranes of target molecules . This property facilitates its favorable intracellular penetration, exhibiting bacteriostatic activity against a wide range of bacteria .
Cellular Effects
This compound has been found to alter the metabolism and proliferation of human cell lines . It changes gene expression patterns and shifts metabolism towards a more glycolytic phenotype, evidenced by increased lactate secretion and reduced oxygen consumption . These concentrations of this compound are also sufficient to slow proliferation .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound exerts its effects at the molecular level primarily by inhibiting protein synthesis . It does this by interacting with the 30S ribosomal subunits, thereby slowing or killing bacteria . It also kills malaria by targeting a plastid organelle, the apicoplast .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, commonly used concentrations of this compound have been observed to change gene expression patterns over time . This results in a shift in metabolism towards a more glycolytic phenotype, evidenced by increased lactate secretion and reduced oxygen consumption . These concentrations are also sufficient to slow cell proliferation .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models . For instance, in donkeys, it has been observed that the concentration of this compound reached in all fluids and tissues analyzed would unlikely result in therapeutic concentration against common equine pathogens .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in various metabolic pathways. It has been reported to shift metabolism towards a more glycolytic phenotype in human cell lines . This is evidenced by increased lactate secretion and reduced oxygen consumption .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is more or less completely absorbed and is 3–5 times more lipophilic than drugs in group 1 . This may improve their tissue distribution but convincing data is absent . It is available in oral and intravenous formulations .
Subcellular Localization
As a highly lipophilic drug, this compound is known to cross multiple membranes of target molecules, which may influence its subcellular localization .
Méthodes De Préparation
La doxycycline est dérivée synthétiquement de l’oxytétracycline. La préparation implique plusieurs étapes :
Chloration et Déshydratation : L’oxytétracycline subit une chloration et une déshydratation pour former le p-toluènesulfonate de 11 alpha-chloro-6-méthényl oxytétracycline.
Hydrogénation : Ce composé intermédiaire est ensuite soumis à un processus d’hydrogénation en une ou deux étapes pour produire le p-toluènesulfonate de this compound.
Raffinage : Enfin, le produit est raffiné pour former le chlorhydrate de this compound.
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
La doxycycline subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Photodégradation : La this compound est sensible à la lumière et subit une photodégradation, qui peut être atténuée en formant des complexes de cyclodextrine.
Hydrolyse : Le composé peut également subir une hydrolyse dans certaines conditions.
Les réactifs couramment utilisés dans ces réactions comprennent le peroxyde d’hydrogène pour la péroxydation et l’ozone pour l’ozonation. Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions sont généralement des formes dégradées de la this compound avec une activité antimicrobienne réduite .
4. Applications de la Recherche Scientifique
La this compound a une large gamme d’applications de recherche scientifique :
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
La doxycycline est souvent comparée à d’autres tétracyclines telles que la tétracycline, l’oxytétracycline, la chlortétracycline, la déméclocycline, la lymecycline, la méthacycline et la minocycline . Comparée à ces composés, la this compound présente plusieurs caractéristiques uniques :
Absorption : La this compound est absorbée par voie orale de manière plus fiable que les anciennes tétracyclines.
Lipophilie : Elle est plus lipophiles, ce qui lui permet de traverser plus facilement les bicouches lipidiques bactériennes.
Demi-vie : La this compound a une demi-vie sérique plus longue, ce qui permet des posologies moins fréquentes.
Les composés similaires comprennent :
Minocycline : Une autre tétracycline de deuxième génération présentant des propriétés d’absorption et de lipophilie similaires.
Tétracycline : Une tétracycline plus ancienne présentant une absorption moins bonne et une demi-vie plus courte.
Tigecycline : Une glycylcycline présentant un spectre antibactérien amélioré, mais uniquement disponible sous forme injectable.
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aR)-4-(dimethylamino)-1,5,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-3,12-dioxo-4a,5,5a,6-tetrahydro-4H-tetracene-2-carboxamide | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C22H24N2O8/c1-7-8-5-4-6-9(25)11(8)16(26)12-10(7)17(27)14-15(24(2)3)18(28)13(21(23)31)20(30)22(14,32)19(12)29/h4-7,10,14-15,17,25-27,30,32H,1-3H3,(H2,23,31)/t7-,10+,14+,15-,17-,22-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
SGKRLCUYIXIAHR-AKNGSSGZSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1C2C(C3C(C(=O)C(=C(C3(C(=O)C2=C(C4=C1C=CC=C4O)O)O)O)C(=O)N)N(C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C[C@@H]1[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]3[C@@H](C(=O)C(=C([C@]3(C(=O)C2=C(C4=C1C=CC=C4O)O)O)O)C(=O)N)N(C)C)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C22H24N2O8 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
17086-28-1 (mono-hydrate), 41411-66-9 (6-epimer, mono-hydrochloride), 69935-17-7 (mono-hydrochloride, di-hydrate), 94088-85-4 (calcium salt (1:2)) | |
| Record name | Doxycycline [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000564250 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID0037653, DTXSID80992212 | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0037653 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 4-(Dimethylamino)-1,5,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-3,12-dioxo-3,4,4a,5,5a,6,12,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboximidic acid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID80992212 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
444.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
SOL IN WATER /DOXYCYCLINE HYDROCHLORIDE/, VERY SLIGHTLY SOL IN WATER; SPARINGLY SOL IN ALC; FREELY SOL IN DIL ACID & ALKALI HYDROXIDE SOLN; PRACTICALLY INSOL IN CHLOROFORM & ETHER. | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00254 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | DOXYCYCLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3071 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Protein synthesis is essential for survival and functioning of cells, including bacteria. Doxycycline inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by allosterically binding to the 30S prokaryotic ribosomal subunit. The drug blocks the association charged aminoacyl-tRNA (aa-tRNA) with the ribosomal A site, which is the acceptor site on the mRNA-ribosome complex. Doxycycline ultimately impedes the elongation phase of protein synthesis and halts the production of essential proteins for bacterial survival and functioning. Doxycycline mediates anti-inflammatory actions by preventing calcium-dependent microtubular assembly and lymphocytic proliferation, thereby inhibiting leukocyte movement during inflammation. It also inhibits nitric oxide synthase, which is an enzyme that produces nitric oxide, an inflammatory signaling molecule., TETRACYCLINES INHIBIT BACTERIAL PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. ... ONCE TETRACYCLINES GAIN ACCESS TO THE BACTERIAL CELL, THEY BIND PRINCIPALLY TO 30 S SUBUNITS OF BACTERIAL RIBOSOMES. THEY APPEAR TO PREVENT ACCESS OF AMINOACYL T-RNA TO M-RNA-RIBOSOME COMPLEX. ... ONLY SMALL PORTION OF DRUG IS IRREVERSIBLY BOUND, & INHIBITORY EFFECTS OF THE TETRACYCLINESARE REVERSIBLE WHEN THE DRUG IS REMOVED. /TETRACYCLINES/ | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00254 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | DOXYCYCLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3071 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
YELLOW, CRYSTALLINE POWDER | |
CAS No. |
564-25-0, 7164-70-7, 24390-14-5 | |
| Record name | Doxycycline [USAN:INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000564250 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00254 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID0037653 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 4-(Dimethylamino)-1,5,10,11,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-3,12-dioxo-3,4,4a,5,5a,6,12,12a-octahydrotetracene-2-carboximidic acid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID80992212 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Doxycycline | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.008.429 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | 2-Naphthacenecarboxamide, 4-(dimethylamino)-1,4,4a,5,5a,6,11,12a-octahydro-3,5,10,12,12a-pentahydroxy-6-methyl-1,11-dioxo-, hydrochloride, (4S,4aR,5S,5aR,6R,12aS)-, compd. with ethanol, hydrate (2:2:1:1) | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.106.555 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Doxycycline Hyclate | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DOXYCYCLINE ANHYDROUS | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/334895S862 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | DOXYCYCLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3071 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Q1: What is doxycycline's primary mechanism of action?
A1: this compound is a tetracycline antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, effectively blocking the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA to the ribosomal acceptor (A) site. []
Q2: How does this compound affect Brugia malayi infections?
A2: this compound targets the endosymbiotic bacteria Wolbachia, which is essential for Brugia malayi survival and reproduction. By reducing Wolbachia loads, this compound effectively decreases microfilaremia and reduces adverse reactions associated with standard antifilarial treatment. []
Q3: Does this compound impact matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)?
A3: Yes, this compound has been shown to inhibit MMP activity, particularly MMP-2 and MMP-9. This inhibition is attributed to its chelating properties, where it binds to metal ions essential for MMP catalytic activity. [, ]
Q4: How does this compound influence epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)?
A4: this compound has been shown to inhibit TGF-beta1-induced EMT and cell migration in respiratory epithelial cells by suppressing the activation of Smad2/3 and p38 signaling pathways. []
Q5: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A5: this compound hyclate, the commonly used form, has a molecular formula of C22H24N2O8 • HCl • 1/2 C2H6O • 1/2 H2O and a molecular weight of 512.94 g/mol.
Q6: Is there any spectroscopic data available for this compound?
A6: While the provided research papers don't detail specific spectroscopic data, FTIR analysis has been used to evaluate drug-drug interactions between this compound and monocaprin in a hydrogel formulation. []
Q7: How stable is this compound in different formulations?
A7: this compound stability can be affected by various factors, including formulation components and storage conditions. For instance, the addition of monocaprin to this compound in situ hydrogel negatively impacted this compound stability in a concentration-dependent manner. []
Q8: Can you provide an example of this compound's compatibility in a specific application?
A8: this compound has been successfully incorporated into biodegradable poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanofibers for targeted drug delivery in tendon rupture repair. []
Q9: How do structural modifications affect this compound's activity?
A9: While the provided papers do not directly investigate SAR, research on optimized tetracyclines with modifications at the 7-position shows enhanced in vitro and in vivo antimalarial activity compared to this compound. []
Q10: What strategies are employed to enhance this compound's stability and bioavailability?
A10: Various formulation strategies, such as encapsulation in nanofibers [] and incorporation into in situ hydrogels [], are being explored to improve this compound's stability, solubility, and controlled release for targeted delivery and enhanced therapeutic outcomes.
Q11: How is this compound absorbed and distributed in the body?
A11: this compound is well-absorbed orally and achieves therapeutic concentrations in serum and tissues, including lung and synovial fluid. Its lipid solubility allows for good tissue penetration. [, ]
Q12: What factors can influence this compound's pharmacokinetics?
A12: Co-administration of certain drugs can alter this compound's PK profile. For example, oral antacid administration was found to enhance the clearance of intravenous this compound, shortening its half-life and increasing total body clearance. []
Q13: Does this compound cross the blood-brain barrier?
A13: Yes, this compound can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and achieve therapeutic concentrations in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), making it effective for treating neuroborreliosis. []
Q14: How is this compound eliminated from the body?
A14: this compound is primarily eliminated through both renal and non-renal pathways. It is excreted in urine and feces. []
Q15: Can this compound levels be measured in biological samples?
A15: Yes, various analytical methods like high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) are used to quantify this compound concentrations in biological samples such as serum, plasma, CSF, and tears. [, , ]
Q16: What cell lines have been used to study this compound's effects?
A16: Researchers have employed various cell lines, including A549 lung cells [], primary human corneal epithelial cells [], and equine synoviocytes [], to investigate this compound's impact on EMT, MMP expression, and other cellular processes.
Q17: Are there animal models used in this compound research?
A17: Yes, this compound's efficacy and safety have been evaluated in animal models, including rat models for tendon rupture repair [], murine models for Mycobacterium avium infection [], and canine models for monocytic ehrlichiosis. []
Q18: Has this compound been tested in clinical trials?
A18: Yes, several clinical trials have investigated the efficacy and safety of this compound for various conditions. For example, a randomized controlled trial assessed the effect of this compound on MMP expression in atherosclerotic plaques in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy. []
Q19: Are there known mechanisms of resistance to this compound?
A19: Yes, bacterial resistance to this compound can occur through mechanisms such as efflux pump overexpression, ribosomal protection proteins, and enzymatic inactivation. []
Q20: Is there cross-resistance between this compound and other antibiotics?
A20: Cross-resistance can occur between this compound and other tetracycline-class antibiotics due to shared mechanisms of resistance. []
Q21: What drug delivery strategies have been explored for this compound?
A21: Researchers are investigating novel drug delivery systems for this compound, including electrospun nanofibrous membranes for localized and sustained release in tendon rupture repair. []
Q22: What analytical methods are used to quantify this compound?
A22: Common analytical techniques include HPLC, LC-MS, and microbial assays. These methods are employed to measure this compound concentrations in various biological samples and assess its pharmacokinetics, residues, and stability in different formulations. [, , ]
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![Methyl 1,5-dibromo-11,17-dimethoxy-18-[(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)oxy]yohimban-16-carboxylate](/img/structure/B607107.png)