Cobimetinib
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le Cobimetinib, commercialisé sous le nom de marque Cotellic, est un médicament anticancéreux utilisé principalement en association avec le vemurafenib pour traiter le mélanome. Il s'agit d'un inhibiteur sélectif de la kinase 1 activatrice du mitogène et de la protéine kinase 2 (MEK1 et MEK2), qui font partie de la voie de signalisation des kinases activées par les mitogènes/kinases régulées par le signal extracellulaire (MAPK/ERK) . Cette voie est souvent suractivée dans divers cancers, ce qui fait du this compound un agent thérapeutique précieux .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Cobimetinib has several scientific research applications:
Chemistry: It is used as a model compound to study MEK inhibition and its effects on the MAPK/ERK pathway.
Medicine: It is primarily used in combination with vemurafenib to treat unresectable or metastatic melanoma with BRAF V600 mutations It is also being studied for its potential in treating other cancers, such as breast cancer.
Industry: This compound is produced and marketed by pharmaceutical companies for therapeutic use.
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Cobimetinib is a highly selective small molecule that primarily targets the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MAP2K1 or MEK1) . MEK1 is a central component of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signal transduction pathway , which plays a crucial role in regulating cell cycle, proliferation, differentiation, and secretion .
Mode of Action
This compound acts as a reversible inhibitor of MEK1 and MEK2 . It binds to these kinases and selectively inhibits their activity, even when MEK is already phosphorylated . This inhibition results in decreased ERK1/2 phosphorylation .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound is the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway . This pathway is activated in response to various stimuli and regulates the proliferation and survival of several types of eukaryotic cells . By inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2, this compound disrupts this pathway, leading to decreased ERK1/2 phosphorylation .
Pharmacokinetics
This compound is an orally active compound .
Result of Action
The inhibition of MEK1 and MEK2 by this compound leads to a decrease in ERK1/2 phosphorylation . This disruption of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway can slow or stop the proliferation of cancer cells . In addition, this compound has been found to induce damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), such as cell-surface translocation of calreticulin (CRT), extracellular release of ATP, and increase in high-mobility group box protein B1 (HMGB1) release from dying tumor cells .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Cobimetinib plays a crucial role in biochemical reactions by inhibiting the activity of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 2 (MEK2). These enzymes are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation . By inhibiting MEK1 and MEK2, this compound effectively reduces the phosphorylation and activation of ERK1 and ERK2, leading to decreased cellular proliferation . This compound interacts with these enzymes through reversible binding, which allows it to inhibit their activity without permanently altering their structure .
Cellular Effects
This compound has significant effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It primarily influences cell function by inhibiting the MEK/ERK signaling pathway, which is crucial for cell proliferation and survival . In cancer cells, this compound induces apoptosis and inhibits cell growth by reducing the phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition leads to decreased expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression and survival, ultimately resulting in reduced cellular proliferation and increased cell death . Additionally, this compound has been shown to induce immunogenic cell death in certain cancer cell lines, further enhancing its anti-tumor effects .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its selective inhibition of MEK1 and MEK2, which are key components of the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway . This compound binds to the allosteric site of MEK1 and MEK2, preventing their activation and subsequent phosphorylation of ERK1 and ERK2 . This inhibition disrupts the downstream signaling cascade, leading to decreased cellular proliferation and increased apoptosis . This compound’s ability to maintain its inhibitory effect even when MEK is already phosphorylated further enhances its efficacy in targeting cancer cells .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. At lower doses, this compound effectively inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis without causing significant toxicity . At higher doses, this compound can cause adverse effects, including gastrointestinal toxicity, hepatotoxicity, and cardiotoxicity . These toxic effects highlight the importance of optimizing the dosage of this compound to achieve maximum therapeutic benefit while minimizing adverse effects .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized through the cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4) pathway . This metabolic pathway involves the oxidation of this compound, leading to the formation of various metabolites that are subsequently excreted in the feces and urine . The metabolism of this compound can be influenced by other drugs that inhibit or induce CYP3A4, potentially affecting its efficacy and safety . Additionally, this compound’s interaction with other enzymes and cofactors involved in its metabolism can impact its pharmacokinetics and overall therapeutic profile .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues through various mechanisms. It is highly protein-bound, with approximately 95% of the drug bound to plasma proteins . This high protein binding affects its distribution and bioavailability, as only the unbound fraction of this compound is pharmacologically active . This compound is also subject to active transport by efflux transporters, such as P-glycoprotein, which can influence its intracellular concentration and distribution . These transport mechanisms play a crucial role in determining the localization and accumulation of this compound within different tissues and cells .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of this compound is primarily determined by its interaction with specific targeting signals and post-translational modifications. This compound is known to localize to the cytoplasm, where it exerts its inhibitory effects on MEK1 and MEK2 . The presence of specific targeting signals, such as nuclear localization signals, can also influence the subcellular distribution of this compound, directing it to specific compartments or organelles . These localization patterns are critical for this compound’s activity and function, as they determine its ability to effectively inhibit the MEK/ERK signaling pathway and exert its anti-tumor effects .
Méthodes De Préparation
La synthèse du cobimetinib implique plusieurs étapes à partir de l'acide (2S)-2-pipéridinecarboxylique. Le processus comprend la nitration, l'hydrolyse, l'estérification et la protection tert-butoxycarbonyle (Boc) pour produire un intermédiaire, l'acétate de [2-oxo-2-((2S)-1-tert-butoxycarbonylpipéridin-2-yl)] . Cet intermédiaire subit des réactions d'addition, de réduction et de cyclisation pour former la (2S)-1-tert-butoxycarbonyl-2-(3-hydroxyazétidin-3-yl)pipéridine, qui est ensuite condensée avec une chaîne latérale pour donner le this compound . Le processus est conçu pour être économique, respectueux de l'environnement et adapté à la production industrielle .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Le Cobimetinib subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Le this compound est métabolisé principalement par oxydation du cytochrome P450 3A4 (CYP3A4).
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction font partie de sa voie de synthèse.
Substitution : La synthèse implique des réactions de substitution pour introduire des groupes fonctionnels
Les réactifs et conditions courants utilisés dans ces réactions comprennent le chlorure de tert-butoxycarbonyle pour la protection Boc, et divers agents réducteurs pour les étapes de réduction . Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions sont des intermédiaires conduisant à la molécule finale de this compound .
4. Applications de recherche scientifique
Le this compound a plusieurs applications de recherche scientifique :
Médecine : Il est principalement utilisé en association avec le vemurafenib pour traiter le mélanome non résécable ou métastatique avec des mutations BRAF V600 Il est également étudié pour son potentiel dans le traitement d'autres cancers, comme le cancer du sein.
Industrie : Le this compound est produit et commercialisé par des sociétés pharmaceutiques pour un usage thérapeutique.
5. Mécanisme d'action
Le this compound est un inhibiteur réversible de la MEK1 et de la MEK2, qui sont des régulateurs en amont de la voie ERK . En inhibant ces kinases, le this compound empêche la phosphorylation et l'activation de l'ERK, ce qui entraîne une réduction de la prolifération cellulaire et une augmentation de l'apoptose dans les cellules cancéreuses . Ce mécanisme est particulièrement efficace dans les cancers avec des mutations du gène BRAF, qui conduisent à une activation constitutive de la voie MAPK/ERK .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Le Cobimetinib est l'un des nombreux inhibiteurs de la MEK utilisés dans le traitement du cancer. Des composés similaires comprennent :
Trametinib : Un autre inhibiteur de la MEK utilisé pour traiter le mélanome.
Binimetinib : Utilisé en association avec d'autres médicaments pour le traitement du mélanome et d'autres cancers.
Selumetinib : Utilisé pour traiter la neurofibromatose de type 1 et d'autres cancers.
Le this compound est unique en son utilisation combinée avec le vemurafenib, qui cible une kinase différente dans la voie MAPK/ERK, conduisant à des effets synergiques et à des résultats thérapeutiques améliorés .
Propriétés
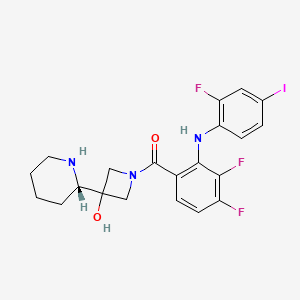
IUPAC Name |
[3,4-difluoro-2-(2-fluoro-4-iodoanilino)phenyl]-[3-hydroxy-3-[(2S)-piperidin-2-yl]azetidin-1-yl]methanone | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H21F3IN3O2/c22-14-6-5-13(19(18(14)24)27-16-7-4-12(25)9-15(16)23)20(29)28-10-21(30,11-28)17-3-1-2-8-26-17/h4-7,9,17,26-27,30H,1-3,8,10-11H2/t17-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
BSMCAPRUBJMWDF-KRWDZBQOSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CCNC(C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CCN[C@@H](C1)C2(CN(C2)C(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3)F)F)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)I)F)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H21F3IN3O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60239435 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
531.3 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Cobimetinib is a reversible inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2. MEK proteins are upstream regulators of the extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK) pathway, which promotes cellular proliferation. BRAF V600E and K mutations result in constitutive activation of the BRAF pathway which includes MEK1 and MEK2. In mice implanted with tumor cell lines expressing BRAF V600E, cobimetinib inhibited tumor cell growth. Cobimetinib and vemurafenib target two different kinases in the RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway. Compared to either drug alone, coadministration of cobimetinib and vemurafenib resulted in increased apoptosis in vitro and reduced tumor growth in mouse implantation models of tumor cell lines harboring BRAF V600E mutations. Cobimetinib also prevented vemurafenib-mediated growth enhancement of a wild-type BRAF tumor cell line in an in vivo mouse implantation model. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
934660-93-2 | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=934660-93-2 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib [USAN:INN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0934660932 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05239 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Cobimetinib | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60239435 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | COBIMETINIB | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/ER29L26N1X | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.



![14-[[[(2R)-1,4-dioxan-2-yl]methyl-methylsulfamoyl]amino]-5-(1-methylpyrazol-4-yl)-2-oxo-7-azatricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(11),3(8),4,6,9,12,14-heptaene](/img/structure/B612127.png)
![ethyl 3-cyano-2-(3-pyridin-3-ylprop-2-enoylamino)-5,7-dihydro-4H-thieno[2,3-c]pyridine-6-carboxylate](/img/structure/B612141.png)
