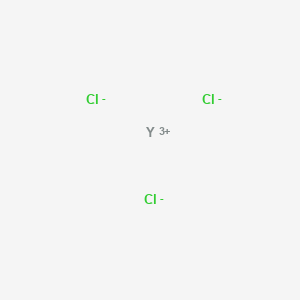
塩化イットリウム(III)
- 専門家チームからの見積もりを受け取るには、QUICK INQUIRYをクリックしてください。
- 品質商品を競争力のある価格で提供し、研究に集中できます。
説明
Yttrium chloride is an inorganic compound composed of yttrium and chloride. It exists in two forms: the hydrate (YCl₃·6H₂O) and the anhydrous form (YCl₃). Both forms are colorless salts that are highly soluble in water and deliquescent . Yttrium chloride is used in various applications, including as a precursor for the synthesis of other yttrium compounds and in materials science.
科学的研究の応用
Yttrium chloride has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: It is used as a precursor for the synthesis of yttrium-based materials, including phosphors and ceramics.
Medicine: Yttrium-based materials are used in medical lasers and biomedical implants.
作用機序
Target of Action
Yttrium(III) chloride, also known as Yttrium chloride(III), is an inorganic compound of yttrium and chloride . It is used as a precursor to synthesize yttrium-based nanomaterials such as yttrium aluminum garnet nanopowder and organometallic yttrium complexes . These materials find application in the field of catalysis, electroluminescent devices, and superconductors . Therefore, the primary targets of Yttrium(III) chloride are these yttrium-based nanomaterials and their associated applications.
Mode of Action
Yttrium(III) chloride reacts with potassium alkoxotitanates to form precursors for titanium-containing ceramics . It is also used in the production of yttrium alkyl alkoxide complexes . The compound interacts with its targets through chemical reactions, leading to the formation of new compounds with desired properties.
Biochemical Pathways
It is known to be involved in the synthesis of yttrium-based nanomaterials and organometallic yttrium complexes , which can have various downstream effects depending on their specific applications.
Pharmacokinetics
It has been documented that most of the yttrium administered was distributed into liver, bone, and spleen . Yttrium disappeared from the blood within 1 day but was retained in the organs for a long time . These findings suggest that Yttrium(III) chloride may have low bioavailability due to its rapid clearance from the blood and long retention in the organs.
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of Yttrium(III) chloride’s action largely depend on its application. For instance, when used as a precursor to synthesize yttrium-based nanomaterials, the result of its action is the formation of these nanomaterials with desired properties .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of Yttrium(III) chloride can be influenced by various environmental factors. For example, its solubility in water and other solvents can affect its availability for reactions . Moreover, its reactivity with other substances can be influenced by factors such as temperature and pH.
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
The biological effects of Yttrium refer to the activity, behavior, and toxicity of Yttrium element or compounds in cells, tissues, organs, and organisms . Yttrium is present in low abundance in soil, water bodies, and organisms . It is not an essential element for organisms and its bioavailability is very low .
Cellular Effects
Yttrium(III) chloride has been found to have acute hepatic injury and transient increase of plasma Ca following the injection . A significant and tremendous amount of Ca was deposited in the liver (over 10-fold) and spleen (over 100-fold), while Ca concentration was only slightly increased in the lung and kidney (less than 1.5-fold) . These results indicate that liver and spleen are primary target organs of intravenous-injected Yttrium(III) chloride .
Molecular Mechanism
Yttrium(III) chloride is taken up by phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen . Electron microscopic analyzes revealed that the colloidal yttrium-containing material was taken up by phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
The elimination half-time of liver Y was 144 days at a dose of 1 mg Y/rat . Yttrium disappeared from the blood within 1 day but was retained in the organs for a long time .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The acute toxicity of Yttrium ion (Y3+), the deposition, retention, metabolism, and clearance have been documented in the previous reports . Hirano et al. studied time-course and dose-related changes in tissue distribution, subcellular localization, clearance, and acute toxicity of intravenous-injected Yttrium(III) chloride in rats .
Metabolic Pathways
Changes in Ca concentrations in liver, spleen, and lungs were in accordance with those of Yttrium(III) chloride . Two mechanisms of REE metabolism in the case of intravenous administration are suggested: (1) The REEs may be transported partly contained in serum protein and partly incorporated into phagocytes, and taken mostly into the reticuloendothelial system by the phagocytic mechanism and deposited there. (2) The major route of excretion of REEs may be biliary excretion and the REEs might be excreted gradually into feces .
Transport and Distribution
Yttrium(III) chloride is transported and distributed within cells and tissues . It is taken up by phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen .
Subcellular Localization
The subcellular localization of Yttrium(III) chloride is within the phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen . Electron microscopic analyzes revealed that the colloidal yttrium-containing material was taken up by phagocytic cells in the liver and spleen .
準備方法
Yttrium chloride is often prepared by the “ammonium chloride route,” starting from either yttrium oxide (Y₂O₃) or hydrated chloride or oxychloride . The synthetic route involves the following reactions:
From Y₂O₃: [ 10 \text{NH}_4\text{Cl} + \text{Y}_2\text{O}_3 \rightarrow 2 (\text{NH}_4)_2[\text{YCl}_5] + 6 \text{NH}_3 + 3 \text{H}_2\text{O} ]
From YCl₃·6H₂O: [ \text{YCl}_3·6\text{H}_2\text{O} + 2 \text{NH}_4\text{Cl} \rightarrow (\text{NH}_4)_2[\text{YCl}_5] + 6 \text{H}_2\text{O} ]
The pentachloride decomposes thermally to yield yttrium chloride(III): [ (\text{NH}_4)_2[\text{YCl}_5] \rightarrow 2 \text{NH}_4\text{Cl} + \text{YCl}_3 ]
化学反応の分析
Yttrium chloride undergoes various types of chemical reactions, including:
Oxidation: Yttrium chloride can be oxidized to form yttrium oxychloride (YClO).
Reduction: It can be reduced to elemental yttrium using strong reducing agents.
Substitution: Yttrium chloride reacts with potassium alkoxotitanates to form precursors for titanium-containing ceramics.
Common reagents and conditions used in these reactions include ammonium chloride, potassium alkoxotitanates, and high temperatures. Major products formed from these reactions include yttrium oxychloride and yttrium alkyl alkoxide complexes.
類似化合物との比較
Yttrium chloride can be compared with other similar compounds, such as:
- Yttrium fluoride(III) (YF₃)
- Yttrium bromide(III) (YBr₃)
- Yttrium iodide(III) (YI₃)
- Scandium chloride(III) (ScCl₃)
- Lutetium chloride(III) (LuCl₃)
Yttrium chloride is unique due to its high solubility in water and its ability to form various yttrium-based materials. Its layered crystal structure, shared by compounds like aluminum chloride (AlCl₃), also contributes to its distinct properties .
特性
CAS番号 |
10361-92-9 |
|---|---|
分子式 |
Cl3Y |
分子量 |
195.26 g/mol |
IUPAC名 |
trichloroyttrium |
InChI |
InChI=1S/3ClH.Y/h3*1H;/q;;;+3/p-3 |
InChIキー |
PCMOZDDGXKIOLL-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
SMILES |
[Cl-].[Cl-].[Cl-].[Y+3] |
正規SMILES |
Cl[Y](Cl)Cl |
| 10361-92-9 | |
物理的記述 |
WetSolid |
関連するCAS |
10025-94-2 (hexahydrate) |
同義語 |
YCl3 yttrium chloride yttrium chloride hexahydrate yttrium chloride, (88)Y-labeled yttrium chloride, (90)Y-labeled yttrium chloride, (91)Y-labeled |
製品の起源 |
United States |
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。


![2-[(5-Chloropentyl)oxy]tetrahydro-2H-pyran](/img/structure/B85234.png)
![Dispiro[5.0.5.1]tridecane-1,5,8,12-tetrone](/img/structure/B85239.png)
![n-[(1e)-4-{Bis[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]methylidene}naphthalen-1(4h)-ylidene]cyclohexanaminium chloride](/img/structure/B85264.png)
