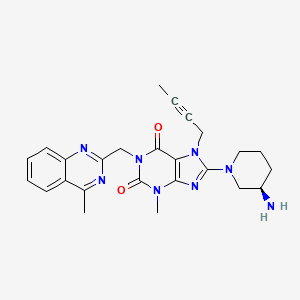
リナグリプチン
概要
説明
リナグリプチンは、2型糖尿病の治療に使用される薬剤です。 これは、ジペプチジルペプチダーゼ-4(DPP-4)阻害剤であり、膵臓によるインスリン産生の増加とグルカゴン産生の減少を誘導することによって作用します . リナグリプチンは経口投与され、商品名Tradjenta、Trajenta、Trazentaで販売されています .
作用機序
科学的研究の応用
Linagliptin has a wide range of scientific research applications, particularly in the fields of medicine and biology. It is primarily used to manage hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by inhibiting the DPP-4 enzyme . Additionally, Linagliptin has shown neuroprotective properties, making it a potential candidate for treating neurodegenerative diseases and cerebral ischemia . Research has also indicated its beneficial effects on vascular functions and its ability to reduce inflammation .
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Linagliptin interacts with the enzyme DPP-4, inhibiting its activity . This inhibition slows the breakdown of incretin hormones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), which play crucial roles in regulating insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis .
Cellular Effects
Linagliptin has been shown to decrease the concentration of proinflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6, and increase the number of anti-inflammatory patrolling monocytes CX3CR1 bright . It also improves vascular functions by increasing the production of nitric oxide (NO) and limiting the concentration of apolipoprotein B .
Molecular Mechanism
Linagliptin is a competitive, reversible DPP-4 inhibitor . By inhibiting DPP-4, it slows the inactivation of GLP-1 and GIP, promoting blood glucose level reduction in a glucose-dependent manner .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In clinical trials, linagliptin demonstrated efficacy in reducing glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in type 2 diabetes patients over time, while maintaining a placebo-like safety and tolerability profile .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models of diabetes, linagliptin has shown significant reductions in plasma leptin levels and hepatic steatosis when administered at doses of 3 or 30 mg/kg .
Metabolic Pathways
Linagliptin is involved in the incretin metabolic pathway. It inhibits the DPP-4 enzyme, slowing the breakdown of incretin hormones and thereby increasing their levels .
Transport and Distribution
Linagliptin exhibits concentration-dependent protein binding in human plasma in vitro and has a large apparent volume of distribution, demonstrating extensive distribution into tissues .
準備方法
リナグリプチンは、中間体を用いた一連の化学反応によって合成されます。 リナグリプチンを調製するための改良された方法の1つは、中間体を精製し、リナグリプチンに変換することです . この合成は、通常、高収率と高純度を実現するために、縮合反応、精製、結晶化などの工程が含まれます . 工業生産方法では、これらの工程を最適化して、品質と効率の一貫性を確保することに重点を置いています .
化学反応の分析
リナグリプチンは、酸化、還元、置換など、さまざまな化学反応を起こします。 これらの反応に使用される一般的な試薬には、酸化剤、還元剤、触媒などがあります . たとえば、リナグリプチンは、酸や過酸化物にさらされると、特に分解されやすく、分解生成物が生成されます . これらの反応を理解することは、その製剤を最適化し、治療効果を保証するために不可欠です .
科学研究への応用
リナグリプチンは、特に医学と生物学の分野において、幅広い科学研究への応用があります。 これは、主にDPP-4酵素を阻害することによって、2型糖尿病患者の高血糖を管理するために使用されます . さらに、リナグリプチンは神経保護効果を示しており、神経変性疾患や脳虚血の治療のための候補として期待されています . 研究では、血管機能に対する有益な効果や炎症を抑制する能力も示されています .
類似化合物との比較
リナグリプチンは、2型糖尿病の治療に使用されるいくつかのDPP-4阻害剤の1つです。 その他の類似化合物には、シタグリプチン、サクサグリプチン、アログリプチンなどがあります . これらの化合物と比較して、リナグリプチンは、長い末期半減期と主に腎臓以外の排泄を特徴とする独自の薬物動態プロファイルを持っています . これにより、腎機能障害のある患者でも、1日1回の投与で用量調整をする必要はありません . さらに、リナグリプチンは、他のDPP-4阻害剤では見られない持続的かつ最大限のDPP-4活性阻害を示しました .
特性
IUPAC Name |
8-[(3R)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2-yl)methyl]purine-2,6-dione | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H28N8O2/c1-4-5-13-32-21-22(29-24(32)31-12-8-9-17(26)14-31)30(3)25(35)33(23(21)34)15-20-27-16(2)18-10-6-7-11-19(18)28-20/h6-7,10-11,17H,8-9,12-15,26H2,1-3H3/t17-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
LTXREWYXXSTFRX-QGZVFWFLSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC#CCN1C2=C(N=C1N3CCCC(C3)N)N(C(=O)N(C2=O)CC4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C(=N4)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CC#CCN1C2=C(N=C1N3CCC[C@H](C3)N)N(C(=O)N(C2=O)CC4=NC5=CC=CC=C5C(=N4)C)C | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C25H28N8O2 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID201021653 | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201021653 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
472.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
<1 mg/mL, Soluble in methanol; sparingly soluble in ethanol; very slightly soluble in isopropanol, alcohol | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08882 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8204 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Linagliptin is a competitive, reversible DPP-4 inhibitor. Inhibition of this enzyme slows the breakdown of GLP-1 and glucose-dependant insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). GLP-1 and GIP stimulate the release of insulin from beta cells in the pancreas while inhibiting release of glucagon from pancreatic beta cells. These effects together reduce the breakdown of glycogen in the liver and increase insulin release in response to glucose., Linagliptin is an inhibitor of DPP-4, an enzyme that degrades the incretin hormones glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Thus, linagliptin increases the concentrations of active incretin hormones, stimulating the release of insulin in a glucose-dependent manner and decreasing the levels of glucagon in the circulation. Both incretin hormones are involved in the physiological regulation of glucose homeostasis. Incretin hormones are secreted at a low basal level throughout the day and levels rise immediately after meal intake. GLP-1 and GIP increase insulin biosynthesis and secretion from pancreatic beta-cells in the presence of normal and elevated blood glucose levels. Furthermore, GLP-1 also reduces glucagon secretion from pancreatic alpha-cells, resulting in a reduction in hepatic glucose output. | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08882 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8204 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
White to yellow solid; also reported as a crystalline solid | |
CAS No. |
668270-12-0 | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=668270-12-0 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Linagliptin [USAN:INN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0668270120 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08882 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID201021653 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 8-[(3R)-3-aminopiperidin-1-yl]-7-but-2-ynyl-3-methyl-1-[(4-methylquinazolin-2yl)methyl]purine-2,6-dione | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LINAGLIPTIN | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/3X29ZEJ4R2 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8204 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
190-196, 202 °C | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB08882 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Linagliptin | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8204 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
A: Linagliptin is a highly selective inhibitor of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). [] This enzyme is responsible for the rapid degradation of incretin hormones, such as glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). [, , ] By inhibiting DPP-4, linagliptin increases the levels of these incretin hormones, which in turn stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells and suppress glucagon secretion from alpha cells, ultimately leading to improved glycemic control. [, , , ]
A: Research suggests that linagliptin can improve insulin sensitivity, particularly in the liver. Studies in diet-induced obese mice showed that long-term linagliptin treatment improved glucose disposal rates and suppressed hepatic glucose production during a euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp, indicating enhanced insulin sensitivity. []
A: The molecular formula of linagliptin is C25H28N8O2, and its molecular weight is 472.54 g/mol. [, ]
A: While the provided abstracts don't delve into detailed spectroscopic analysis, they do mention techniques like X-ray crystallography being used to understand linagliptin's interaction with the DPP-4 enzyme. [] This technique helps visualize the drug's binding mode within the enzyme's active site.
ANone: The provided abstracts focus primarily on the pharmacological aspects of linagliptin and do not provide information on its material compatibility or stability in various conditions beyond standard pharmaceutical formulations.
ANone: Linagliptin itself doesn't possess catalytic properties. Its action relies on inhibiting the catalytic activity of the DPP-4 enzyme.
A: While not explicitly detailed in the provided abstracts, computational chemistry techniques like QSAR (Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship) are likely employed in the drug discovery and optimization process of linagliptin. [] These methods correlate structural features with biological activity, aiding in the design of more potent and selective DPP-4 inhibitors.
A: Linagliptin is typically formulated as oral tablets for once-daily administration. [, , ] One study explored the bioequivalence of a fixed-dose combination tablet containing linagliptin, empagliflozin, and extended-release metformin compared to separate tablets, aiming to improve patient adherence. []
ANone: The provided abstracts primarily focus on preclinical and clinical research findings related to linagliptin and do not delve into specific SHE (Safety, Health, and Environment) regulations.
A: Linagliptin demonstrates good oral absorption. [] Studies in rats using high-resolution autoradiography revealed that after intravenous administration, linagliptin-related radioactivity exhibited time- and dose-dependent localization in the kidneys, liver, and small intestine, reflecting the known distribution of DPP-4. [, ]
A: Unlike many other DPP-4 inhibitors primarily cleared by the kidneys, linagliptin is predominantly excreted via the enterohepatic system, with a small portion eliminated renally. [, ] This characteristic allows for its use without dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment. [, , ]
A: One study investigated the effect of food on linagliptin bioavailability when administered as a fixed-dose combination tablet with metformin. It concluded that food did not significantly impact linagliptin's bioavailability. []
A: Yes, in diet-induced obese mice, linagliptin significantly reduced liver fat content and improved glycemic control, as evidenced by lower blood glucose levels and improved glucose tolerance. [, ]
A: Numerous clinical trials have demonstrated that linagliptin effectively improves glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. It significantly reduces HbA1c levels when used as monotherapy or in combination with other antidiabetic drugs. [, , , , , , , , ]
A: The CAROLINA trial, a large cardiovascular outcome trial, compared linagliptin to glimepiride (a sulfonylurea) in patients with type 2 diabetes and established cardiovascular disease or high cardiovascular risk. The results showed that linagliptin was non-inferior to glimepiride in reducing the risk of cardiovascular events. []
ANone: The provided abstracts don't specifically address resistance mechanisms to linagliptin or cross-resistance with other DPP-4 inhibitors or drug classes.
ANone: The provided abstracts focus primarily on oral administration of linagliptin and don't explore alternative drug delivery systems or targeting strategies.
ANone: The research presented in the abstracts doesn't specifically investigate biomarkers for predicting linagliptin efficacy, monitoring treatment response, or identifying potential adverse effects.
A: While not extensively discussed in the provided abstracts, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is a widely used technique for quantifying linagliptin in biological samples. [, ]
ANone: The ecological impact and degradation pathways of linagliptin aren't discussed in the provided research abstracts.
A: A dedicated study examined the impact of varying tablet dissolution characteristics on the bioavailability of linagliptin in a fixed-dose combination with metformin. It concluded that the observed differences in dissolution profiles did not significantly affect the bioavailability of either drug. []
ANone: While the provided research abstracts don't elaborate on specific analytical method validation details for linagliptin, it's crucial to adhere to established guidelines to ensure accuracy, precision, and specificity when quantifying this drug in various matrices.
ANone: The provided abstracts don't specifically address the immunogenicity potential of linagliptin or any immunological responses associated with its use.
A: Research indicates that linagliptin is a substrate for P-glycoprotein (P-gp), a drug efflux transporter. [, ] This interaction could potentially influence its absorption and distribution, particularly in organs with high P-gp expression, such as the intestine and brain. [, ]
ANone: The abstracts primarily focus on linagliptin's pharmacological properties and don't delve into its biocompatibility or biodegradability aspects.
ANone: The abstracts don't provide information related to the recycling or waste management of linagliptin.
A: The research abstracts highlight the use of various research tools and resources, including animal models like diabetic db/db mice and ZDF rats, cell-based assays using human U937 monocytes and brain microvascular endothelial cells, and clinical trials involving diverse patient populations. [, , , , ] These resources are essential for investigating linagliptin's efficacy and safety.
A: The approval of linagliptin by the US Food and Drug Administration on May 2, 2011, marked a significant milestone in the development of DPP-4 inhibitors for treating type 2 diabetes. [, ] This approval was based on a comprehensive clinical development program involving thousands of patients and demonstrating the drug's efficacy and safety profile.
A: The research on linagliptin highlights the importance of interdisciplinary collaboration, involving scientists from various fields such as pharmacology, endocrinology, cardiology, and medicinal chemistry. [, , , ] For instance, understanding linagliptin's effects on cardiovascular outcomes requires expertise from both cardiologists and endocrinologists. Similarly, developing and optimizing the drug's formulation and delivery systems necessitate contributions from pharmaceutical scientists.
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。


![5-[2-(3-azidophenyl)ethyl-methylamino]-2-propan-2-yl-2-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)pentanenitrile;hydrochloride](/img/structure/B1675342.png)
![Benzamide, 4-[(3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl)amino]-3,5-difluoro-N-2-thiazolyl-](/img/structure/B1675344.png)