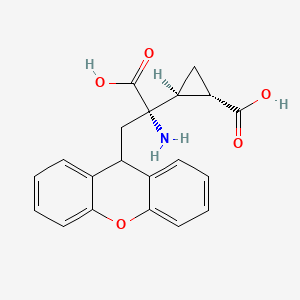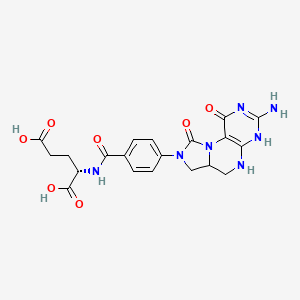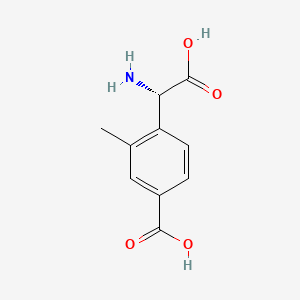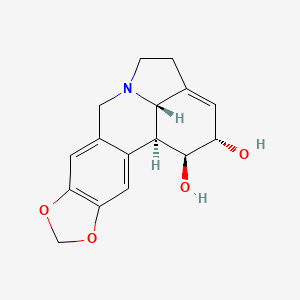
石蒜碱
描述
科学研究应用
石蒜碱具有广泛的科学研究应用:
化学: 石蒜碱用作合成具有潜在治疗应用的各种衍生物的先导化合物.
生物学: 研究它对蛋白质合成和抗坏血酸生物合成的影响.
医学: 石蒜碱已显示出治疗癌症、病毒感染和炎症性疾病的潜力. .
作用机制
石蒜碱通过多种机制发挥其作用。 它抑制蛋白质合成,并可能抑制抗坏血酸的生物合成 . 在癌细胞中,石蒜碱通过靶向 TCRP1/Akt/mTOR 轴等途径诱导细胞凋亡和自噬 . 它还通过与 PDGFRα 对接抑制血管生成,从而抑制其活性 .
生化分析
Biochemical Properties
Lycorine interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It has been found to inhibit acetylcholinesterase and topoisomerase . The nature of these interactions contributes to its multiple biological functions and pharmacological effects .
Cellular Effects
Lycorine influences cell function by impacting cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism . It has shown strong pharmacological effects on many diseases, including anti-leukemia, anti-tumor, anti-angiogenesis, anti-virus, anti-bacteria, anti-inflammation, and antimalaria .
Molecular Mechanism
Lycorine exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression . For instance, it has been found to have strong binding efficiency with key genes involved in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM), inducing apoptosis and reactive oxygen species production .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Over time, lycorine has shown stability and long-term effects on cellular function in both in vitro and in vivo studies . It has been produced sustainably in in vitro culture due to the pharmaceutical industries dramatically increasing demand for it .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of lycorine vary with different dosages in animal models . It exhibits numerous pharmacological effects on various diseases with very low toxicity and mild side effects .
Metabolic Pathways
Lycorine is involved in metabolic pathways formed by a coupling reaction of L-phenylalanine and L-tyrosine through intermediate o-methylnorbelladine—a common precursor of all Amaryllidaceae alkaloids .
准备方法
合成路线和反应条件
石蒜碱可以通过多种方法合成。 一种值得注意的合成路线涉及使用环丙基酰亚胺离子扩展和重排,然后进行狄尔斯-阿尔德反应构建关键的二烯中间体 . 该方法由 Boeckman 等人开发,被认为是石蒜碱最优雅的合成路线之一 .
工业生产方法
石蒜碱的工业生产通常涉及从植物来源提取。 使用风干粉末的植物鳞茎,例如 Sternbergia fischeriana,来分离石蒜碱 . 还采用先进的技术,例如体外植物细胞悬浮培养物和生物反应器,来可持续生产石蒜碱 .
化学反应分析
反应类型
石蒜碱会发生各种化学反应,包括氧化、还原和取代。 已知它会抑制蛋白质合成,并可能抑制抗坏血酸的生物合成 .
常用试剂和条件
石蒜碱反应中常用的试剂包括氧化剂,用于氧化反应,还原剂,用于还原反应。具体条件取决于所需的反应和产物。
主要形成的产物
石蒜碱反应形成的主要产物包括具有增强生物活性的衍生物。 例如,二氢石蒜碱,通过石蒜碱的氢化生成,由于其对阿米巴痢疾的抵抗力更强且毒性更低,已在临床上使用 .
相似化合物的比较
石蒜碱在生物碱中独一无二,因为它具有刚性的环骨架和连续的手性中心 . 类似化合物包括:
加兰他敏: 用于治疗阿尔茨海默病。
石蒜胺: 用于治疗后脊髓灰质炎综合征.
二氢石蒜碱: 在临床上使用,因为它毒性更低,对阿米巴痢疾的抵抗力更强.
这些化合物与石蒜碱在结构上相似,但具有不同的药理特性和应用。
属性
IUPAC Name |
(1S,17S,18S,19S)-5,7-dioxa-12-azapentacyclo[10.6.1.02,10.04,8.015,19]nonadeca-2,4(8),9,15-tetraene-17,18-diol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H17NO4/c18-11-3-8-1-2-17-6-9-4-12-13(21-7-20-12)5-10(9)14(15(8)17)16(11)19/h3-5,11,14-16,18-19H,1-2,6-7H2/t11-,14-,15+,16+/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XGVJWXAYKUHDOO-DANNLKNASA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3C5C2C1=CC(C5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3[C@H]5[C@H]2C1=C[C@@H]([C@H]5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H17NO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60197208 | |
| Record name | Lycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60197208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
287.31 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
476-28-8 | |
| Record name | Lycorine | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=476-28-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Lycorine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000476288 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | lycorine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=683873 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | lycorine | |
| Source | DTP/NCI | |
| URL | https://dtp.cancer.gov/dtpstandard/servlet/dwindex?searchtype=NSC&outputformat=html&searchlist=401360 | |
| Description | The NCI Development Therapeutics Program (DTP) provides services and resources to the academic and private-sector research communities worldwide to facilitate the discovery and development of new cancer therapeutic agents. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise indicated, all text within NCI products is free of copyright and may be reused without our permission. Credit the National Cancer Institute as the source. | |
| Record name | Lycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60197208 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Lycorine | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.006.822 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LYCORINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/I9Q105R5BU | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
体外研究产品的免责声明和信息
请注意,BenchChem 上展示的所有文章和产品信息仅供信息参考。 BenchChem 上可购买的产品专为体外研究设计,这些研究在生物体外进行。体外研究,源自拉丁语 "in glass",涉及在受控实验室环境中使用细胞或组织进行的实验。重要的是要注意,这些产品没有被归类为药物或药品,他们没有得到 FDA 的批准,用于预防、治疗或治愈任何医疗状况、疾病或疾病。我们必须强调,将这些产品以任何形式引入人类或动物的身体都是法律严格禁止的。遵守这些指南对确保研究和实验的法律和道德标准的符合性至关重要。


![(2S,4S)-4-(4-carboxyphenoxy)-1-[(2R)-2-[4-[(2-sulfobenzoyl)amino]imidazol-1-yl]octanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid](/img/structure/B1675661.png)
![(3-{[3-(2-Amino-2-Oxoethyl)-1-Benzyl-2-Ethyl-1h-Indol-5-Yl]oxy}propyl)phosphonic Acid](/img/structure/B1675666.png)
![2-[(E)-[4-[(3-hydroxy-4-propanoyl-2-propylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methylideneamino]guanidine](/img/structure/B1675669.png)
![[(2R,3R)-1,1-dioxo-2-propan-2-ylthiolan-3-yl] N-[(2R,3R)-4-[(3aR,6S,7aS)-6-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-3,3a,4,6,7,7a-hexahydro-2H-thieno[3,2-c]pyridin-5-yl]-3-hydroxy-1-phenylsulfanylbutan-2-yl]carbamate](/img/structure/B1675670.png)
![2-[(E)-[3-[(4-benzoylphenyl)methoxy]phenyl]methylideneamino]guanidine](/img/structure/B1675674.png)