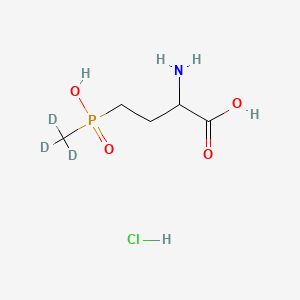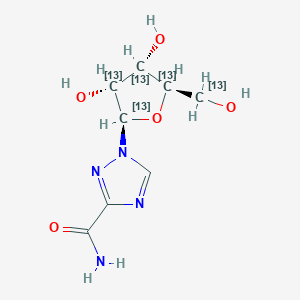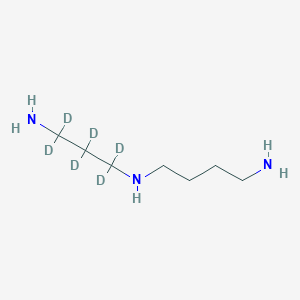
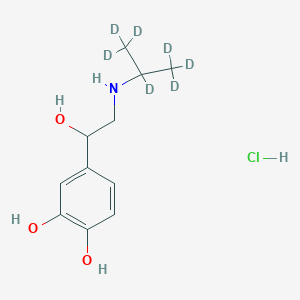
Spermidine-d6
Übersicht
Beschreibung
- Es spielt wesentliche Rollen beim Zellwachstum, der Genexpression und zellulären Prozessen.
- Spermidin-d6 dient als interner Standard zur Quantifizierung von natürlichem Spermidin mittels GC- oder LC-MS-Methoden .
Spermidin-d6: (CAS 2514812-10-1) ist eine deuteriummarkierte Form von Spermidin, einem endogenen Polyamin.
Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege: Spermidin-d6 wird synthetisiert, indem deuteriummarkierte Vorläufer während seiner Bildung eingebaut werden.
Reaktionsbedingungen: Die spezifischen Synthesewege und Bedingungen werden in den verfügbaren Informationen nicht angegeben.
Industrielle Produktion: Details zu industriellen Produktionsmethoden sind spärlich.
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes: Spermidine-d6 is synthesized by incorporating deuterium-labeled precursors during its formation.
Reaction Conditions: The specific synthetic route and conditions are not provided in the available information.
Industrial Production: Details regarding industrial-scale production methods are scarce.
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Reaktionen: Spermidin-d6 kann verschiedene chemische Reaktionen eingehen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution.
Häufige Reagenzien: Spezifische Reagenzien werden nicht erwähnt, aber typische Reaktionsbedingungen für Polyamine gelten.
Hauptprodukte: Die Hauptprodukte hängen von der jeweiligen Reaktion und den Ausgangsmaterialien ab.
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Chemie: Spermidin-d6 unterstützt die Erforschung des Polyamin-Stoffwechsels und verwandter Stoffwechselwege.
Biologie: Es trägt zur Forschung über Zellwachstum, Autophagie und Alterung bei.
Medizin: Spermidin hat potenzielle therapeutische Wirkungen, wie z. B. die Förderung der Langlebigkeit und die Reduzierung der Neurodegeneration.
Industrie: Formulierungen, die Spermidin enthalten, werden als Nahrungsergänzungsmittel verwendet.
Wirkmechanismus
- Spermidin beeinflusst verschiedene molekulare Ziele und Stoffwechselwege.
- Es induziert Autophagie, verstärkt antioxidative Abwehrmechanismen und moduliert die Genexpression.
- Die genauen Mechanismen sind komplex und kontextabhängig.
Wirkmechanismus
- Spermidine influences various molecular targets and pathways.
- It induces autophagy, enhances antioxidant defenses, and modulates gene expression.
- The exact mechanisms are complex and context-dependent.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen: Andere Polyamine wie Spermin und Putrescin weisen Ähnlichkeiten auf.
Einzigartigkeit: Die Deuteriummarkierung von Spermidin-d6 unterscheidet es von natürlichem Spermidin.
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
N'-(3-amino-1,1,2,2,3,3-hexadeuteriopropyl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Details | Computed by LexiChem 2.6.6 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C7H19N3/c8-4-1-2-6-10-7-3-5-9/h10H,1-9H2/i3D2,5D2,7D2 | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
ATHGHQPFGPMSJY-RCKJUGKUSA-N | |
| Details | Computed by InChI 1.0.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C(CCNCCCN)CN | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.1.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
[2H]C([2H])(C([2H])([2H])N)C([2H])([2H])NCCCCN | |
| Details | Computed by OEChem 2.1.5 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C7H19N3 | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2019.06.18) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Weight |
151.28 g/mol | |
| Details | Computed by PubChem 2.1 (PubChem release 2021.05.07) | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods IV
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.

![2-(1-benzylpyrazol-4-yl)oxy-1H-pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one](/img/structure/B8084114.png)