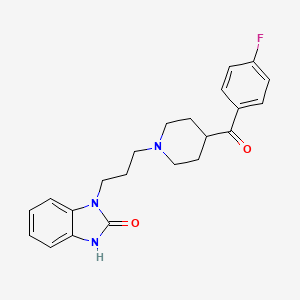
デラマンイド
概要
説明
デラマンイドは、主に多剤耐性結核(MDR-TB)の治療に使用されるニトロジヒドロイミダゾオキサゾール誘導体です。 薬剤感受性株および薬剤耐性株の結核菌に対する強力なin vitroおよびin vivo抗結核活性で知られています 。 デラマンイドは、デルティバという商品名で販売されており、日本や欧州連合などのいくつかの国で承認されています .
2. 製法
合成経路と反応条件: デラマンイドは、イミダゾオキサゾールコアの形成とそれに続く様々な官能基の導入を含む、複数段階のプロセスによって合成されます。主要なステップには以下が含まれます。
- イミダゾオキサゾール環の形成。
- ニトロ基の導入。
- トリフルオロメトキシフェノキシ基とピペリジニルフェノキシ基の付加。
工業的製造方法: デラマンイドの工業的製造には、高収率と高純度を確保するために最適化された反応条件を用いた大規模合成が含まれます。
- 乳化のための高圧ホモジナイザーの使用。
- 乾燥粉末を形成するための噴霧乾燥。
- ナノカプセル化による安定化は、水性溶解速度論を向上させます .
科学的研究の応用
Delamanid has a wide range of scientific research applications, including:
Chemistry: Used as a model compound for studying nitroimidazole derivatives.
Biology: Investigated for its effects on Mycobacterium tuberculosis and other bacterial strains.
Medicine: Primarily used in the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. .
Industry: Employed in the development of new antitubercular drugs and formulations.
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Delamanid inhibits the synthesis of methoxy-mycolic and keto-mycolic acid, which are essential components of the mycobacterial cell wall . This inhibition is achieved through the F420 coenzyme mycobacteria system, which generates nitrous oxide . The interaction between Delamanid and these biomolecules disrupts the integrity of the bacterial cell wall, thereby exerting its antimycobacterial properties .
Cellular Effects
Delamanid’s impact on cellular processes is primarily observed in its effects on Mycobacterium tuberculosis. By inhibiting the synthesis of key cell wall components, Delamanid disrupts the normal function of the bacteria, leading to their eventual death . This includes impacts on cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism associated with the synthesis and maintenance of the cell wall .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of Delamanid involves the inhibition of methoxy- and keto-mycolic acid synthesis through the F420 coenzyme mycobacteria system . This system generates nitrous oxide, which contributes to the antimycobacterial properties of Delamanid . The active free radical produced by the mycobacterial F420-dependent nitroreductase coenzyme system is also a part of Delamanid’s mechanism of action .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Its stability and long-term effects on cellular function have been observed in in vitro studies
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
Preliminary studies suggest that Delamanid has a dose-dependent effect on the treatment of MDR-TB
Metabolic Pathways
Delamanid is involved in the metabolic pathways related to the synthesis of mycolic acids . It interacts with the F420 coenzyme mycobacteria system, which plays a crucial role in these metabolic pathways
Transport and Distribution
It is known that Delamanid is primarily metabolized by albumin into the metabolite DM-6705
Subcellular Localization
Given its role in inhibiting the synthesis of cell wall components, it is likely that Delamanid localizes to areas of the cell where these synthesis processes occur
準備方法
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Delamanid is synthesized through a multi-step process involving the formation of the imidazooxazole core followed by the introduction of various functional groups. The key steps include:
- Formation of the imidazooxazole ring.
- Introduction of the nitro group.
- Attachment of the trifluoromethoxyphenoxy and piperidinylphenoxy groups.
Industrial Production Methods: Industrial production of delamanid involves large-scale synthesis using optimized reaction conditions to ensure high yield and purity. The process includes:
- Use of high-pressure homogenization for emulsification.
- Spray-drying to form a dried powder.
- Ensuring stability through nanoencapsulation to enhance aqueous dissolution kinetics .
化学反応の分析
反応の種類: デラマンイドは、以下を含む様々な化学反応を受けます。
還元: ニトロ基はアミンに還元されます。
酸化: イミダゾオキサゾール環は、特定の条件下で酸化を受ける可能性があります。
置換: イミダゾオキサゾール環上の官能基は、他の基で置換される可能性があります。
一般的な試薬と条件:
還元: 炭素担持パラジウムを用いた触媒的加水素化。
酸化: 過マンガン酸カリウムなどの酸化剤の使用。
置換: 適切な求核剤を用いた求核置換反応。
主要な生成物:
- ニトロ基の還元は、アミン誘導体の形成につながります。
- イミダゾオキサゾール環の酸化は、様々な酸化誘導体の生成をもたらす可能性があります。
- 置換反応は、様々な置換されたイミダゾオキサゾール化合物を生じます .
4. 科学研究への応用
デラマンイドは、以下を含む広範囲の科学研究への応用を持っています。
化学: ニトロイミダゾール誘導体の研究のためのモデル化合物として使用されます。
生物学: 結核菌やその他の細菌株に対するその影響について調査されています。
作用機序
デラマンイドは、結核菌細胞壁の必須成分であるメトキシおよびケトミコレート酸の合成を阻害することにより効果を発揮します。これは、デアザフラビン依存性ニトロレダクターゼを含む結核菌のF420補酵素系による活性化を必要とするプロドラッグです。 この活性化は、反応性窒素種の生成につながり、ミコレート酸の合成を阻害し、最終的に細菌を殺します .
類似の化合物:
プレトマンイド: 結核の治療に使用される別のニトロイミダゾール誘導体。
イソニアジド: ミコレート酸合成を阻害する第一選択の抗結核薬。
リファンピシン: 細菌のRNA合成を阻害する抗生物質。
比較:
デラマンイド対プレトマンイド: デラマンイドは、プレトマンイドと比較して、多剤耐性および広範耐性結核株に対してin vitroでより強力な活性を示します.
デラマンイド対イソニアジド: どちらもミコレート酸合成を阻害しますが、デラマンイドはF420補酵素系を含む異なるメカニズムを持っています。
デラマンイド対リファンピシン: デラマンイドはミコレート酸合成を標的とする一方、リファンピシンはRNA合成を阻害するため、併用療法では相補的な存在となります
デラマンイドのユニークな作用機序と薬剤耐性株に対する有効性は、抗結核薬の武器庫への貴重な追加となります。
類似化合物との比較
Pretomanid: Another nitroimidazole derivative used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
Isoniazid: A first-line antitubercular drug that inhibits mycolic acid synthesis.
Rifampicin: An antibiotic that inhibits bacterial RNA synthesis.
Comparison:
Delamanid vs. Pretomanid: Delamanid exhibits greater in vitro potency against multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis strains compared to pretomanid.
Delamanid vs. Isoniazid: While both inhibit mycolic acid synthesis, delamanid has a distinct mechanism involving the F420 coenzyme system.
Delamanid vs. Rifampicin: Delamanid targets mycolic acid synthesis, whereas rifampicin inhibits RNA synthesis, making them complementary in combination therapy
Delamanid’s unique mechanism of action and its efficacy against drug-resistant strains make it a valuable addition to the arsenal of antitubercular drugs.
特性
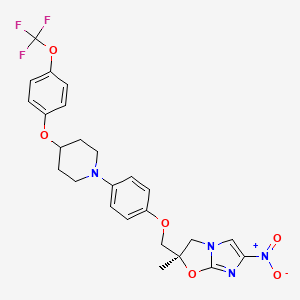
IUPAC Name |
(2R)-2-methyl-6-nitro-2-[[4-[4-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenoxy]piperidin-1-yl]phenoxy]methyl]-3H-imidazo[2,1-b][1,3]oxazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H25F3N4O6/c1-24(15-31-14-22(32(33)34)29-23(31)38-24)16-35-18-4-2-17(3-5-18)30-12-10-20(11-13-30)36-19-6-8-21(9-7-19)37-25(26,27)28/h2-9,14,20H,10-13,15-16H2,1H3/t24-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
XDAOLTSRNUSPPH-XMMPIXPASA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CC1(CN2C=C(N=C2O1)[N+](=O)[O-])COC3=CC=C(C=C3)N4CCC(CC4)OC5=CC=C(C=C5)OC(F)(F)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C[C@@]1(CN2C=C(N=C2O1)[N+](=O)[O-])COC3=CC=C(C=C3)N4CCC(CC4)OC5=CC=C(C=C5)OC(F)(F)F | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C25H25F3N4O6 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60218326 | |
| Record name | Delamanid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60218326 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
534.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Delamanid is a prodrug that requires biotransformation via via the mycobacterial F420 coenzyme system, including the deazaflavin dependent nitroreductase (Rv3547), to mediate its antimycobacterial activity against both growing and nongrowing mycobacteria. Mutations in one of five coenzyme F420 genes, _fgd, Rv3547, fbiA, fbiB, and fbiC_ has been proposed as the mechanism of resistance to delamanid. Upon activation, the radical intermediate formed between delamanid and desnitro-imidazooxazole derivative is thought to mediate antimycobacterial actions via inhibition of methoxy-mycolic and keto-mycolic acid synthesis, leading to depletion of mycobacterial cell wall components and destruction of the mycobacteria. Nitroimidazooxazole derivative is thought to generate reactive nitrogen species, including nitrogen oxide (NO). However unlike isoniazid, delamanid does not alpha-mycolic acid. | |
| Record name | Delamanid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11637 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
681492-22-8 | |
| Record name | Delamanid | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=681492-22-8 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Delamanid [USAN:INN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0681492228 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Delamanid | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB11637 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Delamanid | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60218326 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | DELAMANID | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/8OOT6M1PC7 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。