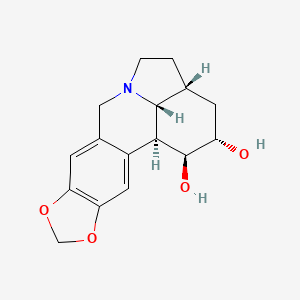
ジヒドロリコリン
概要
説明
ジヒドロリコリンは、リコリス・ラディアータ (Lycoris radiata) から得られるアルカロイドです。これは、様々な薬理効果で知られるリコリンの誘導体です。 ジヒドロリコリンは、特に心臓血管保護、神経保護、抗腫瘍活性において、潜在的な治療用途について研究されています .
科学的研究の応用
Cardiovascular Protection: Dihydrolycorine has been shown to attenuate cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction by downregulating Runx1 following myocardial infarction.
Antitumor Activity: Dihydrolycorine has demonstrated significant antitumor activity in cancer cells that display resistance to proapoptotic stimuli.
Anti-inflammatory: It has anti-inflammatory effects, making it useful in the treatment of various inflammatory conditions.
作用機序
ジヒドロリコリンは、様々な分子標的と経路を通じてその効果を発揮します。
心臓血管保護: これは、心臓のリモデリングの悪化に関連する遺伝子であるRunx1の発現を阻害します。
神経保護: ジヒドロリコリンは、分離したウサギの大動脈輪およびラットの肛門尾骨筋のメトキサミン誘発収縮を阻害し、平均動脈圧と高血圧を減少させます.
抗腫瘍活性: これは、真核細胞におけるタンパク質合成を、ペプチド結合形成段階を標的にすることで阻害し、その抗腫瘍効果を発揮します.
類似の化合物との比較
ジヒドロリコリンは、次のような他の類似の化合物と比較されます。
シュードリコリン: 類似の薬理学的特性を持つリコリンの別の誘導体.
リコラミン: 構造と薬理作用が類似した化合物.
生化学分析
Biochemical Properties
Dihydrolycorine plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by interacting with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It has been shown to inhibit methoxamine-induced contraction of isolated rabbit aortic rings and rat anococcygeus muscle . Additionally, dihydrolycorine interacts with fibrotic genes such as collagen I, TGF β, and p-smad3, as well as apoptosis-related genes like Bax and Bcl-2 . These interactions suggest that dihydrolycorine can modulate cellular processes related to fibrosis and apoptosis.
Cellular Effects
Dihydrolycorine exerts notable effects on various cell types and cellular processes. In cardiomyocytes, it has been observed to reduce fibrosis and apoptosis, thereby improving cardiac function following myocardial infarction . Dihydrolycorine influences cell signaling pathways by downregulating Runx1, a gene associated with adverse cardiac remodeling . This regulation leads to improved cardiac contractile function and reduced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, dihydrolycorine exerts its effects through several mechanisms. It binds to Runx1, inhibiting its expression and activity . This inhibition results in the downregulation of fibrotic and apoptotic genes, thereby preventing adverse cardiac remodeling. Molecular docking and binding modeling studies have identified potential dihydrolycorine-binding sites in Runx1, further elucidating its mechanism of action .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of dihydrolycorine have been studied over various time periods. It has been shown to maintain stability and efficacy in reducing cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction over extended periods . Long-term studies indicate that dihydrolycorine can sustain its therapeutic effects, with minimal degradation observed in in vitro and in vivo models .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of dihydrolycorine vary with different dosages in animal models. At a dose of 80 mg/kg, dihydrolycorine significantly reduces mean arterial pressure in normotensive rats . Higher doses have been associated with increased efficacy in reducing infarct size and cerebral edema in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury . Toxic or adverse effects at high doses have not been extensively reported, suggesting a favorable safety profile.
Metabolic Pathways
Dihydrolycorine is involved in several metabolic pathways, interacting with enzymes and cofactors that modulate its activity. It is metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes biotransformation to produce active metabolites . These metabolites contribute to its overall pharmacological effects, influencing metabolic flux and metabolite levels in various tissues.
Transport and Distribution
Within cells and tissues, dihydrolycorine is transported and distributed through specific transporters and binding proteins. It is known to accumulate in cardiac tissues, where it exerts its therapeutic effects . The distribution of dihydrolycorine is influenced by factors such as blood flow, tissue binding, and membrane permeability .
Subcellular Localization
Dihydrolycorine localizes to specific subcellular compartments, where it interacts with target biomolecules. It has been observed to accumulate in the cytoplasm and nucleus of cardiomyocytes, where it modulates gene expression and cellular function . The subcellular localization of dihydrolycorine is directed by targeting signals and post-translational modifications that ensure its proper distribution within the cell .
準備方法
ジヒドロリコリンは、リコリンの水素化によって合成されます。このプロセスは、触媒(通常は炭素上のパラジウム (Pd/C))の存在下で、リコリンを水素ガスで還元することを伴います。 この反応は、リコリンの二重結合を選択的に還元してジヒドロリコリンを生成するために、制御された条件下で行われます .
化学反応の分析
ジヒドロリコリンは、次のような様々な化学反応を受けます。
酸化: ジヒドロリコリンは、対応する酸化物を生成するために酸化することができます。一般的な酸化剤には、過マンガン酸カリウム (KMnO₄) や過酸化水素 (H₂O₂) があります。
還元: 前述のように、ジヒドロリコリンはリコリンの還元によって生成されます。さらなる還元は、より飽和した誘導体の生成につながる可能性があります。
置換: ジヒドロリコリンは、特に窒素原子で置換反応を受けます。これらの反応の一般的な試薬には、ハロゲン化アルキルやアシルクロリドがあります。
これらの反応から生成される主要な生成物は、使用する特定の条件と試薬によって異なります .
科学研究の応用
心臓血管保護: ジヒドロリコリンは、心筋梗塞後にRunx1をダウンレギュレートすることにより、心臓線維化と機能不全を軽減することが示されています。
神経保護: これは、脳虚血再灌流損傷モデルにおける梗塞サイズ、脳浮腫、ミエロペルオキシダーゼ活性を減少させることにより、神経保護作用を示します.
類似化合物との比較
Dihydrolycorine is compared with other similar compounds, such as:
Lycorine: The parent compound from which dihydrolycorine is derived.
Pseudolycorine: Another derivative of lycorine with similar pharmacological properties.
Lycoramine: A compound with similar structure and pharmacological activities.
Galantamine: Known for its use in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, it shares structural similarities with dihydrolycorine.
Dihydrolycorine stands out due to its lower toxicity and better resistance against certain diseases, such as amebic dysentery .
特性
IUPAC Name |
(1S,15R,17S,18S,19R)-5,7-dioxa-12-azapentacyclo[10.6.1.02,10.04,8.015,19]nonadeca-2,4(8),9-triene-17,18-diol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H19NO4/c18-11-3-8-1-2-17-6-9-4-12-13(21-7-20-12)5-10(9)14(15(8)17)16(11)19/h4-5,8,11,14-16,18-19H,1-3,6-7H2/t8-,11+,14+,15-,16-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VJILFEGOWCJNIK-MGRBZGILSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3C5C2C1CC(C5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3[C@H]5[C@H]2[C@H]1C[C@@H]([C@H]5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H19NO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID701346488 | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701346488 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
289.33 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
6271-21-2 | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0006271212 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701346488 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 6271-21-2 | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DIHYDROLYCORINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/Z7N4S72301 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
試験管内研究製品の免責事項と情報
BenchChemで提示されるすべての記事および製品情報は、情報提供を目的としています。BenchChemで購入可能な製品は、生体外研究のために特別に設計されています。生体外研究は、ラテン語の "in glass" に由来し、生物体の外で行われる実験を指します。これらの製品は医薬品または薬として分類されておらず、FDAから任何の医療状態、病気、または疾患の予防、治療、または治癒のために承認されていません。これらの製品を人間または動物に体内に導入する形態は、法律により厳格に禁止されています。これらのガイドラインに従うことは、研究と実験において法的および倫理的な基準の遵守を確実にするために重要です。


![Diethyl [2,2'-bipyridine]-5,5'-dicarboxylate](/img/structure/B1670527.png)