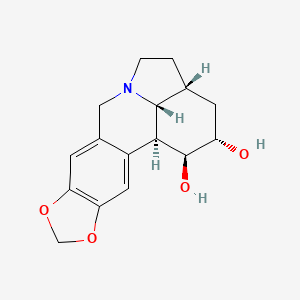
Dihydrolycorine
Vue d'ensemble
Description
La dihydrolycorine est un alcaloïde dérivé de la plante Lycoris radiata. C'est un dérivé de la lycorine, connue pour ses divers effets pharmacologiques. La this compound a été étudiée pour ses applications thérapeutiques potentielles, notamment dans la protection cardiovasculaire, la neuroprotection et les activités antitumorales .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Cardiovascular Protection: Dihydrolycorine has been shown to attenuate cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction by downregulating Runx1 following myocardial infarction.
Antitumor Activity: This compound has demonstrated significant antitumor activity in cancer cells that display resistance to proapoptotic stimuli.
Anti-inflammatory: It has anti-inflammatory effects, making it useful in the treatment of various inflammatory conditions.
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Dihydrolycorine, an alkaloid derived from lycorine , primarily targets the Runt-related transcription factor 1 (Runx1) . Runx1 is a gene that plays a crucial role in cardiac function .
Mode of Action
This compound acts as an inhibitor of Runx1 . It interacts with Runx1, leading to its downregulation . This interaction results in a decrease in the expression of fibrotic genes (such as collagen I, TGFβ, and p-smad3), a decrease in the apoptosis gene Bax, and an increase in the apoptosis gene Bcl-2 .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by this compound involves the downregulation of Runx1 . This downregulation leads to a series of downstream effects, including the prevention of adverse cardiac remodeling . Specifically, it results in the downregulation of fibrotic genes, modulation of apoptosis genes, and improvement of cardiac functions .
Pharmacokinetics
It’s known that this compound has been used clinically due to its better resistance against amebic dysentery and lower toxicity .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of this compound’s action are primarily seen in its ability to prevent adverse cardiac remodeling . This is achieved through the downregulation of fibrotic genes, modulation of apoptosis genes, and improvement of cardiac functions . Additionally, this compound treatment can rescue cardiomyocyte hypertrophy .
Action Environment
For instance, increased Runx1 expression under pathological conditions results in decreased cardiac contractile function, and this compound can counteract this effect .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Dihydrolycorine plays a significant role in biochemical reactions by interacting with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. It has been shown to inhibit methoxamine-induced contraction of isolated rabbit aortic rings and rat anococcygeus muscle . Additionally, this compound interacts with fibrotic genes such as collagen I, TGF β, and p-smad3, as well as apoptosis-related genes like Bax and Bcl-2 . These interactions suggest that this compound can modulate cellular processes related to fibrosis and apoptosis.
Cellular Effects
This compound exerts notable effects on various cell types and cellular processes. In cardiomyocytes, it has been observed to reduce fibrosis and apoptosis, thereby improving cardiac function following myocardial infarction . This compound influences cell signaling pathways by downregulating Runx1, a gene associated with adverse cardiac remodeling . This regulation leads to improved cardiac contractile function and reduced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
Molecular Mechanism
At the molecular level, this compound exerts its effects through several mechanisms. It binds to Runx1, inhibiting its expression and activity . This inhibition results in the downregulation of fibrotic and apoptotic genes, thereby preventing adverse cardiac remodeling. Molecular docking and binding modeling studies have identified potential this compound-binding sites in Runx1, further elucidating its mechanism of action .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of this compound have been studied over various time periods. It has been shown to maintain stability and efficacy in reducing cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction over extended periods . Long-term studies indicate that this compound can sustain its therapeutic effects, with minimal degradation observed in in vitro and in vivo models .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. At a dose of 80 mg/kg, this compound significantly reduces mean arterial pressure in normotensive rats . Higher doses have been associated with increased efficacy in reducing infarct size and cerebral edema in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury . Toxic or adverse effects at high doses have not been extensively reported, suggesting a favorable safety profile.
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in several metabolic pathways, interacting with enzymes and cofactors that modulate its activity. It is metabolized in the liver, where it undergoes biotransformation to produce active metabolites . These metabolites contribute to its overall pharmacological effects, influencing metabolic flux and metabolite levels in various tissues.
Transport and Distribution
Within cells and tissues, this compound is transported and distributed through specific transporters and binding proteins. It is known to accumulate in cardiac tissues, where it exerts its therapeutic effects . The distribution of this compound is influenced by factors such as blood flow, tissue binding, and membrane permeability .
Subcellular Localization
This compound localizes to specific subcellular compartments, where it interacts with target biomolecules. It has been observed to accumulate in the cytoplasm and nucleus of cardiomyocytes, where it modulates gene expression and cellular function . The subcellular localization of this compound is directed by targeting signals and post-translational modifications that ensure its proper distribution within the cell .
Méthodes De Préparation
La dihydrolycorine est synthétisée par hydrogénation de la lycorine. Le processus implique la réduction de la lycorine à l'aide d'hydrogène gazeux en présence d'un catalyseur, généralement du palladium sur charbon (Pd/C). Cette réaction est réalisée dans des conditions contrôlées pour assurer la réduction sélective des doubles liaisons de la lycorine, ce qui conduit à la formation de this compound .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
La dihydrolycorine subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : La this compound peut être oxydée pour former des oxydes correspondants. Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le permanganate de potassium (KMnO₄) et le peroxyde d'hydrogène (H₂O₂).
Réduction : Comme mentionné, la this compound est formée par la réduction de la lycorine. Une réduction supplémentaire peut conduire à la formation de dérivés plus saturés.
Substitution : La this compound peut subir des réactions de substitution, en particulier au niveau de l'atome d'azote. Les réactifs courants pour ces réactions comprennent les halogénures d'alkyle et les chlorures d'acyle.
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions dépendent des conditions et des réactifs spécifiques utilisés .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Protection cardiovasculaire : Il a été démontré que la this compound atténue la fibrose cardiaque et le dysfonctionnement en régulant à la baisse Runx1 après un infarctus du myocarde.
Activité antitumorale : La this compound a montré une activité antitumorale significative dans les cellules cancéreuses qui présentent une résistance aux stimuli proapoptotiques.
Anti-inflammatoire : Elle possède des effets anti-inflammatoires, ce qui la rend utile dans le traitement de diverses affections inflammatoires.
Mécanisme d'action
La this compound exerce ses effets par le biais de diverses cibles moléculaires et voies :
Protection cardiovasculaire : Elle inhibe l'expression de Runx1, un gène associé au remodelage cardiaque défavorable.
Activité antitumorale : Elle inhibe la synthèse protéique dans les cellules eucaryotes en ciblant l'étape de formation de la liaison peptidique, exerçant ainsi ses effets antitumoraux.
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
La dihydrolycorine est comparée à d'autres composés similaires, tels que :
Lycorine : Le composé parent à partir duquel la this compound est dérivée.
Pseudolycorine : Un autre dérivé de la lycorine présentant des propriétés pharmacologiques similaires.
Lycoramine : Un composé de structure et d'activités pharmacologiques similaires.
Galantamine : Connu pour son utilisation dans le traitement de la maladie d'Alzheimer, il présente des similitudes structurales avec la this compound.
La this compound se distingue par sa faible toxicité et sa meilleure résistance à certaines maladies, telles que la dysenterie amibienne .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(1S,15R,17S,18S,19R)-5,7-dioxa-12-azapentacyclo[10.6.1.02,10.04,8.015,19]nonadeca-2,4(8),9-triene-17,18-diol | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C16H19NO4/c18-11-3-8-1-2-17-6-9-4-12-13(21-7-20-12)5-10(9)14(15(8)17)16(11)19/h4-5,8,11,14-16,18-19H,1-3,6-7H2/t8-,11+,14+,15-,16-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VJILFEGOWCJNIK-MGRBZGILSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3C5C2C1CC(C5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3[C@H]5[C@H]2[C@H]1C[C@@H]([C@H]5O)O)OCO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C16H19NO4 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID701346488 | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701346488 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
289.33 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
CAS No. |
6271-21-2 | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0006271212 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Dihydrolycorine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID701346488 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | 6271-21-2 | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | DIHYDROLYCORINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/Z7N4S72301 | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.


![Diethyl [2,2'-bipyridine]-5,5'-dicarboxylate](/img/structure/B1670527.png)