Levamisol
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Levamisol ist eine synthetische Verbindung, die zur Klasse der Imidazothiazole gehört. Es wurde ursprünglich als Anthelminthikum entwickelt, um parasitäre Wurmbefall sowohl bei Menschen als auch bei Tieren zu behandeln . Im Laufe der Zeit wurden seine Anwendungen auf immunmodulatorische und krebshemmende Eigenschaften erweitert . This compound ist bekannt für seine Fähigkeit, das Immunsystem zu stimulieren und wurde in verschiedenen medizinischen und veterinärmedizinischen Behandlungen eingesetzt .
Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
This compound kann durch verschiedene Verfahren synthetisiert werden. Eine übliche Methode beinhaltet die Reaktion von 2-Imino-1,3-Thiazolidin mit 2-Phenyl-2-hydroxyethylamin . Diese Reaktion wird gefolgt von einer Cyclisierung, um die Imidazothiazol-Ringstruktur zu bilden. Die Reaktionsbedingungen umfassen typischerweise die Verwendung von Thionylchlorid und Essigsäureanhydrid .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von Levamisolhydrochlorid beinhaltet das Auflösen von L-Tetramisol in Aceton und das Hinzufügen von Natriumselenit . Die Mischung wird dann mit Aktivkohle entfärbt und filtriert. Trockenes Chlorwasserstoffgas wird unter Rühren eingeleitet, bis der pH-Wert 3-5 erreicht. Das Reaktionsgemisch wird dann abgetrennt und gereinigt, um das Endprodukt zu erhalten .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Levamisol hat eine große Bandbreite an Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Als chirales Hilfsmittel in der asymmetrischen Synthese eingesetzt.
Medizin: Als unterstützende Therapie bei der Behandlung von Darmkrebs und anderen malignen Erkrankungen eingesetzt.
Industrie: In der Veterinärmedizin eingesetzt, um parasitäre Infektionen bei Nutztieren zu behandeln.
Wirkmechanismus
This compound wirkt als Agonist des nikotinischen Acetylcholinrezeptors und verursacht eine kontinuierliche Stimulation der Muskeln von parasitären Würmern, was zu Lähmung und Ausstoß führt . In seiner immunmodulatorischen Rolle stimuliert this compound die Bildung von Antikörpern, verstärkt die T-Zell-Reaktionen und potenziert die Monozyten- und Makrophagenfunktionen . Es erhöht auch die Beweglichkeit, Adhäsion und Chemotaxis von Neutrophilen .
Wirkmechanismus
- Levamisole is a nicotinic receptor agonist primarily used to treat helminth infections and some skin infections .
- This action paralyzes the worms by reducing the males’ ability to control their reproductive muscles and limiting their copulation capacity .
- The affected pathways include:
- Impact on Bioavailability : Levamisole’s pharmacokinetics contribute to its efficacy and safety profile .
- At the molecular and cellular level, levamisole:
- Environmental factors can influence levamisole’s efficacy and stability:
Target of Action
Mode of Action
Biochemical Pathways
Pharmacokinetics
Result of Action
Action Environment
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Levamisole plays a significant role in biochemical reactions. It interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. The evaluation of biochemical analysis of Levamisole was performed based on the Shapiro-Wilk normality test .
Cellular Effects
Levamisole has profound effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function, including impacts on cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism .
Molecular Mechanism
Levamisole exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Over time, the effects of Levamisole change in laboratory settings. Information on Levamisole’s stability, degradation, and any long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies is currently being researched .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Levamisole vary with different dosages in animal models. Threshold effects observed in these studies, as well as any toxic or adverse effects at high doses, are being studied .
Metabolic Pathways
Levamisole is involved in various metabolic pathways, interacting with enzymes or cofactors. It also affects metabolic flux or metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
Levamisole is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It interacts with transporters or binding proteins, affecting its localization or accumulation .
Subcellular Localization
This includes any targeting signals or post-translational modifications that direct it to specific compartments or organelles .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
Levamisole can be synthesized through several methods. One common method involves the reaction of 2-imino-1,3-thiazolidine with 2-phenyl-2-hydroxyethylamine . This reaction is followed by cyclization to form the imidazothiazole ring structure. The reaction conditions typically involve the use of thionyl chloride and acetic anhydride .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of levamisole hydrochloride involves dissolving L-tetramisole in acetone and adding sodium selenite . The mixture is then decolorized and filtered using activated carbon. Dry hydrogen chloride gas is introduced while stirring until the pH value reaches 3-5. The reaction mixture is then separated and purified to obtain the final product .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Levamisol unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation, Reduktion und Substitution .
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen beinhalten häufig Nukleophile wie Halogenide oder Amine unter basischen Bedingungen.
Hauptprodukte
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, hängen von den verwendeten spezifischen Reagenzien und Bedingungen ab. Beispielsweise kann die Oxidation von this compound zur Bildung von Sulfoxiden oder Sulfonen führen .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Tetramisol: Ein racemisches Gemisch aus Levamisol und seinem Enantiomer, Dexamisol.
Pyrantel: Ein weiteres Anthelminthikum, das durch spastische Lähmung von Würmern wirkt.
Ivermectin: Ein Breitband-Antiparasitikum, das sowohl in der Human- als auch in der Veterinärmedizin eingesetzt wird.
Einzigartigkeit von this compound
This compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seiner doppelten Rolle als Anthelminthikum und Immunmodulator .
Eigenschaften
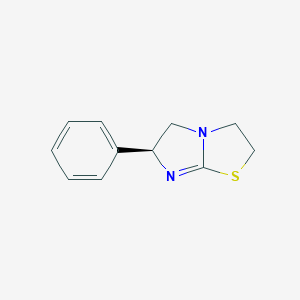
IUPAC Name |
(6S)-6-phenyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H12N2S/c1-2-4-9(5-3-1)10-8-13-6-7-14-11(13)12-10/h1-5,10H,6-8H2/t10-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
HLFSDGLLUJUHTE-SNVBAGLBSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CSC2=NC(CN21)C3=CC=CC=C3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CSC2=N[C@H](CN21)C3=CC=CC=C3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C11H12N2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
16595-80-5 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Levamisole [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0014769734 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4023206 | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4023206 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
204.29 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
1.44e+00 g/L, Water 210 (mg/mL), Methanol sol. (mg/mL), Propylene glycol sol. (mg/mL), Ethanol sl. sol. (mg/mL) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | LEVAMISOLE | |
| Source | NCI Investigational Drugs | |
| URL | http://dtp.nci.nih.gov/NCI-InvestigationalDrugsCI92/177023%20(1992).txt | |
| Description | An investigational drug is one that is under study but does not have permission from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be legally marketed and sold in the United States. NCI provides the investigational drug to the physicians who are participating in clinical trials or TRC protocols. For more information please visit NCI investigational drug website: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
Mechanism of Action |
The mechanism of action of levamisole as an antiparasitic agent appears to be tied to its agnositic activity towards the L-subtype nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in nematode muscles. This agonistic action reduces the capacity of the males to control their reproductive muscles and limits their ability to copulate. The mechanism of action of Levamisole as an anticancer drug in combination with fluorouracil is unknown. The effects of levamisole on the immune system are complex. The drug appears to restore depressed immune function rather than to stimulate response to above-normal levels. Levamisole can stimulate formation of antibodies to various antigens, enhance T-cell responses by stimulating T-cell activation and proliferation, potentiate monocyte and macrophage functions including phagocytosis and chemotaxis, and increase neutrophil mobility, adherence, and chemotaxis. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
14769-73-4 | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=14769-73-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Levamisole [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0014769734 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4023206 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.035.290 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LEVAMISOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2880D3468G | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
227-227.5, 264 - 265 °C | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of levamisole?
A1: Levamisole is known to exert its effects through various mechanisms. One well-documented action is its ability to restore deficient cell-mediated immune responses. [] This immunomodulatory effect is believed to be central to its therapeutic benefits in certain conditions.
Q2: How does levamisole impact neutrophils, and what are the implications for autoimmune reactions?
A2: Research suggests that levamisole can induce the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) by engaging with the muscarinic subtype 3 receptor on neutrophils. [] This process, termed NETosis, involves the release of chromatin decorated with granule proteins. While NET formation is a natural immune response, excessive or dysregulated NETosis, as potentially triggered by levamisole, has been implicated in autoimmune reactions and vascular damage. []
Q3: Does levamisole directly interact with cancer cells?
A3: While the exact mechanism of levamisole’s anticancer activity is not fully understood, studies suggest it may not solely target cancer cells directly. For instance, research using myeloma cells demonstrated that levamisole undergoes metabolic transformation in cell culture. [] This finding, along with observations of its immunomodulatory effects, points to a possible indirect anticancer action through the modulation of the immune system rather than direct cytotoxicity towards cancer cells.
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of levamisole?
A4: Levamisole's molecular formula is C11H12N2S, and its molecular weight is 204.3 g/mol.
Q5: What is the stability of levamisole in different formulations?
A5: While specific stability data for various levamisole formulations was not extensively discussed in the provided papers, one study focusing on an abamectin/levamisole combination in a medium-chain mono and diglyceride-based vehicle demonstrated sustained release properties. [] This suggests that the formulation strategy can impact the release kinetics of levamisole.
Q6: How is levamisole absorbed and distributed in the body?
A6: Levamisole is well-absorbed after oral administration, but its bioavailability is lower than after intramuscular administration in sheep. [] This suggests that the route of administration can influence its pharmacokinetic profile.
Q7: What is the elimination route of levamisole?
A7: Following oral or subcutaneous administration to lactating cows, levamisole is primarily eliminated through urine (83-84%), with a smaller portion excreted in feces (9-11%). []
Q8: Does the route of administration affect levamisole's efficacy?
A8: Yes, the route of administration can impact levamisole's efficacy. In sheep, oral administration is recommended for gastrointestinal nematodes, while the intramuscular route is preferred for extragastric nematodes. []
Q9: Can levamisole enhance the immune response in fish?
A9: Yes, studies in fish, specifically rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), have shown that levamisole can enhance various immune parameters, including phagocytic activity, serum bactericidal activity, and leukocyte counts. [, ] This suggests its potential as an immunostimulant in aquaculture.
Q10: What is the evidence for levamisole's effectiveness in treating parasitic infections?
A10: Levamisole is a recognized anthelmintic drug, effective against various parasitic worms. Studies in calves demonstrated its efficacy against lungworm (Dictyocaulus viviparus) infection, with sequential treatments providing better protection compared to a single dose. [] Research in guinea fowl also highlighted the efficacy of levamisole, particularly when combined with piperazine, in controlling gastrointestinal worms. []
Q11: Is there evidence of anthelmintic resistance to levamisole?
A11: Yes, unfortunately, anthelmintic resistance, including resistance to levamisole, is a growing concern. A study conducted in sheep farms in India revealed a high level of resistance to levamisole in gastrointestinal nematodes, particularly Haemonchus contortus. [] This underscores the need for responsible anthelmintic use and the development of novel parasite control strategies.
Q12: What are the known toxicities associated with levamisole?
A12: Levamisole has been associated with various adverse effects, with agranulocytosis being a significant concern. [, , ] This serious condition, characterized by a severe decrease in white blood cells, led to the withdrawal of levamisole from the human market in some countries. []
Q13: Can levamisole contamination in illicit drugs pose a health risk?
A13: Yes, the adulteration of cocaine with levamisole has emerged as a serious public health issue. [, , ] Levamisole-tainted cocaine has been linked to severe cases of vasculitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels. [, , ] The presence of levamisole in illicit drugs poses significant health risks and highlights the dangers of drug adulteration.
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.