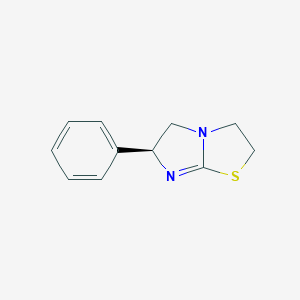
Levamisole
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Le lévamisole est un composé synthétique appartenant à la classe des imidazothiazoles. Il a été initialement développé comme un agent anthelminthique pour traiter les infections parasitaires par des vers chez l'homme et les animaux . Au fil du temps, ses applications se sont étendues pour inclure des propriétés immunomodulatrices et anticancéreuses . Le lévamisole est connu pour sa capacité à stimuler le système immunitaire et a été utilisé dans divers traitements médicaux et vétérinaires .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Levamisole has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a chiral auxiliary in asymmetric synthesis.
Biology: Studied for its effects on the immune system, including T-cell activation and proliferation.
Medicine: Used as an adjuvant therapy in the treatment of colon cancer and other malignancies.
Industry: Employed in veterinary medicine to treat parasitic infections in livestock.
Mécanisme D'action
- Levamisole is a nicotinic receptor agonist primarily used to treat helminth infections and some skin infections .
- This action paralyzes the worms by reducing the males’ ability to control their reproductive muscles and limiting their copulation capacity .
- The affected pathways include:
- Impact on Bioavailability : this compound’s pharmacokinetics contribute to its efficacy and safety profile .
- At the molecular and cellular level, this compound:
- Environmental factors can influence this compound’s efficacy and stability:
Target of Action
Mode of Action
Biochemical Pathways
Pharmacokinetics
Result of Action
Action Environment
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
Levamisole plays a significant role in biochemical reactions. It interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. The evaluation of biochemical analysis of this compound was performed based on the Shapiro-Wilk normality test .
Cellular Effects
This compound has profound effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function, including impacts on cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism .
Molecular Mechanism
This compound exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
Over time, the effects of this compound change in laboratory settings. Information on this compound’s stability, degradation, and any long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies is currently being researched .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of this compound vary with different dosages in animal models. Threshold effects observed in these studies, as well as any toxic or adverse effects at high doses, are being studied .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is involved in various metabolic pathways, interacting with enzymes or cofactors. It also affects metabolic flux or metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
This compound is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It interacts with transporters or binding proteins, affecting its localization or accumulation .
Subcellular Localization
This includes any targeting signals or post-translational modifications that direct it to specific compartments or organelles .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies synthétiques et conditions de réaction
Le lévamisole peut être synthétisé par plusieurs méthodes. Une méthode courante implique la réaction de la 2-imino-1,3-thiazolidine avec la 2-phényl-2-hydroxyéthylamine . Cette réaction est suivie d'une cyclisation pour former la structure cyclique imidazothiazole. Les conditions de réaction impliquent généralement l'utilisation de chlorure de thionyle et d'anhydride acétique .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle de chlorhydrate de lévamisole implique la dissolution du L-tétramisole dans l'acétone et l'ajout de sélénite de sodium . Le mélange est ensuite décoloré et filtré à l'aide de charbon actif. Du gaz chlorhydrique sec est introduit sous agitation jusqu'à ce que la valeur du pH atteigne 3-5. Le mélange réactionnel est ensuite séparé et purifié pour obtenir le produit final .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
Le lévamisole subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment l'oxydation, la réduction et la substitution .
Réactifs et conditions courants
Substitution : Les réactions de substitution impliquent souvent des nucléophiles comme les halogénures ou les amines en conditions basiques.
Principaux produits
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions dépendent des réactifs et des conditions spécifiques utilisés. Par exemple, l'oxydation du lévamisole peut conduire à la formation de sulfoxydes ou de sulfones .
Applications de la recherche scientifique
Le lévamisole a un large éventail d'applications de recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme auxiliaire chiral dans la synthèse asymétrique.
Médecine : Utilisé comme thérapie adjuvante dans le traitement du cancer du côlon et d'autres malignités.
Industrie : Employé en médecine vétérinaire pour traiter les infections parasitaires chez le bétail.
Mécanisme d'action
Le lévamisole agit comme un agoniste du récepteur nicotinique de l'acétylcholine, provoquant une stimulation continue des muscles des vers parasites, conduisant à une paralysie et une expulsion . Dans son rôle immunomodulateur, le lévamisole stimule la formation d'anticorps, améliore les réponses des lymphocytes T et potentialise les fonctions des monocytes et des macrophages . Il augmente également la mobilité, l'adhérence et la chimiotaxie des neutrophiles .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Composés similaires
Tétramisole : Un mélange racémique de lévamisole et de son énantiomère, le dexamisole.
Pyrantel : Un autre agent anthelminthique qui agit en provoquant une paralysie spastique des vers.
Ivermectine : Un agent antiparasitaire à large spectre utilisé en médecine humaine et vétérinaire.
Unicité du lévamisole
Le lévamisole est unique en raison de son double rôle d'agent anthelminthique et immunomodulateur .
Propriétés
IUPAC Name |
(6S)-6-phenyl-2,3,5,6-tetrahydroimidazo[2,1-b][1,3]thiazole | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C11H12N2S/c1-2-4-9(5-3-1)10-8-13-6-7-14-11(13)12-10/h1-5,10H,6-8H2/t10-/m1/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
HLFSDGLLUJUHTE-SNVBAGLBSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CSC2=NC(CN21)C3=CC=CC=C3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1CSC2=N[C@H](CN21)C3=CC=CC=C3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C11H12N2S | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
16595-80-5 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Levamisole [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0014769734 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID4023206 | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4023206 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
204.29 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Solubility |
1.44e+00 g/L, Water 210 (mg/mL), Methanol sol. (mg/mL), Propylene glycol sol. (mg/mL), Ethanol sl. sol. (mg/mL) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
| Record name | LEVAMISOLE | |
| Source | NCI Investigational Drugs | |
| URL | http://dtp.nci.nih.gov/NCI-InvestigationalDrugsCI92/177023%20(1992).txt | |
| Description | An investigational drug is one that is under study but does not have permission from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to be legally marketed and sold in the United States. NCI provides the investigational drug to the physicians who are participating in clinical trials or TRC protocols. For more information please visit NCI investigational drug website: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/investigational-drug-access-fact-sheet | |
Mechanism of Action |
The mechanism of action of levamisole as an antiparasitic agent appears to be tied to its agnositic activity towards the L-subtype nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in nematode muscles. This agonistic action reduces the capacity of the males to control their reproductive muscles and limits their ability to copulate. The mechanism of action of Levamisole as an anticancer drug in combination with fluorouracil is unknown. The effects of levamisole on the immune system are complex. The drug appears to restore depressed immune function rather than to stimulate response to above-normal levels. Levamisole can stimulate formation of antibodies to various antigens, enhance T-cell responses by stimulating T-cell activation and proliferation, potentiate monocyte and macrophage functions including phagocytosis and chemotaxis, and increase neutrophil mobility, adherence, and chemotaxis. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
14769-73-4 | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=14769-73-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Levamisole [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0014769734 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID4023206 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.035.290 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | LEVAMISOLE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/2880D3468G | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
227-227.5, 264 - 265 °C | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00848 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Levamisole | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014986 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details





Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Q1: What is the primary mechanism of action of levamisole?
A1: this compound is known to exert its effects through various mechanisms. One well-documented action is its ability to restore deficient cell-mediated immune responses. [] This immunomodulatory effect is believed to be central to its therapeutic benefits in certain conditions.
Q2: How does this compound impact neutrophils, and what are the implications for autoimmune reactions?
A2: Research suggests that this compound can induce the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) by engaging with the muscarinic subtype 3 receptor on neutrophils. [] This process, termed NETosis, involves the release of chromatin decorated with granule proteins. While NET formation is a natural immune response, excessive or dysregulated NETosis, as potentially triggered by this compound, has been implicated in autoimmune reactions and vascular damage. []
Q3: Does this compound directly interact with cancer cells?
A3: While the exact mechanism of this compound’s anticancer activity is not fully understood, studies suggest it may not solely target cancer cells directly. For instance, research using myeloma cells demonstrated that this compound undergoes metabolic transformation in cell culture. [] This finding, along with observations of its immunomodulatory effects, points to a possible indirect anticancer action through the modulation of the immune system rather than direct cytotoxicity towards cancer cells.
Q4: What is the molecular formula and weight of this compound?
A4: this compound's molecular formula is C11H12N2S, and its molecular weight is 204.3 g/mol.
Q5: What is the stability of this compound in different formulations?
A5: While specific stability data for various this compound formulations was not extensively discussed in the provided papers, one study focusing on an abamectin/levamisole combination in a medium-chain mono and diglyceride-based vehicle demonstrated sustained release properties. [] This suggests that the formulation strategy can impact the release kinetics of this compound.
Q6: How is this compound absorbed and distributed in the body?
A6: this compound is well-absorbed after oral administration, but its bioavailability is lower than after intramuscular administration in sheep. [] This suggests that the route of administration can influence its pharmacokinetic profile.
Q7: What is the elimination route of this compound?
A7: Following oral or subcutaneous administration to lactating cows, this compound is primarily eliminated through urine (83-84%), with a smaller portion excreted in feces (9-11%). []
Q8: Does the route of administration affect this compound's efficacy?
A8: Yes, the route of administration can impact this compound's efficacy. In sheep, oral administration is recommended for gastrointestinal nematodes, while the intramuscular route is preferred for extragastric nematodes. []
Q9: Can this compound enhance the immune response in fish?
A9: Yes, studies in fish, specifically rockfish (Sebastes schlegeli) and Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus), have shown that this compound can enhance various immune parameters, including phagocytic activity, serum bactericidal activity, and leukocyte counts. [, ] This suggests its potential as an immunostimulant in aquaculture.
Q10: What is the evidence for this compound's effectiveness in treating parasitic infections?
A10: this compound is a recognized anthelmintic drug, effective against various parasitic worms. Studies in calves demonstrated its efficacy against lungworm (Dictyocaulus viviparus) infection, with sequential treatments providing better protection compared to a single dose. [] Research in guinea fowl also highlighted the efficacy of this compound, particularly when combined with piperazine, in controlling gastrointestinal worms. []
Q11: Is there evidence of anthelmintic resistance to this compound?
A11: Yes, unfortunately, anthelmintic resistance, including resistance to this compound, is a growing concern. A study conducted in sheep farms in India revealed a high level of resistance to this compound in gastrointestinal nematodes, particularly Haemonchus contortus. [] This underscores the need for responsible anthelmintic use and the development of novel parasite control strategies.
Q12: What are the known toxicities associated with this compound?
A12: this compound has been associated with various adverse effects, with agranulocytosis being a significant concern. [, , ] This serious condition, characterized by a severe decrease in white blood cells, led to the withdrawal of this compound from the human market in some countries. []
Q13: Can this compound contamination in illicit drugs pose a health risk?
A13: Yes, the adulteration of cocaine with this compound has emerged as a serious public health issue. [, , ] this compound-tainted cocaine has been linked to severe cases of vasculitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of blood vessels. [, , ] The presence of this compound in illicit drugs poses significant health risks and highlights the dangers of drug adulteration.
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.

![5H-Naphtho[1,8-bc]thiophen-5-one, 3,4-dihydro-2-methyl-](/img/structure/B84213.png)
![[1R-(1alpha,4abeta,4balpha,10aalpha)]-1,2,3,4,4a,4b,5,6,10,10a-decahydro-1,4a-dimethyl-7-(isopropyl)phenanthrene-1-carboxylic acid, copper salt](/img/structure/B84220.png)