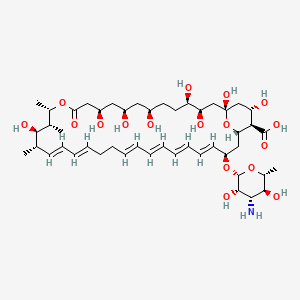
Nystatin
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Nystatin ist ein Polyen-Antimykotikum, das eine breite fungizide und fungistatische Wirkung gegen eine Vielzahl von Hefen und Pilzen, insbesondere Candida-Arten, aufweist . Es wurde 1950 von Rachel Fuller Brown und Elizabeth Lee Hazen entdeckt und wird vom Bakterium Streptomyces noursei produziert . This compound wird zur Behandlung von kutanen, mukoku-taneousen und gastrointestinalen Mykose-Infektionen eingesetzt .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Nystatin wird typischerweise aus der Fermentationsbrühe von Streptomyces noursei unter Verwendung eines wasserlöslichen organischen Lösungsmittels extrahiert. Die Verbindung wird dann gereinigt und kristallisiert . Die industrielle Produktion von this compound umfasst eine Reihe von Schritten, darunter Fermentation, Extraktion, Reinigung und Kristallisation, um hoch-ertragreiche und hochreine this compound-Kristalle zu erhalten .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Nystatin unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter Oxidation und Reduktion. Die Verbindung ist amphoter aufgrund des Vorhandenseins von Carboxyl- und Aminogruppen . Es ist praktisch unlöslich in Wasser, aber leicht löslich in polaren organischen Lösungsmitteln . Die Löslichkeit von this compound erhöht sich in wässrig-organischen Systemen, wobei die höchste Löslichkeit in Lösungen mit 30-40% Wasser erreicht wird .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound wird häufig in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung eingesetzt, insbesondere in den Bereichen Chemie, Biologie, Medizin und Industrie. In der Medizin wird es zur Behandlung von oraler Candidiasis, intestinaler Candidiasis und analer Candidiasis eingesetzt . Es wird auch topisch zur Behandlung von vulvovaginaler Candidiasis und anderen kutanen Candida-Infektionen eingesetzt . Zusätzlich wird this compound in Kombination mit anderen Medikamenten zur Behandlung von Mischinfektionen eingesetzt . In der wissenschaftlichen Forschung wird this compound verwendet, um die Auswirkungen von Antimykotika auf Pilzzellmembranen zu untersuchen und die molekularen Mechanismen von Pilzinfektionen zu erforschen .
Wirkmechanismus
This compound übt seine antimykotische Wirkung aus, indem es an Ergosterol bindet, ein Schlüsselbestandteil von Pilzzellmembranen . Diese Bindung führt zur Bildung von Poren in der Membran, was zum Auslaufen von Kaliumionen und anderen Zellinhalten führt und letztendlich zum Zelltod führt . Der Wirkmechanismus von this compound ist komplex und hängt vom Vorhandensein und der Art der Membransterole ab . Die Bildung und Stabilisierung von this compound-induzierten Poren werden durch die biophysikalischen Eigenschaften und die Lipidzusammensetzung der Membran beeinflusst .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Nystatin is widely used in scientific research, particularly in the fields of chemistry, biology, medicine, and industry. In medicine, it is used to treat oral candidiasis, intestinal candidiasis, and anal candidiasis . It is also used topically for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis and other cutaneous candida infections . Additionally, this compound is used in combination with other drugs to treat mixed infections . In scientific research, this compound is used to study the effects of antifungal agents on fungal cell membranes and to investigate the molecular mechanisms of fungal infections .
Wirkmechanismus
Nystatin exerts its antifungal effects by binding to ergosterol, a key component of fungal cell membranes . This binding causes the formation of pores in the membrane, leading to the leakage of potassium ions and other cellular contents, ultimately resulting in cell death . This compound’s mechanism of action is complex and depends on the presence and type of membrane sterols . The formation and stabilization of this compound-induced pores are influenced by the biophysical properties and lipid composition of the membrane .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Nystatin wird oft mit anderen Antimykotika wie Fluconazol und Amphotericin B verglichen. Während this compound wirksam zur Behandlung von lokalisierten Pilzinfektionen ist, ist es aufgrund seiner signifikanten Toxizität bei parenteraler Verabreichung nicht für die systemische Anwendung geeignet . Fluconazol hingegen ist wirksam bei systemischen Pilzinfektionen, kann aber Nebenwirkungen wie Kopfschmerzen, Übelkeit und Bauchschmerzen haben . Amphotericin B ist strukturell eng verwandt mit this compound und hat eine breitere antimykotische Wirkung, hat aber auch ein höheres Toxizitätsprofil . Andere ähnliche Verbindungen umfassen neu synthetisierte Thiazol-Derivate, die vielversprechende antimykotische Aktivität gegen Candida-Arten gezeigt haben .
Die einzigartige Fähigkeit von this compound, an Ergosterol zu binden und Pilzzellmembranen zu stören, macht es zu einem wertvollen Antimykotikum, insbesondere zur Behandlung von lokalisierten Infektionen .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
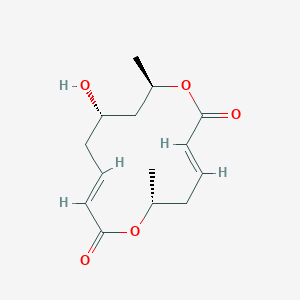
(1S,3R,4R,7R,9R,11R,15S,16R,17R,18S,19E,21E,25E,27E,29E,31E,33R,35S,36R,37S)-33-[(2R,3S,4S,5S,6R)-4-amino-3,5-dihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl]oxy-1,3,4,7,9,11,17,37-octahydroxy-15,16,18-trimethyl-13-oxo-14,39-dioxabicyclo[33.3.1]nonatriaconta-19,21,25,27,29,31-hexaene-36-carboxylic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C47H75NO17/c1-27-17-15-13-11-9-7-5-6-8-10-12-14-16-18-34(64-46-44(58)41(48)43(57)30(4)63-46)24-38-40(45(59)60)37(54)26-47(61,65-38)25-36(53)35(52)20-19-31(49)21-32(50)22-33(51)23-39(55)62-29(3)28(2)42(27)56/h5-6,8,10-18,27-38,40-44,46,49-54,56-58,61H,7,9,19-26,48H2,1-4H3,(H,59,60)/b6-5+,10-8+,13-11+,14-12+,17-15+,18-16+/t27-,28-,29-,30+,31+,32+,33+,34-,35+,36+,37-,38-,40+,41-,42+,43+,44-,46-,47+/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
VQOXZBDYSJBXMA-NQTDYLQESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
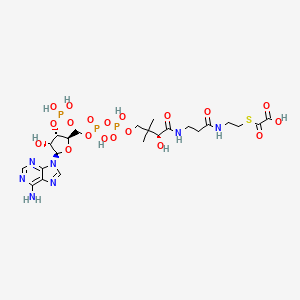
Canonical SMILES |
CC1C=CC=CCCC=CC=CC=CC=CC(CC2C(C(CC(O2)(CC(C(CCC(CC(CC(CC(=O)OC(C(C1O)C)C)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)C(=O)O)OC3C(C(C(C(O3)C)O)N)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C[C@H]1/C=C/C=C/CC/C=C/C=C/C=C/C=C/[C@@H](C[C@H]2[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@](O2)(C[C@H]([C@@H](CC[C@H](C[C@H](C[C@H](CC(=O)O[C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H]1O)C)C)O)O)O)O)O)O)O)C(=O)O)O[C@H]3[C@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)C)O)N)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C47H75NO17 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID80872323 | |
| Record name | (7R,10R)-8,9-Dideoxy-28,29-dihydro-7,10-dihydroxyamphotericin B | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID80872323 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
926.1 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Solubility |
MW: 926.12 /Form not specified/, Mg/ml at about 28 °C: methanol 11.2, ethanol 1.2, chloroform 0.48, carbon tetrachloride 1.23, benzene 0.28, toluene 0.285, acetone 0.390, ethyl acetate 0.75, ethylene glycol 8.75, Insol in ether, In water, 3.60X10+2 mg/L at 24 °C | |
| Record name | NYSTATIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3138 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Mechanism of Action |
Nystatin exerts its antifungal activity by binding to sterols in the fungal cell membrane. The drug is not active against organisms (e.g., bacteria) that do not contain sterols in their cell membrane. As a result of this binding, the membrane is no longer able to function as a selective barrier, and potassium and other cellular constituents are lost., ... /Antimicrobial/ agents that act directly on the cell membrane of the microorganism, affecting permeability and leading to leakage of intracellular compounds; these include ... the polyene antifungal agents nystatin ... which bind to cell-wall sterols ... | |
| Record name | NYSTATIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3138 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Light yellow powder, Yellow to tan powder | |
CAS No. |
34786-70-4, 1400-61-9 | |
| Record name | Nystatin A1 | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=34786-70-4 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Nystatin A1 | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0034786704 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | (7R,10R)-8,9-Dideoxy-28,29-dihydro-7,10-dihydroxyamphotericin B | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID80872323 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Nystatin | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.014.317 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | NYSTATIN A1 | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/W1LX4T91WI | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | NYSTATIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3138 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Melting Point |
Gradually decomp above 160 °C without melting by 250 °C | |
| Record name | NYSTATIN | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3138 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.


![3,7-bis[3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1,5,3,7-dioxadiazocane](/img/structure/B1249386.png)
![(E)-3-[(1S,2R,3S,4R)-2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-4-[(E)-2-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)ethenyl]-3-(piperidine-1-carbonyl)cyclobutyl]-1-piperidin-1-ylprop-2-en-1-one](/img/structure/B1249399.png)