AMD-070
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Mavorixafor ist ein oral bioverfügbarer, selektiver Antagonist des C-X-C-Chemokinrezeptors 4 (CXCR4). Es wird hauptsächlich zur Behandlung des WHIM-Syndroms (Warts, Hypogammaglobulinämie, Infektionen und Myelokathexis), einer seltenen primären Immundefizienzstörung, entwickelt. Mavorixafor wird auch auf sein Potenzial zur Behandlung verschiedener Krebsarten, einschließlich Melanom, und anderer chronischer neutropenischer Erkrankungen untersucht .
Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
Die Synthese von Mavorixafor umfasst mehrere Schritte, ausgehend von kommerziell erhältlichen Ausgangsmaterialien. Die Reaktionsbedingungen beinhalten typischerweise die Verwendung organischer Lösungsmittel, Katalysatoren und kontrollierter Temperaturen, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit zu gewährleisten .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von Mavorixafor folgt einem ähnlichen Syntheseweg, wird aber für die großtechnische Herstellung optimiert. Dazu gehören die Verwendung von Durchflussreaktoren, automatisierten Reinigungssystemen und strengen Qualitätskontrollmaßnahmen, um Konsistenz und Einhaltung der behördlichen Standards zu gewährleisten .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Mavorixafor hat eine breite Palette an Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Wird als Werkzeugverbindung verwendet, um den CXCR4-Rezeptor und seine Wechselwirkungen mit Liganden zu untersuchen.
Biologie: Untersucht auf seine Rolle bei der Modulation der Immunzellmigration und seine Auswirkungen auf das Tumor-Mikromilieu.
Medizin: Als Therapeutikum für das WHIM-Syndrom, das Melanom und andere Krebsarten entwickelt. .
Wirkmechanismus
Mavorixafor übt seine Wirkung aus, indem es selektiv an den CXCR4-Rezeptor bindet und die Bindung seines natürlichen Liganden, des C-X-C-Chemokin-Liganden 12 (auch bekannt als stroma-abgeleiteter Faktor-1), blockiert. Diese Hemmung verhindert die Aktivierung von CXCR4-Signalwegen, die an der Immunzellmigration, dem Homing hämatopoetischer Stammzellen und der Tumorprogression beteiligt sind. Durch die Modulation dieser Signalwege verbessert Mavorixafor die Infiltration und Aktivierung von Immunzellen im Tumor-Mikromilieu, was zu verbesserten Antitumor-Reaktionen führt .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Mavorixafor, also known as AMD-070, primarily targets the CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) . CXCR4 is a G protein-coupled receptor that plays a crucial role in cell signaling and function . It is involved in various physiological processes, including immune response and hematopoiesis .
Mode of Action
Mavorixafor acts as a selective and reversible antagonist of CXCR4 . It binds to CXCR4 and prevents the interaction of CXCR4 with its natural ligand, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1 or CXCL12) . This inhibition of receptor activation results in decreased proliferation and migration of cells that overexpress CXCR4 .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by Mavorixafor involves the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway . In conditions such as WHIM syndrome, mutations in the CXCR4 gene lead to overactivation of this pathway . By blocking CXCR4, Mavorixafor counteracts the effects of these disease-causing mutations, thereby modulating the downstream effects of the SDF-1/CXCR4 pathway .
Pharmacokinetics
Mavorixafor demonstrates nonlinear pharmacokinetics with greater than dose-proportional increases in maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) over a dose range of 50 mg to 400 mg . Steady-state concentrations of Mavorixafor are reached after approximately 9 to 12 days at the highest approved recommended dosage in healthy subjects . Mavorixafor is primarily eliminated by metabolism, with less than 1% of the administered oral dose appearing unchanged in the urine .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of Mavorixafor’s action primarily involve an increase in the mobilization and trafficking of white blood cells from the bone marrow . This leads to an increase in the number of circulating mature neutrophils and lymphocytes . Mavorixafor dose-dependently increases absolute neutrophil count and absolute lymphocyte count .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of Mavorixafor can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, food intake has been shown to reduce the bioavailability of Mavorixafor, leading to a decrease in its maximum concentration and area under the curve . Therefore, the timing of Mavorixafor administration in relation to meals may be an important consideration in its use .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
AMD-070 interacts with the CXCR4 chemokine receptor, acting as an antagonist . It binds to the transmembrane regions of the coreceptor, blocking the interaction of the CD4-gp120 complex with the ECL2 domain of the CXCR4 coreceptor .
Cellular Effects
This compound has shown to significantly suppress the anchorage-dependent growth, migration, and matrigel invasion of B88-SDF-1 cells . It also inhibits the replication of T-tropic HIV-1 (NL4.3 strain) in MT-4 cells and PBMCs .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its binding to the transmembrane regions of the CXCR4 coreceptor, thereby preventing CXCR4-mediated viral entry of T-cell tropic synctium-inducing HIV . This action blocks the interaction of the CD4-gp120 complex with the ECL2 domain of the CXCR4 coreceptor .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
It has been shown that this compound (2 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduces the number of metastatic lung nodules in mice .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and to a lesser extent, CYP2D6 . It is also a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) .
Transport and Distribution
It is known that this compound is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which plays a role in drug transport .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
The synthesis of mavorixafor involves multiple steps, starting from commercially available starting materialsThe reaction conditions typically involve the use of organic solvents, catalysts, and controlled temperatures to ensure high yield and purity .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of mavorixafor follows a similar synthetic route but is optimized for large-scale manufacturing. This includes the use of continuous flow reactors, automated purification systems, and stringent quality control measures to ensure consistency and compliance with regulatory standards .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen
Mavorixafor unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: Mavorixafor kann unter bestimmten Bedingungen oxidiert werden, um oxidierte Derivate zu bilden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen können verwendet werden, um die Chinolin-Einheit zu modifizieren.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen werden verwendet, um verschiedene funktionelle Gruppen in den Benzimidazol-Kern einzuführen.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Kaliumpermanganat.
Reduktion: Es werden Reduktionsmittel wie Natriumborhydrid und Lithiumaluminiumhydrid verwendet.
Substitution: Reagenzien wie Alkylhalogenide und Arylhalogenide werden für Substitutionsreaktionen verwendet.
Hauptprodukte
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, umfassen verschiedene Derivate von Mavorixafor mit modifizierten funktionellen Gruppen, die weiter auf ihre pharmakologischen Eigenschaften untersucht werden können .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Plerixafor: Ein weiterer CXCR4-Antagonist, der zur Stammzellmobilisierung bei Patienten mit Non-Hodgkin-Lymphom und multiplem Myelom eingesetzt wird.
Einzigartigkeit
Mavorixafor ist einzigartig in seiner oralen Bioverfügbarkeit und Selektivität für den CXCR4-Rezeptor. Im Gegensatz zu Plerixafor und AMD3100, die injiziert werden, kann Mavorixafor oral eingenommen werden, was es für Patienten bequemer macht. Darüber hinaus reduziert seine Selektivität für CXCR4 die Wahrscheinlichkeit von Off-Target-Effekten, was sein Sicherheitsprofil verbessert .
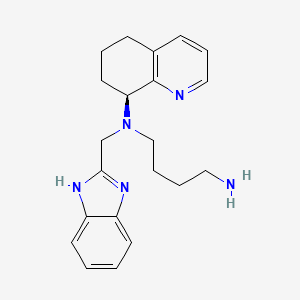
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
N'-(1H-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-N'-[(8S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]butane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H27N5/c22-12-3-4-14-26(15-20-24-17-9-1-2-10-18(17)25-20)19-11-5-7-16-8-6-13-23-21(16)19/h1-2,6,8-10,13,19H,3-5,7,11-12,14-15,22H2,(H,24,25)/t19-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WVLHHLRVNDMIAR-IBGZPJMESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1C[C@@H](C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H27N5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60971247 | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
349.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Chemokine receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells are known to play a critical role in virus infection and transmission. CXCR4, and another chemokine receptor CCR5, are involved in HIV infection. The process of HIV entry begins with binding of the viral envelope glycoprotein to both the CD4 receptor and one of only two chemokine receptors, and ends with fusion of viral and cell membranes. Viral entry provides novel therapeutic targets against HIV. To date, at least 3 sub classes of HIV viral entry/fusion inhibitors have emerged: 1. CD4 binding or attachment - targets initial recognition and binding of the viral glycoprotein gp120 to the cell-surface CD4 antigen. 2. Chemokine co-receptor binding - targets binding of virus to the CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptor. 3. Fusion Inhibition - targets the viral glycoprotein gp41 inhibiting the fusion of virus with the cell. Different strains of HIV prefer one receptor or the other, or may use either receptor to infect cells. * 35% of strains use both CXCR4 and CCR5 * 5% of strains are pure CXCR4 using * 60% of strains are pure CCR5 using * An infected individual may harbor different levels of both CXCR4 and CCR5 using virus * CXCR4 using virus independently predicts CD4 decline and HIV clinical progression and is associated with earlier mortality | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
558447-26-0 | |
| Record name | Mavorixafor [USAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0558447260 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | MAVORIXAFOR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0G9LGB5O2W | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.
![2-[4-[[4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]methoxy]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid](/img/structure/B1662810.png)