AMD-070
Vue d'ensemble
Description
Mavorixafor est un antagoniste sélectif du récepteur 4 de la chimiokine C-X-C (CXCR4) biodisponible par voie orale. Il est principalement développé pour le traitement du syndrome WHIM (Warts, Hypogammaglobulinémie, Infections et Myelokathexis), une maladie immunodéficitaire primaire rare. Mavorixafor est également étudié pour son potentiel dans le traitement de divers cancers, notamment le mélanome, et d'autres troubles neutropéniques chroniques .
Applications De Recherche Scientifique
Mavorixafor a une large gamme d'applications en recherche scientifique :
Chimie : Utilisé comme composé d'outil pour étudier le récepteur CXCR4 et ses interactions avec les ligands.
Biologie : Étudié pour son rôle dans la modulation du trafic des cellules immunitaires et ses effets sur le microenvironnement tumoral.
Médecine : Développé comme agent thérapeutique pour le syndrome WHIM, le mélanome et d'autres cancers. .
Industrie : Utilisé dans le développement de nouveaux médicaments ciblant le récepteur CXCR4 et les voies associées.
Mécanisme d'action
Mavorixafor exerce ses effets en se liant sélectivement au récepteur CXCR4, bloquant la liaison de son ligand naturel, le ligand 12 de la chimiokine C-X-C (également connu sous le nom de facteur dérivé du stroma-1). Cette inhibition empêche l'activation des voies de signalisation CXCR4, qui sont impliquées dans le trafic des cellules immunitaires, l'homing des cellules souches hématopoïétiques et la progression tumorale. En modulant ces voies, mavorixafor améliore l'infiltration et l'activation des cellules immunitaires dans le microenvironnement tumoral, conduisant à des réponses antitumorales améliorées .
Mécanisme D'action
Target of Action
Mavorixafor, also known as AMD-070, primarily targets the CXC chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) . CXCR4 is a G protein-coupled receptor that plays a crucial role in cell signaling and function . It is involved in various physiological processes, including immune response and hematopoiesis .
Mode of Action
Mavorixafor acts as a selective and reversible antagonist of CXCR4 . It binds to CXCR4 and prevents the interaction of CXCR4 with its natural ligand, stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1 or CXCL12) . This inhibition of receptor activation results in decreased proliferation and migration of cells that overexpress CXCR4 .
Biochemical Pathways
The primary biochemical pathway affected by Mavorixafor involves the SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling pathway . In conditions such as WHIM syndrome, mutations in the CXCR4 gene lead to overactivation of this pathway . By blocking CXCR4, Mavorixafor counteracts the effects of these disease-causing mutations, thereby modulating the downstream effects of the SDF-1/CXCR4 pathway .
Pharmacokinetics
Mavorixafor demonstrates nonlinear pharmacokinetics with greater than dose-proportional increases in maximum concentration (Cmax) and area under the curve (AUC) over a dose range of 50 mg to 400 mg . Steady-state concentrations of Mavorixafor are reached after approximately 9 to 12 days at the highest approved recommended dosage in healthy subjects . Mavorixafor is primarily eliminated by metabolism, with less than 1% of the administered oral dose appearing unchanged in the urine .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of Mavorixafor’s action primarily involve an increase in the mobilization and trafficking of white blood cells from the bone marrow . This leads to an increase in the number of circulating mature neutrophils and lymphocytes . Mavorixafor dose-dependently increases absolute neutrophil count and absolute lymphocyte count .
Action Environment
The action, efficacy, and stability of Mavorixafor can be influenced by various environmental factors. For instance, food intake has been shown to reduce the bioavailability of Mavorixafor, leading to a decrease in its maximum concentration and area under the curve . Therefore, the timing of Mavorixafor administration in relation to meals may be an important consideration in its use .
Analyse Biochimique
Biochemical Properties
AMD-070 interacts with the CXCR4 chemokine receptor, acting as an antagonist . It binds to the transmembrane regions of the coreceptor, blocking the interaction of the CD4-gp120 complex with the ECL2 domain of the CXCR4 coreceptor .
Cellular Effects
This compound has shown to significantly suppress the anchorage-dependent growth, migration, and matrigel invasion of B88-SDF-1 cells . It also inhibits the replication of T-tropic HIV-1 (NL4.3 strain) in MT-4 cells and PBMCs .
Molecular Mechanism
The molecular mechanism of this compound involves its binding to the transmembrane regions of the CXCR4 coreceptor, thereby preventing CXCR4-mediated viral entry of T-cell tropic synctium-inducing HIV . This action blocks the interaction of the CD4-gp120 complex with the ECL2 domain of the CXCR4 coreceptor .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
It has been shown that this compound (2 mg/kg, p.o.) significantly reduces the number of metastatic lung nodules in mice .
Metabolic Pathways
This compound is primarily metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 and to a lesser extent, CYP2D6 . It is also a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) .
Transport and Distribution
It is known that this compound is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp), which plays a role in drug transport .
Méthodes De Préparation
Voies de synthèse et conditions réactionnelles
La synthèse du mavorixafor implique plusieurs étapes, en commençant par des matières premières disponibles dans le commerceLes conditions réactionnelles impliquent généralement l'utilisation de solvants organiques, de catalyseurs et de températures contrôlées pour garantir un rendement et une pureté élevés .
Méthodes de production industrielle
La production industrielle de mavorixafor suit une voie de synthèse similaire, mais est optimisée pour une fabrication à grande échelle. Cela inclut l'utilisation de réacteurs à écoulement continu, de systèmes de purification automatisés et de mesures de contrôle qualité strictes pour assurer la cohérence et la conformité aux normes réglementaires .
Analyse Des Réactions Chimiques
Types de réactions
Mavorixafor subit diverses réactions chimiques, notamment :
Oxydation : Mavorixafor peut être oxydé dans des conditions spécifiques pour former des dérivés oxydés.
Réduction : Les réactions de réduction peuvent être utilisées pour modifier la partie quinoléine.
Substitution : Les réactions de substitution sont utilisées pour introduire différents groupes fonctionnels dans le noyau benzimidazole.
Réactifs et conditions courants
Oxydation : Les agents oxydants courants comprennent le peroxyde d'hydrogène et le permanganate de potassium.
Réduction : Les agents réducteurs tels que le borohydrure de sodium et l'hydrure de lithium et d'aluminium sont utilisés.
Substitution : Des réactifs comme les halogénoalcanes et les halogénoarènes sont utilisés pour les réactions de substitution.
Produits principaux
Les principaux produits formés à partir de ces réactions comprennent divers dérivés de mavorixafor avec des groupes fonctionnels modifiés, qui peuvent être étudiés plus avant pour leurs propriétés pharmacologiques .
Comparaison Avec Des Composés Similaires
Composés similaires
Plerixafor : Un autre antagoniste du CXCR4 utilisé pour la mobilisation des cellules souches chez les patients atteints de lymphome non hodgkinien et de myélome multiple.
Unicité
Mavorixafor est unique par sa biodisponibilité orale et sa sélectivité pour le récepteur CXCR4. Contrairement au plerixafor et à l'AMD3100, qui sont administrés par injection, mavorixafor peut être pris par voie orale, ce qui le rend plus pratique pour les patients. De plus, sa sélectivité pour le CXCR4 réduit la probabilité d'effets hors cible, améliorant son profil de sécurité .
Propriétés
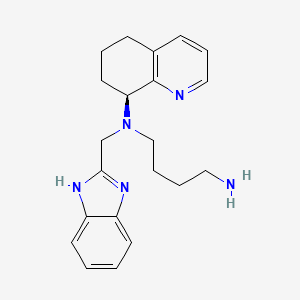
IUPAC Name |
N'-(1H-benzimidazol-2-ylmethyl)-N'-[(8S)-5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl]butane-1,4-diamine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C21H27N5/c22-12-3-4-14-26(15-20-24-17-9-1-2-10-18(17)25-20)19-11-5-7-16-8-6-13-23-21(16)19/h1-2,6,8-10,13,19H,3-5,7,11-12,14-15,22H2,(H,24,25)/t19-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
WVLHHLRVNDMIAR-IBGZPJMESA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
C1CC(C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
C1C[C@@H](C2=C(C1)C=CC=N2)N(CCCCN)CC3=NC4=CC=CC=C4N3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C21H27N5 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60971247 | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
349.5 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Chemokine receptors expressed on the surface of immune cells are known to play a critical role in virus infection and transmission. CXCR4, and another chemokine receptor CCR5, are involved in HIV infection. The process of HIV entry begins with binding of the viral envelope glycoprotein to both the CD4 receptor and one of only two chemokine receptors, and ends with fusion of viral and cell membranes. Viral entry provides novel therapeutic targets against HIV. To date, at least 3 sub classes of HIV viral entry/fusion inhibitors have emerged: 1. CD4 binding or attachment - targets initial recognition and binding of the viral glycoprotein gp120 to the cell-surface CD4 antigen. 2. Chemokine co-receptor binding - targets binding of virus to the CCR5 or CXCR4 co-receptor. 3. Fusion Inhibition - targets the viral glycoprotein gp41 inhibiting the fusion of virus with the cell. Different strains of HIV prefer one receptor or the other, or may use either receptor to infect cells. * 35% of strains use both CXCR4 and CCR5 * 5% of strains are pure CXCR4 using * 60% of strains are pure CCR5 using * An infected individual may harbor different levels of both CXCR4 and CCR5 using virus * CXCR4 using virus independently predicts CD4 decline and HIV clinical progression and is associated with earlier mortality | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
CAS No. |
558447-26-0 | |
| Record name | Mavorixafor [USAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0558447260 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | AMD-070 | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB05501 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | N~1~-[(1H-Benzimidazol-2-yl)methyl]-N~1~-(5,6,7,8-tetrahydroquinolin-8-yl)butane-1,4-diamine | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60971247 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | MAVORIXAFOR | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/0G9LGB5O2W | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details







Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Avertissement et informations sur les produits de recherche in vitro
Veuillez noter que tous les articles et informations sur les produits présentés sur BenchChem sont destinés uniquement à des fins informatives. Les produits disponibles à l'achat sur BenchChem sont spécifiquement conçus pour des études in vitro, qui sont réalisées en dehors des organismes vivants. Les études in vitro, dérivées du terme latin "in verre", impliquent des expériences réalisées dans des environnements de laboratoire contrôlés à l'aide de cellules ou de tissus. Il est important de noter que ces produits ne sont pas classés comme médicaments et n'ont pas reçu l'approbation de la FDA pour la prévention, le traitement ou la guérison de toute condition médicale, affection ou maladie. Nous devons souligner que toute forme d'introduction corporelle de ces produits chez les humains ou les animaux est strictement interdite par la loi. Il est essentiel de respecter ces directives pour assurer la conformité aux normes légales et éthiques en matière de recherche et d'expérimentation.
![2-[4-[[4-(2-chlorophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]methoxy]-2-methylphenoxy]acetic acid](/img/structure/B1662810.png)