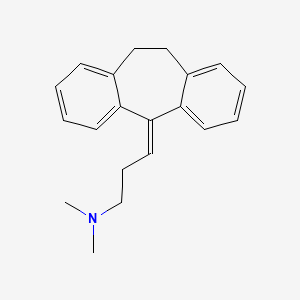
Amitriptylin
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Amitriptyline is a tricyclic antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and various pain syndromes such as neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia, migraine, and tension headaches . It was discovered in the late 1950s by scientists at Merck and approved by the US Food and Drug Administration in 1961 . Amitriptyline is also listed on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, primarily targets the neuronal reuptake transporters of norepinephrine and serotonin . These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in regulating mood, sleep, and pain perception .
Mode of Action
Amitriptyline’s key mechanism of action lies in the elevation of extracellular biogenic amine levels, notably those of norepinephrine and serotonin . By inhibiting the membrane pump mechanism responsible for the re-uptake of these transmitter amines, amitriptyline increases their concentration at the synaptic clefts of the brain .
Biochemical Pathways
Amitriptyline interferes with the autophagy-mediated clearance of protein aggregates by inhibiting autophagosome maturation in neuronal cells . This interference exacerbates the accumulation of abnormal aggregates, affecting both the formation of aggresome-like aggregates and the autophagy-mediated clearance of these aggregates . Amitriptyline is also metabolized mainly via the CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 pathways .
Pharmacokinetics
Amitriptyline is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with a bioavailability of 45%-53% . It undergoes extensive first-pass metabolism in the liver, leading to an average bioavailability of about 50% . The elimination half-life varies from 10 to 50 hours, with an average of 15 hours . Amitriptyline is also known to have strong anticholinergic properties and may cause ECG changes and quinidine-like effects on the heart .
Result of Action
The molecular and cellular effects of amitriptyline’s action include the elevation of extracellular biogenic amine levels, interference with autophagy-mediated clearance of protein aggregates, and potential effects on cardiac function . These actions contribute to its therapeutic effects in treating depressive illness, anxiety disorders, and other mental illnesses .
Action Environment
Environmental factors can influence the action, efficacy, and stability of amitriptyline. For instance, exposure to amitriptyline can alter behavior and increase the activity of acetylcholinesterase . Moreover, degradation pathways such as oxidation, hydrolysis, and photodegradation can affect the stability and potency of amitriptyline . It’s also worth noting that amitriptyline can be considered an emerging pollutant with potential consequences for human health and wellbeing .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Amitriptylin hat eine breite Palette an Anwendungen in der wissenschaftlichen Forschung:
Chemie: Als Modellverbindung in Studien zu trizyklischen Antidepressiva verwendet.
Biologie: Untersucht wegen seiner Auswirkungen auf Neurotransmittersysteme und Rezeptorbindung.
5. Wirkmechanismus
Der genaue Wirkmechanismus von this compound ist nicht vollständig geklärt. Es wird angenommen, dass es durch die Hemmung der Wiederaufnahme von Neurotransmittern wie Noradrenalin und Serotonin wirkt, wodurch ihre Konzentration im synaptischen Spalt im Gehirn erhöht wird . This compound hat auch starke anticholinerge Eigenschaften und kann verschiedene periphere Rezeptoren blockieren, darunter alpha-adrenerge, muskarinische, histaminerge, nikotinische und NMDA-Rezeptoren .
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Amitriptyline works by increasing the synaptic concentration of serotonin and/or norepinephrine in the central nervous system by inhibiting their reuptake by the presynaptic neuronal membrane pump . This action prolongs the sympathetic activity of these biogenic amines .
Cellular Effects
Amitriptyline has been shown to interfere with the formation of aggresome-like aggregates and autophagy-mediated clearance of aggregates . It also has immunomodulatory effects, such as lowering the production of typical T H 2-cytokines in T lymphocytes of asthmatic mice .
Molecular Mechanism
Amitriptyline’s key mechanism of action lies in the elevation of extracellular biogenic amine levels, notably those of noradrenaline and serotonin, by its blockade of cellular noradrenaline and serotonin reuptake transporters . This response may underlie chronic amitriptyline action on dopamine and norepinephrine neurotransmission .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
You may have flu-like symptoms like feeling sick, muscle pain, and feeling tired or restless . To help prevent this from happening, your doctor will probably recommend reducing your dose gradually over several weeks .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
In animal models, oral administration of amitriptyline provides a valid model for behavioral assessment of antidepressant-like effects . The effectiveness of oral amitriptyline varies depending on sex, duration of treatment, and the depression model used .
Metabolic Pathways
Amitriptyline is readily absorbed in the GI tract and subject to extensive hepatic metabolism with less than 5% of the drug eliminated unchanged . The main metabolizing enzymes with clinical significance for amitriptyline are CYP2C19 and CYP2D6 .
Transport and Distribution
Amitriptyline is transported and distributed within cells and tissues via absorption in the GI tract . It is subject to extensive hepatic metabolism .
Subcellular Localization
Given its mechanism of action, it is likely that Amitriptyline localizes to the synapses in neurons where it can inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions: Amitriptyline can be synthesized through several methods. One common method involves the reaction of dibenzosuberone with dimethylamine in the presence of a reducing agent such as lithium aluminum hydride. The reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate, which is then cyclized to form amitriptyline .
Industrial Production Methods: In industrial settings, amitriptyline is typically produced through a multi-step synthesis process that ensures high yield and purity. The process involves the use of advanced techniques such as high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for purification and quality control .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Arten von Reaktionen: Amitriptylin unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Oxidation: this compound kann zu seinem N-Oxid-Derivat oxidiert werden.
Reduktion: Die Reduktion von this compound kann zur Bildung von sekundären Aminen führen.
Substitution: this compound kann nucleophile Substitutionsreaktionen eingehen, insbesondere am Stickstoffatom.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen:
Oxidation: Häufige Oxidationsmittel sind Wasserstoffperoxid und Persäuren.
Reduktion: Reduktionsmittel wie Lithiumaluminiumhydrid oder Natriumborhydrid werden üblicherweise verwendet.
Substitution: Nucleophile wie Alkylhalogenide oder Acylchloride können unter basischen Bedingungen eingesetzt werden.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden:
Oxidation: Bildung von N-Oxid-Derivaten.
Reduktion: Bildung von sekundären Aminen.
Substitution: Bildung von substituierten this compound-Derivaten.
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Amitriptylin wird oft mit anderen trizyklischen Antidepressiva verglichen, wie z. B.:
Nortriptylin: Ähnlich in der Struktur, hat aber weniger Nebenwirkungen.
Desipramin: Bekannt für seine höhere Selektivität für die Hemmung der Noradrenalin-Wiederaufnahme.
Imipramin: Für ähnliche Indikationen eingesetzt, hat aber ein anderes Nebenwirkungsprofil.
Doxepin: Wird auch für Depressionen und Angstzustände eingesetzt, hat aber zusätzliche antihistaminerge Eigenschaften
This compound ist einzigartig aufgrund seines breiten Wirkungsspektrums, das mehrere Neurotransmittersysteme und Rezeptoren beeinflusst, was zu seiner Wirksamkeit bei der Behandlung einer Vielzahl von Erkrankungen beiträgt .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
N,N-dimethyl-3-(2-tricyclo[9.4.0.03,8]pentadeca-1(15),3,5,7,11,13-hexaenylidene)propan-1-amine | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C20H23N/c1-21(2)15-7-12-20-18-10-5-3-8-16(18)13-14-17-9-4-6-11-19(17)20/h3-6,8-12H,7,13-15H2,1-2H3 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
KRMDCWKBEZIMAB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CN(C)CCC=C1C2=CC=CC=C2CCC3=CC=CC=C31 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C20H23N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Related CAS |
17086-03-2 (pamoate (2:1)), 30227-34-0 (maleate (1:1)), 549-18-8 (hydrochloride) | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000050486 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID7022594 | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022594 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
277.4 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Physical Description |
Solid | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014466 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Boiling Point |
410.26°C (rough estimate) | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00321 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
Solubility |
freely soluble in water, In water, 9.71 mg/L at 24 °C, 4.50e-03 g/L | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00321 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | AMITRIPTYLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3007 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014466 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Mechanism of Action |
The mechanism of action of this drug is not fully elucidated. It is suggested that amitriptyline inhibits the membrane pump mechanism responsible for the re-uptake of transmitter amines, such as norepinephrine and serotonin, thereby increasing their concentration at the synaptic clefts of the brain,. These amines are important in regulating mood. The monoamine hypothesis in depression, one of the oldest hypotheses, postulates that deficiencies of serotonin (5-HT) and/or norepinephrine (NE) neurotransmission in the brain lead to depressive effects. This drug counteracts these mechanisms, and this may be the mechanism of amitriptyline in improving depressive symptoms. Whether its analgesic effects are related to its mood-altering activities or attributable to a different, less obvious pharmacological action (or a combination of both) is unknown., Acute and chronic effects of the antidepressant drugs tranylcypromine, a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, and amitriptyline, a monoamine uptake inhibitor, were studied on beta-adrenergic receptor function in mouse astrocytes in primary cultures. In clinically relevant concentrations, acute administration of either antidepressant drug had a direct inhibitory effect on the binding of the beta-adrenergic ligand dihydroalprenolol and on the isoproterenol-induced accumulation of cyclic AMP. However, in the absence of isoproterenol, these drugs enhanced the formation of cyclic AMP in the astrocytes. Chronic exposure to amitriptyline or tranylcypromine led to a decrease in isoproterenol-induced accumulation of cyclic AMP, and the time course for the development of this phenomenon was similar to that reported for whole brain in vivo. These findings suggest that these antidepressant drugs act as a partial agonists at beta-adrenergic receptors on astrocytes, and that the down-regulation of beta-adrenergic activity that occurs in vivo after chronic administration of antidepressant drugs may, to a large extent, take place in astrocytes and may result from the partial beta-agonist nature of the drugs., Astrocytes play important roles in guiding the construction of the nervous system, controlling extracellular ions and neurotransmitters, and regulating CNS synaptogenesis. Egr-1 is a transcription factor involved in neuronal differentiation and astrocyte cell proliferation. In this study, we investigated whether the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) amitriptyline induces Egr-1 expression in astrocytes using rat C6 glioma cells as a model. We found that amitriptyline increased the expression of Egr-1 in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The amitriptyline-induced Egr-1 expression was mediated through serum response elements (SREs) in the Egr-1 promoter. SREs were activated by the Ets-domain transcription factor Elk-1 through the ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways. The inhibition of the ERK and JNK MAP kinase signals attenuated amitriptyline-induced transactivation of Gal4-Elk-1 and Egr-1 promoter activity. Our findings suggest that the induction of Egr-1 expression in astrocytes may be required to attain the therapeutic effects of antidepressant drugs., Antidepressants such as serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are frequently used for the management of neuropathic pain. Noradrenaline (NA) and serotonin (5-HT) increase in the spinal cord by reuptake inhibition is considered to be main mechanism of the therapeutic effect of antidepressants in neuropathic pain. In the present study, we examined the analgesic effects of duloxetine (SNRI) and amitriptyline (TCA) in a rat model of neuropathic pain induced by spinal nerve ligation (SNL). Intraperitoneal administration of duloxetine and amitriptyline dose-dependently (3,10 and 30 mg/kg) suppressed hyperalgesia induced by SNL. In vivo microdialysis in the lumbar spinal dorsal horn revealed that NA and 5-HT concentrations increased after intraperitoneal administration of duloxetine and amitriptyline (10 mg/kg, respectively). We further determined NA and 5-HT contents in homogenized samples from the ipsilateral dorsal spinal cord after SNL. Although the NA content in SNL rats 2 weeks after ligation was higher than that in SNL rats 4 weeks after ligation, the analgesic efficacy of duloxetine and amitriptyline was similar between two groups. The present study suggests that NA/5-HT increase in the spinal cord is crucial in the antihyperalgesic effect of duloxetine and amitriptyline. The plastic change of the descending noradrenergic system does not obviously affect the analgesic efficacy of duloxetine and amitriptyline., Recent studies show that neuronal and glial plasticity are important for the therapeutic action of antidepressants. Here, we demonstrated that amitriptyline, a tricyclic antidepressant, significantly increased GDNF mRNA and GDNF release in C6 cells. Furthermore, different classes of antidepressants increased GDNF release, but non-antidepressant psychotropic drugs did not. The amitriptyline-induced GDNF release was completely inhibited by U0126, a mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK) inhibitor, but was not inhibited by H-89, a protein kinase A inhibitor or calphostin C, a protein kinase C inhibitor. These results suggest that the amitriptyline-induced GDNF release may be regulated through a MEK/MAPK pathway. Next, we examined the effects of monoamines on GDNF release, because antidepressants are known to increase monoamines. 5-HT increased GDNF mRNA and GDNF release, but noradrenaline and dopamine did not. The 5-HT-induced GDNF release was partially, but significantly, blocked by ketanserin, a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist. The 5-HT-induced GDNF release was completely inhibited by U0126, but was not inhibited by H-89 or calphostin C. These results suggest that the 5-HT-induced GDNF release was mediated through a MEK/MAPK pathway and, at least, 5-HT2A receptors. GDNF, as well as other neurotrophic factors, may contribute to explain the therapeutic action of antidepressants and suggest a novel strategy of pharmacological intervention., For more Mechanism of Action (Complete) data for AMITRIPTYLINE (13 total), please visit the HSDB record page. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00321 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | AMITRIPTYLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3007 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Color/Form |
Crystals | |
CAS No. |
50-48-6 | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | CAS Common Chemistry | |
| URL | https://commonchemistry.cas.org/detail?cas_rn=50-48-6 | |
| Description | CAS Common Chemistry is an open community resource for accessing chemical information. Nearly 500,000 chemical substances from CAS REGISTRY cover areas of community interest, including common and frequently regulated chemicals, and those relevant to high school and undergraduate chemistry classes. This chemical information, curated by our expert scientists, is provided in alignment with our mission as a division of the American Chemical Society. | |
| Explanation | The data from CAS Common Chemistry is provided under a CC-BY-NC 4.0 license, unless otherwise stated. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline [INN:BAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0000050486 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00321 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID7022594 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.000.038 | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | AMITRIPTYLINE | |
| Source | FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) | |
| URL | https://gsrs.ncats.nih.gov/ginas/app/beta/substances/1806D8D52K | |
| Description | The FDA Global Substance Registration System (GSRS) enables the efficient and accurate exchange of information on what substances are in regulated products. Instead of relying on names, which vary across regulatory domains, countries, and regions, the GSRS knowledge base makes it possible for substances to be defined by standardized, scientific descriptions. | |
| Explanation | Unless otherwise noted, the contents of the FDA website (www.fda.gov), both text and graphics, are not copyrighted. They are in the public domain and may be republished, reprinted and otherwise used freely by anyone without the need to obtain permission from FDA. Credit to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration as the source is appreciated but not required. | |
| Record name | AMITRIPTYLINE | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3007 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014466 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Melting Point |
196-197, 196 - 197 °C | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00321 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Amitriptyline | |
| Source | Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) | |
| URL | http://www.hmdb.ca/metabolites/HMDB0014466 | |
| Description | The Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) is a freely available electronic database containing detailed information about small molecule metabolites found in the human body. | |
| Explanation | HMDB is offered to the public as a freely available resource. Use and re-distribution of the data, in whole or in part, for commercial purposes requires explicit permission of the authors and explicit acknowledgment of the source material (HMDB) and the original publication (see the HMDB citing page). We ask that users who download significant portions of the database cite the HMDB paper in any resulting publications. | |
Synthesis routes and methods I
Procedure details








Synthesis routes and methods II
Procedure details






Synthesis routes and methods III
Procedure details





Retrosynthesis Analysis
AI-Powered Synthesis Planning: Our tool employs the Template_relevance Pistachio, Template_relevance Bkms_metabolic, Template_relevance Pistachio_ringbreaker, Template_relevance Reaxys, Template_relevance Reaxys_biocatalysis model, leveraging a vast database of chemical reactions to predict feasible synthetic routes.
One-Step Synthesis Focus: Specifically designed for one-step synthesis, it provides concise and direct routes for your target compounds, streamlining the synthesis process.
Accurate Predictions: Utilizing the extensive PISTACHIO, BKMS_METABOLIC, PISTACHIO_RINGBREAKER, REAXYS, REAXYS_BIOCATALYSIS database, our tool offers high-accuracy predictions, reflecting the latest in chemical research and data.
Strategy Settings
| Precursor scoring | Relevance Heuristic |
|---|---|
| Min. plausibility | 0.01 |
| Model | Template_relevance |
| Template Set | Pistachio/Bkms_metabolic/Pistachio_ringbreaker/Reaxys/Reaxys_biocatalysis |
| Top-N result to add to graph | 6 |
Feasible Synthetic Routes
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.

![[3-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-methoxy-4-methylsulfanyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-3-oxopropyl]-[(2E,6E)-3,7,11-trimethyldodeca-2,6,10-trienyl]phosphinic acid](/img/structure/B1667168.png)
![N-(Methylsulfonyl)-D-Phenylalanyl-N-[(1-Carbamimidoylpiperidin-4-Yl)methyl]-L-Prolinamide](/img/structure/B1667174.png)