Liraglutid
Übersicht
Beschreibung
Liraglutid ist ein synthetisches Analogon des humanen Glucagon-like Peptids 1 (GLP-1), das hauptsächlich zur Behandlung von Typ-2-Diabetes mellitus und Fettleibigkeit eingesetzt wird . Es wird unter den Markennamen Victoza und Saxenda vermarktet . This compound ahmt die Wirkung des natürlichen Hormons GLP-1 nach, das zur Regulierung des Blutzuckerspiegels und des Appetits beiträgt .
Herstellungsmethoden
Synthesewege und Reaktionsbedingungen
This compound wird synthetisiert, indem eine C-16-Fettsäure (Palmitinsäure) mit einem Glutaminsäure-Spacer an das Lysin-Rest an Position 26 des Peptidvorläufers gekoppelt wird . Die Synthese erfolgt mittels Festphasen-Peptidsynthese-Techniken, bei denen Aminosäuren sequentiell an eine wachsende Peptidkette angehängt werden, die an einem festen Harz verankert ist . Das Endprodukt wird dann vom Harz abgespalten und mittels Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographie gereinigt .
Industrielle Produktionsmethoden
Die industrielle Produktion von this compound erfolgt durch großtechnische Festphasen-Peptidsynthese, gefolgt von der Reinigung mittels Chromatographie-Techniken . Der Prozess ist optimiert, um eine hohe Ausbeute und Reinheit des Endprodukts zu gewährleisten, was für seine therapeutische Wirksamkeit unerlässlich ist .
Wirkmechanismus
Target of Action
Liraglutide is a synthetic analog of human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and acts as a GLP-1 receptor agonist . It is 97% similar to native human GLP-1, differing primarily by substituting arginine for lysine at position 34 .
Mode of Action
Liraglutide interacts with its target, the GLP-1 receptor, leading to increased intracellular cyclic AMP (cAMP). This results in insulin release in the presence of elevated glucose concentrations . The insulin secretion subsides as blood glucose concentrations decrease and approach euglycemia .
Biochemical Pathways
Liraglutide affects multiple biochemical pathways. It activates the AMPK/ACC signaling pathway, which plays a crucial role in cellular energy homeostasis . It also interacts with specific neurons in the hypothalamus, involved in the regulation of appetite and food intake . Furthermore, it has been reported to increase the expression of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in hippocampus tissue in diabetic rats via the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and PI3K/AKT pathways .
Pharmacokinetics
Liraglutide is slowly absorbed following subcutaneous injection, with a maximum concentration time (tmax) of approximately 12 hours . Its absolute bioavailability is around 55% . The mechanism of protraction relates to slowed release from the injection site, and a reduced elimination rate owing to metabolic stabilization and reduced renal filtration .
Result of Action
Liraglutide can alleviate the decrease of cell viability and degradation of muscle protein caused by high glucose, and improves cell metabolism and mitochondrial activity . It also inhibits lung cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo . In addition, liraglutide exhibited anti-aging effects in vivo and in vitro .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
Liraglutide has a wide range of scientific research applications:
Chemistry: Used as a model peptide for studying peptide synthesis and modification techniques.
Biology: Investigated for its role in regulating glucose metabolism and appetite.
Medicine: Extensively studied for its therapeutic effects in type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Industry: Used in the development of new peptide-based therapeutics.
Biochemische Analyse
Biochemical Properties
Liraglutide plays a significant role in biochemical reactions. It interacts with various enzymes, proteins, and other biomolecules. For instance, it has been found to interact with glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R), which is a G protein-coupled receptor . The nature of these interactions involves binding to the receptor, which triggers a series of biochemical reactions leading to the secretion of insulin .
Cellular Effects
Liraglutide has profound effects on various types of cells and cellular processes. It influences cell function by impacting cell signaling pathways, gene expression, and cellular metabolism. For instance, it has been found to preserve pancreatic beta cells via regulation of cell kinetics and suppression of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in a mouse model of diabetes .
Molecular Mechanism
The mechanism of action of Liraglutide is quite complex. It exerts its effects at the molecular level through binding interactions with biomolecules, enzyme inhibition or activation, and changes in gene expression. For instance, it binds to the GLP-1R, which leads to the activation of adenylyl cyclase and an increase in cyclic AMP levels .
Temporal Effects in Laboratory Settings
In laboratory settings, the effects of Liraglutide change over time. It has been found to have a half-life of more than 13 hours, indicating its stability . Long-term effects on cellular function observed in in vitro or in vivo studies include improved insulin sensitivity and glucose homeostasis .
Dosage Effects in Animal Models
The effects of Liraglutide vary with different dosages in animal models. For instance, in db/db mice, Liraglutide treatment improved metabolic variables and insulin sensitivity .
Metabolic Pathways
Liraglutide is involved in several metabolic pathways. It interacts with enzymes such as adenylyl cyclase and influences metabolic flux and metabolite levels .
Transport and Distribution
Liraglutide is transported and distributed within cells and tissues. It is administered as an isotonic solution by subcutaneous injection .
Subcellular Localization
Given its role in activating the GLP-1R, it is likely that it is localized to the cell membrane where this receptor is found .
Vorbereitungsmethoden
Synthetic Routes and Reaction Conditions
Liraglutide is synthesized by attaching a C-16 fatty acid (palmitic acid) with a glutamic acid spacer to the lysine residue at position 26 of the peptide precursor . The synthesis involves solid-phase peptide synthesis techniques, where amino acids are sequentially added to a growing peptide chain anchored to a solid resin . The final product is then cleaved from the resin and purified using high-performance liquid chromatography .
Industrial Production Methods
Industrial production of liraglutide involves large-scale solid-phase peptide synthesis followed by purification using chromatography techniques . The process is optimized to ensure high yield and purity of the final product, which is essential for its therapeutic efficacy .
Analyse Chemischer Reaktionen
Reaktionstypen
Liraglutid unterliegt verschiedenen chemischen Reaktionen, darunter:
Reduktion: Reduktionsreaktionen sind seltener, können aber unter bestimmten Bedingungen auftreten.
Substitution: Substitutionsreaktionen können an den Aminosäure-Resten auftreten, was die Struktur und Funktion des Peptids möglicherweise verändert.
Häufige Reagenzien und Bedingungen
Oxidation: Wasserstoffperoxid oder andere Oxidationsmittel können unter kontrollierten Bedingungen verwendet werden.
Reduktion: Reduktionsmittel wie Dithiothreitol können verwendet werden.
Substitution: Verschiedene chemische Reagenzien können verwendet werden, um Substitutionen an bestimmten Resten einzuführen.
Hauptprodukte, die gebildet werden
Die Hauptprodukte, die aus diesen Reaktionen gebildet werden, umfassen oxidierte oder reduzierte Formen von this compound, die möglicherweise unterschiedliche pharmakologische Eigenschaften aufweisen .
Wissenschaftliche Forschungsanwendungen
This compound hat eine große Bandbreite an wissenschaftlichen Forschungsanwendungen:
Chemie: Als Modellpeptid für die Untersuchung von Peptidsynthese- und Modifikationstechniken verwendet.
Biologie: Untersucht wegen seiner Rolle bei der Regulierung des Glukosestoffwechsels und des Appetits.
Medizin: Ausgiebig für seine therapeutischen Wirkungen bei Typ-2-Diabetes und Fettleibigkeit untersucht.
Industrie: Bei der Entwicklung neuer peptid-basierter Therapeutika verwendet.
Wirkmechanismus
This compound entfaltet seine Wirkung, indem es als Agonist des Glucagon-like Peptide-1-Rezeptors (GLP-1-Rezeptor) wirkt . Dieser Rezeptor ist an der Regulation der Insulinausschüttung, der Glucagonfreisetzung und des Appetits beteiligt . Durch Aktivierung dieses Rezeptors verstärkt this compound die Insulinausschüttung, hemmt die Glucagonfreisetzung, verlangsamt die Magenentleerung und reduziert die Nahrungsaufnahme .
Vergleich Mit ähnlichen Verbindungen
Ähnliche Verbindungen
Semaglutid: Ein weiterer GLP-1-Rezeptoragonist, der für ähnliche Indikationen eingesetzt wird.
Exenatid: Ein kurz wirkender GLP-1-Rezeptoragonist.
Dulaglutid: Ein lang wirkender GLP-1-Rezeptoragonist.
Einzigartigkeit
Liraglutid ist aufgrund seiner einmal täglichen Dosierung und seiner Fähigkeit, neben der Verbesserung der Blutzuckerkontrolle auch das Körpergewicht signifikant zu reduzieren, einzigartig . Im Gegensatz zu einigen anderen GLP-1-Rezeptoragonisten hat sich gezeigt, dass this compound positive Auswirkungen auf kardiovaskuläre Ergebnisse hat .
Eigenschaften
IUPAC Name |
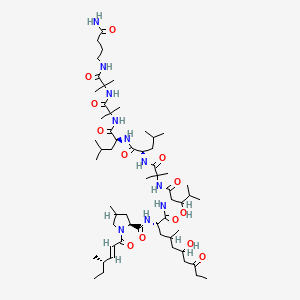
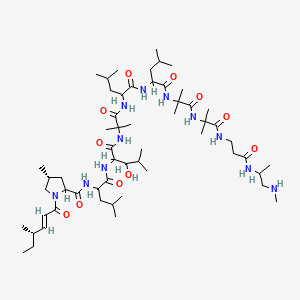
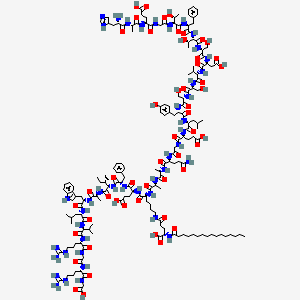
(2S)-5-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2-oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2-(hexadecanoylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
|---|---|---|
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI |
InChI=1S/C172H265N43O51/c1-18-20-21-22-23-24-25-26-27-28-29-30-37-53-129(224)195-116(170(265)266)59-64-128(223)180-68-41-40-50-111(153(248)199-115(62-67-135(232)233)154(249)204-120(73-100-44-33-31-34-45-100)159(254)214-140(93(11)19-2)167(262)192-97(15)146(241)201-122(76-103-79-183-108-49-39-38-48-106(103)108)157(252)203-118(72-90(5)6)158(253)212-138(91(7)8)165(260)200-110(52-43-70-182-172(177)178)149(244)184-81-130(225)193-109(51-42-69-181-171(175)176)148(243)187-84-137(236)237)196-144(239)95(13)189-143(238)94(12)191-152(247)114(58-63-127(174)222)194-131(226)82-185-151(246)113(61-66-134(230)231)198-155(250)117(71-89(3)4)202-156(251)119(75-102-54-56-105(221)57-55-102)205-162(257)124(85-216)208-164(259)126(87-218)209-166(261)139(92(9)10)213-161(256)123(78-136(234)235)206-163(258)125(86-217)210-169(264)142(99(17)220)215-160(255)121(74-101-46-35-32-36-47-101)207-168(263)141(98(16)219)211-132(227)83-186-150(245)112(60-65-133(228)229)197-145(240)96(14)190-147(242)107(173)77-104-80-179-88-188-104/h31-36,38-39,44-49,54-57,79-80,88-99,107,109-126,138-142,183,216-221H,18-30,37,40-43,50-53,58-78,81-87,173H2,1-17H3,(H2,174,222)(H,179,188)(H,180,223)(H,184,244)(H,185,246)(H,186,245)(H,187,243)(H,189,238)(H,190,242)(H,191,247)(H,192,262)(H,193,225)(H,194,226)(H,195,224)(H,196,239)(H,197,240)(H,198,250)(H,199,248)(H,200,260)(H,201,241)(H,202,251)(H,203,252)(H,204,249)(H,205,257)(H,206,258)(H,207,263)(H,208,259)(H,209,261)(H,210,264)(H,211,227)(H,212,253)(H,213,256)(H,214,254)(H,215,255)(H,228,229)(H,230,231)(H,232,233)(H,234,235)(H,236,237)(H,265,266)(H4,175,176,181)(H4,177,178,182)/t93-,94-,95-,96-,97-,98+,99+,107-,109-,110-,111-,112-,113-,114-,115-,116-,117-,118-,119-,120-,121-,122-,123-,124-,125-,126-,138-,139-,140-,141-,142-/m0/s1 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
InChI Key |
YSDQQAXHVYUZIW-QCIJIYAXSA-N | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Canonical SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)NC(CCC(=O)NCCCCC(C(=O)NC(CCC(=O)O)C(=O)NC(CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)NC(C)C(=O)NC(CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C32)C(=O)NC(CC(C)C)C(=O)NC(C(C)C)C(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)NC(CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(CO)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)C(CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)C(C(C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)C(CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(=O)C(CC6=CN=CN6)N)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Isomeric SMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)NCCCC[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](CCC(=O)O)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC1=CC=CC=C1)C(=O)N[C@@H]([C@@H](C)CC)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC2=CNC3=CC=CC=C32)C(=O)N[C@@H](CC(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C(C)C)C(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)N[C@@H](CCCNC(=N)N)C(=O)NCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)N)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC4=CC=C(C=C4)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H](C(C)C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CO)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC5=CC=CC=C5)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)CNC(=O)[C@H](CCC(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](C)NC(=O)[C@H](CC6=CN=CN6)N)C(=O)O | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Molecular Formula |
C172H265N43O51 | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
DSSTOX Substance ID |
DTXSID60174433 | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60174433 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
Molecular Weight |
3751 g/mol | |
| Source | PubChem | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov | |
| Description | Data deposited in or computed by PubChem | |
Mechanism of Action |
Liraglutide is an acylated synthetic glucagon-like peptide-1 analog. Liraglutide is an agonist of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor which is coupled to adenylate cyclase. The increase in cyclic AMP stimulates the glucose dependant release of insulin, inhibits the glucose dependant release of glucagon, and slows gastric emptying to increase control of blood sugar., Liraglutide is an acylated, long-acting, human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist; the synthetic (recombinant DNA origin) peptide precursor of liraglutide has 97% amino acid sequence homology to endogenous human GLP-1-(7-37). Liraglutide is prepared by attaching palmitic acid with a glutamic acid spacer on the lysine residue at position 26 of the peptide precursor. GLP-1-(7-37) represents less than 20% of total circulating endogenous GLP-1. Like GLP-1-(7-37), liraglutide activates the GLP-1 receptor in pancreatic beta cells. Liraglutide also increases intracellular cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) leading to insulin release in the presence of elevated glucose concentrations. This insulin secretion subsides as blood glucose concentrations decrease and approach euglycemia. In addition, liraglutide suppresses glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner but does not impair normal glucagon response to hypoglycemia. Liraglutide delays gastric emptying, reducing the rate at which postprandial glucose appears in the circulation. As a result of these actions resulting in increased insulin secretion, suppression of glucagon secretion, and delays in gastric emptying, liraglutide effectively reduces fasting and postprandial plasma glucose concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus., Liraglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) mimetic used for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes. Similar to the actions of endogenous GLP-1, liraglutide potentiates the post-prandial release of insulin, inhibits glucagon release and increases satiety. Recent epidemiological studies and clinical trials have suggested that treatment with GLP-1 mimetics may also diminish the risk of cardiovascular disease in diabetic patients. The mechanism responsible for this effect has yet to be determined; however, one possibility is that they might do so by a direct effect on vascular endothelium. Since low grade inflammation of the endothelium is an early event in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD), we determined the effects of liraglutide on inflammation in cultured human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs). Liraglutide reduced the inflammatory responses to TNFalpha and LPS stimulation, as evidenced by both reduced protein expression of the adhesion molecules VCAM-1 and E-Selectin, and THP-1 monocyte adhesion. This was found to result from increased cell Ca2+ and several molecules sensitive to Ca2+ with known anti inflammatory actions in endothelial cells, including CaMKKbeta, CaMKI, AMPK, eNOS and CREB. Treatment of the cells with STO-609, a CaMKK inhibitor, diminished both the activation of AMPK, CaMKI and the inhibition of TNFa and LPS-induced monocyte adhesion by liraglutide. Likewise, expression of an shRNA against AMPK nullified the anti-inflammatory effects of liraglutide. The results indicate that liraglutide exerts a strong anti-inflammatory effect on HAECs. They also demonstrate that this is due to its ability to increase intracellular Ca2+ and activate CAMKKbeta, which in turn activates AMPK., In vivo, liraglutide lowers blood glucose and body weight in a number of diabetic and obese models using rodents, pigs and monkeys. The mechanism of action in vivo involved glucose-dependent increase in insulin secretion, lowered glucagon secretion, decreased gastric emptying, loss of body fat, lowered food intake, altered food preference, and maintained energy expenditure. The mechanism of action is consistent with a specific GLP-1 effect., Liraglutide is a long-acting GLP-1 analogue, designed to bind to albumin as the main molecular mechanism of protraction. In vitro, this was shown in the receptor cAMP as well as binding assay where addition of albumin right-shifted the dose-response and/or binding curve. The apparent reduced potency of liraglutide underlines that only the free fraction of liraglutide is responsible for its pharmacological effect in vitro as well as in vivo. Furthermore, liraglutide in a pharmaceutical solution forms a micell-like heptamer which may contribute to the slow absorption from the subcutis. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06655 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8205 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
CAS No. |
204656-20-2 | |
| Record name | Liraglutide [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN] | |
| Source | ChemIDplus | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/?source=chemidplus&sourceid=0204656202 | |
| Description | ChemIDplus is a free, web search system that provides access to the structure and nomenclature authority files used for the identification of chemical substances cited in National Library of Medicine (NLM) databases, including the TOXNET system. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | DrugBank | |
| URL | https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB06655 | |
| Description | The DrugBank database is a unique bioinformatics and cheminformatics resource that combines detailed drug (i.e. chemical, pharmacological and pharmaceutical) data with comprehensive drug target (i.e. sequence, structure, and pathway) information. | |
| Explanation | Creative Common's Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/legalcode) | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | EPA DSSTox | |
| URL | https://comptox.epa.gov/dashboard/DTXSID60174433 | |
| Description | DSSTox provides a high quality public chemistry resource for supporting improved predictive toxicology. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide (2S)-5-[[(5S)-5-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-5-amino-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2- [[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S,3R)-2-[[2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl) propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3- phenylpropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxybutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]- 3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-hydroxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl) propanoyl]amino]-4-methylpentanoyl]amino]-4-carboxybutanoyl]amino]acetyl]amino] 5 oxopentanoyl]amino] propanoyl]amino]propanoyl]amino]-6-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)- 5-carbamimidamido-1-[[2-[[(2S)-5-carbamimidamido-1-(carboxymethylamino)-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-2- oxoethyl]amino]-1-oxopentan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-4-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl] amino]-3-(1H-indol-3-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-3-methyl-1-oxopentan-2-yl] amino]-1-oxo-3-phenylpropan-2-yl]amino]-4-carboxy-1-oxobutan-2-yl]amino]-6-oxohexyl]amino]-2- (hexadecanoylamino)-5-oxopentanoic acid | |
| Source | European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) | |
| URL | https://echa.europa.eu/information-on-chemicals | |
| Description | The European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) is an agency of the European Union which is the driving force among regulatory authorities in implementing the EU's groundbreaking chemicals legislation for the benefit of human health and the environment as well as for innovation and competitiveness. | |
| Explanation | Use of the information, documents and data from the ECHA website is subject to the terms and conditions of this Legal Notice, and subject to other binding limitations provided for under applicable law, the information, documents and data made available on the ECHA website may be reproduced, distributed and/or used, totally or in part, for non-commercial purposes provided that ECHA is acknowledged as the source: "Source: European Chemicals Agency, http://echa.europa.eu/". Such acknowledgement must be included in each copy of the material. ECHA permits and encourages organisations and individuals to create links to the ECHA website under the following cumulative conditions: Links can only be made to webpages that provide a link to the Legal Notice page. | |
| Record name | Liraglutide | |
| Source | Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) | |
| URL | https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/8205 | |
| Description | The Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB) is a toxicology database that focuses on the toxicology of potentially hazardous chemicals. It provides information on human exposure, industrial hygiene, emergency handling procedures, environmental fate, regulatory requirements, nanomaterials, and related areas. The information in HSDB has been assessed by a Scientific Review Panel. | |
Haftungsausschluss und Informationen zu In-Vitro-Forschungsprodukten
Bitte beachten Sie, dass alle Artikel und Produktinformationen, die auf BenchChem präsentiert werden, ausschließlich zu Informationszwecken bestimmt sind. Die auf BenchChem zum Kauf angebotenen Produkte sind speziell für In-vitro-Studien konzipiert, die außerhalb lebender Organismen durchgeführt werden. In-vitro-Studien, abgeleitet von dem lateinischen Begriff "in Glas", beinhalten Experimente, die in kontrollierten Laborumgebungen unter Verwendung von Zellen oder Geweben durchgeführt werden. Es ist wichtig zu beachten, dass diese Produkte nicht als Arzneimittel oder Medikamente eingestuft sind und keine Zulassung der FDA für die Vorbeugung, Behandlung oder Heilung von medizinischen Zuständen, Beschwerden oder Krankheiten erhalten haben. Wir müssen betonen, dass jede Form der körperlichen Einführung dieser Produkte in Menschen oder Tiere gesetzlich strikt untersagt ist. Es ist unerlässlich, sich an diese Richtlinien zu halten, um die Einhaltung rechtlicher und ethischer Standards in Forschung und Experiment zu gewährleisten.